Metabolic neuropathies
Neuropathy - metabolic
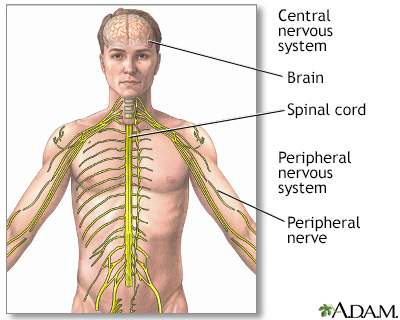
Metabolic neuropathies are nerve disorders that occur with diseases that disrupt the chemical processes in the body
Images
Causes
Nerve damage can be caused by many different things. Metabolic neuropathy may be caused by:
- A problem with the body's ability to use energy, often due to a lack of enough nutrients (nutritional deficiency)
- Dangerous substances (toxins) that build up in the body
Diabetes is one of the most common causes of metabolic neuropathies. People who are at the highest risk for nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy) from diabetes include those who have:
- Damage to the kidneys or eyes
- Poorly controlled blood sugar
Other common causes of metabolic neuropathies include:
- Alcohol use disorder (alcoholic neuropathy)
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Kidney failure
- Inherited conditions, such as porphyria
- Severe infection throughout the body (sepsis)
- Thyroid disease
- Liver disease
- Vitamin deficiencies (including vitamins B12, B6, E, and B1)
Some metabolic disorders are passed down through families (inherited), while others develop due to various diseases.
Symptoms
These symptoms occur because nerves cannot send proper signals to and from your brain:
- Difficulty feeling in any area of the body
- Difficulty using the arms or hands
- Difficulty using the legs or feet
- Difficulty walking
- Pain, burning feeling, a pins and needles feeling or shooting pains in any area of the body (nerve pain)
- Weakness in the face, arms, legs, or other areas of the body
- Dysautonomia, which affects the autonomic (involuntary) nervous system, resulting in symptoms such as rapid heart rate, exercise intolerance, low blood pressure when standing, abnormal sweat patterns, stomach problems, abnormal functioning of the pupils of the eye, and poor erection
These symptoms often start in the toes and feet and move up the legs, eventually affecting the hands and arms.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and ask about your symptoms.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Blood tests
- Electrical test of the muscles (electromyography or EMG)
- Electrical test of nerve conduction
- Nerve tissue biopsy
Treatment
For most metabolic neuropathies, the best treatment is to correct the metabolic problem.
Vitamin deficiencies are treated with diet or with vitamins by mouth or by injection. Abnormal blood sugar level or thyroid function may need medicines to correct the problem. For alcoholic neuropathy, the best treatment is to stop drinking.
In some cases, pain is treated with medicines that reduce abnormal pain signals from the nerves. In some cases, lotions, creams, or medicated patches can provide relief.
Weakness is often treated with physical therapy. You may need to learn how to use a cane or walker if your balance is affected. You may need special ankle braces to help you walk better.
Support Groups
These groups can provide more information on neuropathy:
- Neuropathy Action Foundation -- www.neuropathyaction.org
- The Foundation for Peripheral Neuropathy -- www.foundationforpn.org
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook mainly depends on the cause of the disorder. In some cases, the problem can easily be treated. In other cases, the metabolic problem cannot be controlled, and nerves may continue to become damaged.
Possible Complications
Complications that may result include:
- Deformity
- Injury to feet
- Numbness or weakness
- Pain
- Trouble walking and falls
Prevention
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk for neuropathy.
- Avoid excess alcohol use.
- Eat a balanced diet.
- Quit smoking.
- Visit your provider regularly to find metabolic disorders before neuropathy develops.
If you have neuropathy in your feet, a foot doctor (podiatrist) can teach you how to inspect your feet for signs of injury and infection. Proper fitting shoes can lessen the chance of skin breakdown in sensitive areas of the feet.
References
Goodman BP. Neurologic manifestations of nutritional disorders. In: Aminoff MJ, Josephson SA, eds. Aminoff's Neurology and General Medicine. 6th ed. Cambridge, MA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 15.
Ralph JW, Aminoff MJ. Neuromuscular complications of general medical disorders. In: Aminoff MJ, Josephson SA, eds. Aminoff's Neurology and General Medicine. 6th ed. Cambridge, MA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 60.
Smith G, Shy ME. Peripheral neuropathies. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 392.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 11/9/2021
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
