Ectopic heartbeat
PVB (premature ventricular beat); Premature beats; PVC (premature ventricular complex/contraction); Extrasystole; Premature supraventricular contractions; PAC; Premature atrial contraction; Abnormal heartbeat
Ectopic heartbeats are changes in a heartbeat that is otherwise normal. These changes lead to extra or skipped heartbeats. There is often not a clear cause for these changes. They are common.
The two most common types of ectopic heartbeats are:
- Premature ventricular contractions (PVC)
- Premature atrial contractions (PAC)
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Ectopic heartbeats are sometimes seen with:
- Changes in the blood, such as a low potassium level (hypokalemia)
- Decrease in blood supply to the heart
- When the heart is enlarged or structurally abnormal
Ectopic beats may be caused or made worse by smoking, alcohol use, caffeine, stimulant medicines, and some street drugs.
Ectopic heartbeats are rare in children without heart disease that was present at birth (congenital). Most extra heartbeats in children are PACs. These are often benign.
In adults, ectopic heartbeats are common. They are most often due to PACs or PVCs. Your health care provider should look into the cause when they are frequent. Treatment is directed at symptoms and the underlying cause.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Feeling your heartbeat (palpitations)
- Feeling like your heart stopped or skipped a beat
- Feeling of occasional, forceful beats
Note: There may be no symptoms.
Exams and Tests
A physical exam may show an occasional uneven pulse. If the ectopic heartbeats do not occur very often, your provider may not find them during a physical exam.
Blood pressure is most often normal.
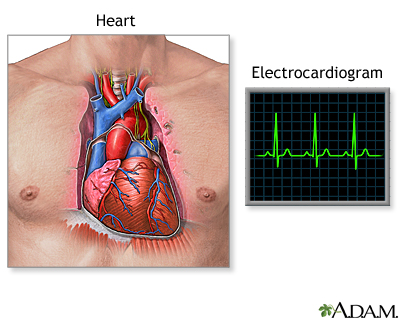
An ECG will be done. Often, no further testing is needed when your ECG is normal and the symptoms are not severe or worrisome.
If your provider wants to know more about your heart rhythm, they may order:
- A monitor that you wear that records and stores your heart rhythm for 24 to 48 hours (Holter monitor)
- A recording device that you wear, and records your heart rhythm whenever you feel a skipped beat
An echocardiogram may be ordered if your provider suspects problems with the size or structure of your heart are the cause.
Treatment
The following may help reduce ectopic heartbeats for some people:
- Limiting caffeine, alcohol, and tobacco
- Regular exercise for people who are inactive
For the most part, ectopic heartbeats do not need to be treated. The condition is only treated if your symptoms are severe or if the extra beats occur very often.
The cause of the heartbeats, if it can be found, may also need to be treated.
Outlook (Prognosis)
In some cases, ectopic heartbeats may mean you are at greater risk for serious abnormal heart rhythms, such as ventricular tachycardia.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You keep feeling the sensation of your heart pounding or racing (palpitations).
- You have palpitations with chest pain or other symptoms.
- You have this condition and your symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment.
Related Information
PulseHeart palpitations
Alcohol use and safe drinking
Caffeine in the diet
Benign
Ventricular tachycardia
References
Fang JC, O'Gara PT. History and physical examination: an evidence-based approach. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 13.
Olgin JE. Approach to the patient with suspected arrhythmias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 49.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 5/8/2024
Reviewed By: Thomas S. Metkus, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
