Folate-deficiency anemia
Folate-deficiency anemia is a decrease in red blood cells (anemia) due to a lack of folate. Folate is a type of B vitamin. It is also called folic acid.
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Folate (folic acid) is needed for red blood cells to form and grow. You can get folate by eating green leafy vegetables and liver. However, your body does not store folate in large amounts. So, you need to eat plenty of folate-rich foods to maintain normal levels of this vitamin.
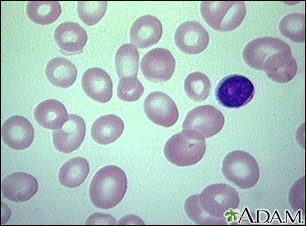
In folate-deficiency anemia, the red blood cells are abnormally large. Such cells are called macrocytes. They are also called megaloblasts, when they are seen in the bone marrow. That is why this anemia is also called a type of megaloblastic anemia.
Causes of this type of anemia include:
- Too little folic acid in your diet
- Hemolytic anemia
- Long-term alcoholism
- Use of certain medicines (such as phenytoin [Dilantin], methotrexate, sulfasalazine, triamterene, pyrimethamine, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and barbiturates)
The following raise your risk for this type of anemia:
- Alcoholism
- Eating overcooked food
- Poor diet (often seen in the poor, the older people, and people who do not eat fresh fruits or vegetables)
- Pregnancy
- Weight loss diets
Folic acid is needed to help a baby in the womb grow properly. Too little folic acid during pregnancy may lead to birth defects in a baby.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. Tests that may be done include:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Red blood cell folate level
In rare cases, a bone marrow aspiration may be done.
Treatment
The goal is to identify and treat the cause of the folate deficiency.
You may receive folic acid supplements by mouth, injected into muscle, or through a vein (in rare cases). If you have low folate levels because of a problem with your intestines, you may need treatment for the rest of your life.
Diet changes can help boost your folate level. Eat more green, leafy vegetables and citrus fruits.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Folate-deficiency anemia most often responds well to treatment within 3 to 6 months. It will likely get better when the underlying cause of the deficiency is treated.
Possible Complications
Symptoms of anemia can cause discomfort. In pregnant women, folate deficiency has been associated with neural tube or spinal defects (such as spina bifida) in the infant.
Other more severe complications may include:
- Curly graying hair
- Increased skin color (pigment)
- Infertility
- Worsening of heart disease or heart failure
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of folate deficiency anemia.
Prevention
Eating plenty of folate-rich foods can help prevent this condition.
Experts recommend that women take 400 to 800 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid every day before they get pregnant and through the first 3 months of their pregnancy.
Related Information
AnemiaFolate deficiency
Malabsorption
Celiac disease – sprue
References
Antony AC. Megaloblastic anemias. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 40.
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC. Hematopoietic and lymphoid systems. In: Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC, Deyrup AT, Das A, eds. Robbins and Kumar Basic Pathology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 10.
Stabler SP. Megaloblastic anemias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 150.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
