Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
ALL; Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Acute lymphoid leukemia; Acute childhood leukemia; Cancer - acute childhood leukemia (ALL); Leukemia - acute childhood (ALL); Acute lymphocytic leukemia
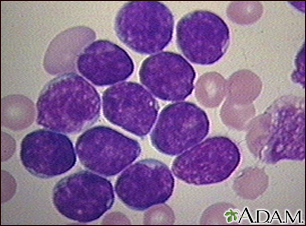
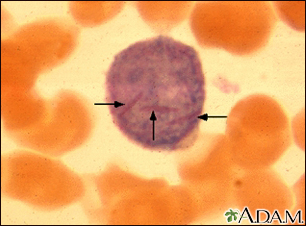
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a fast-growing cancer of a type of white blood cells called lymphocytes.
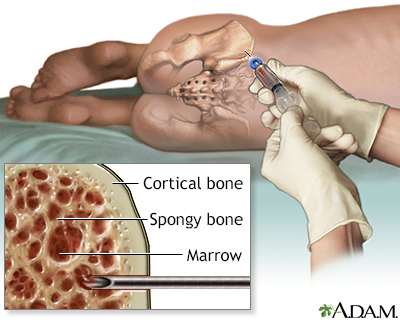
ALL occurs when the bone marrow produces a large number of immature lymphoblasts, a cancerous form of lymphocytes. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside most bones in children and in the front chest bone (sternum) and the pelvis bones in adults that helps form all blood cells. The abnormal lymphoblasts grow quickly and replace normal cells in the bone marrow. ALL prevents healthy blood cells from being made. Life-threatening symptoms can occur as normal blood counts drop.
Images
Causes
Most of the time, no clear cause can be found for ALL.
The following factors may play a role in the development of all types of leukemia:
- Certain chromosome problems
- Exposure to radiation
- Past treatment with chemotherapy medicines
- Receiving a bone marrow transplant
- Toxins, such as benzene
The following factors are known to increase the risk for ALL:
- Down syndrome or some other genetic conditions
- A brother or sister with leukemia
This type of leukemia usually affects children ages 3 to 7. ALL is the most common childhood cancer, but it can also occur in adults.
Symptoms
ALL makes a person more likely to bleed and develop infections. Symptoms include:
- Bone and joint pain
- Easy bruising and bleeding (such as bleeding gums, skin bleeding, nosebleeds, abnormal periods)
- Feeling weak or tired
- Fever
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Paleness
- Pain or feeling of fullness below the ribs from an enlarged liver or spleen
- Pinpoint red spots on the skin (petechiae)
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, under arms, and groin
- Night sweats
These symptoms can occur with other conditions. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of specific symptoms.
Exams and Tests
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms.
Blood tests may include:
- Complete blood count (CBC), including white blood cell (WBC) count and cell differential
- Platelet count
- Bone marrow biopsy
- Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to check for leukemia cells in the spinal fluid
Tests are also done to look for changes in the DNA inside the abnormal white cells. Certain DNA changes may determine how well a person does (prognosis), and what kind of treatment is recommended.
Treatment
The first goal of treatment is to get blood counts back to normal. If this occurs and the bone marrow looks healthy under the microscope, the cancer is said to be in remission.
Chemotherapy is the first treatment tried with the goal of achieving a remission.
- The person may need to stay in the hospital for chemotherapy. Or it may be given at a clinic and the person goes home afterward.
- Chemotherapy is given into the veins (by IV) and sometimes into the fluid around the brain (the spinal fluid). Oral chemotherapy may be given after a remission to maintain it.
- There are also multiple new agents approved for ALL including CAR-T-cell therapy and certain targeted agents, such as Blinatumomab and Inotuzumab ozogamicin, that have improved the outcomes.
After a remission is achieved, more treatment is given to achieve a cure. This treatment can include more IV chemotherapy or radiation to the brain. Stem cell or bone marrow transplant from another person may also be done. Further treatment depends on:
- Age and health of the person
- Genetic changes in the leukemia cells
- How many courses of chemotherapy it took to achieve remission
- If abnormal cell DNA is detected in the bone marrow after remission
- Availability of donors for stem cell or bone marrow transplant
You and your provider may need to manage other concerns during your leukemia treatment, including:
- Having chemotherapy at home
- Managing your pets during chemotherapy
- Bleeding problems
- Dry mouth
- Eating enough calories
- Safe eating during cancer treatment
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Those who respond to treatment right away tend to do better. Most children with ALL can be cured. Children often have a better outcome than adults.
Possible Complications
Both leukemia itself and its treatment can lead to many problems such as bleeding, weight loss, and infections.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you or your child develops symptoms of ALL.
Prevention
The risk for developing ALL may be reduced by avoiding contact with certain toxins, radiation, and chemicals.
Related Information
AcuteToxins
Chemotherapy
Bone marrow transplant
Bone marrow transplant - discharge
Oral mucositis - self-care
Mouth and neck radiation - discharge
Eating extra calories when sick - adults
When you have nausea and vomiting
References
Dinner S, Gurbuxani S, Rojek AE, Jain N, Stock W. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, Heslop HE, Weitz JI, Salama ME, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 68.
National Cancer Institute website. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/adult-all-treatment-pdq. Updated March 28, 2024. Accessed February 7, 2025.
National Cancer Institute website. Childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/child-all-treatment-pdq. Updated December 5, 2024. Accessed February 7, 2025.
Rouce RH, Rau RE. Clinical manifestations and treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, Heslop HE, Weitz JI, Salama ME, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 67.
Walter RB, Appelbaum FR. The acute leukemias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 168.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 2/3/2025
Reviewed By: Warren Brenner, MD, Oncologist, Lynn Cancer Institute, Boca Raton, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
