Chylomicronemia syndrome
Familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency; Familial hyperchylomicronemia syndrome, Type I hyperlipidemia
Chylomicronemia syndrome is a disorder in which the body does not break down fats (lipids) correctly. This causes fat particles called chylomicrons to build up in the blood. The disorder is passed down through families.
Images
Causes
Chylomicronemia syndrome can occur due to a rare genetic disorder in which a protein (enzyme) called lipoprotein lipase (LpL) is broken or missing. It can also be caused by the absence of second factor called apolipoprotein C-II (also called apoCII), which activates LpL. LpL is normally found in fat and muscle. It helps break down certain lipids. When LpL is missing or broken, fat particles called chylomicrons build up in the blood. This buildup is called chylomicronemia.
Defects in apolipoprotein CII and apolipoprotein AV can cause the syndrome as well. It is more likely to occur when people who are predisposed to have high triglycerides (such as those who have familial combined hyperlipidemia or familial hypertriglyceridemia) develop diabetes, obesity or are exposed to certain medicines.
Symptoms
Symptoms may start in infancy and include:
- Abdominal pain due to pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas).
- Symptoms of nerve damage, such as loss of feeling in the feet or legs, and memory loss.
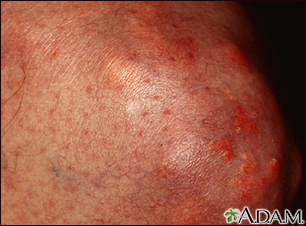
- Yellow deposits of fatty material in the skin called xanthomas. These growths may appear on the back, buttocks, soles of the feet, or ankles, knees and elbows.
Exams and Tests
A physical exam and tests may show:
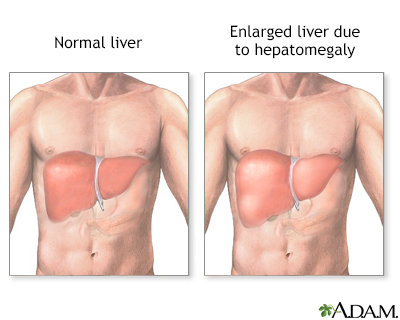
- Enlarged liver and spleen
- Inflammation of the pancreas
- Fatty deposits under the skin
- Possibly fatty deposits in the retina of the eye
A creamy layer will appear when blood spins in a laboratory machine. This layer is due to chylomicrons in the blood.
The triglyceride level is extremely high.
Treatment
A low fat, alcohol-free diet is required. You may need to stop taking certain medicines that can make symptoms worse. Do not stop taking any medicine without first talking to your health care provider. Conditions such as dehydration and diabetes can make symptoms worse. If diagnosed, these conditions need to be treated and controlled.
Outlook (Prognosis)
A low fat diet can reduce symptoms dramatically.
Possible Complications
When untreated, the excess chylomicrons may lead to bouts of pancreatitis. This condition can be very painful and even life threatening.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek medical care right away if you have abdominal pain or other warning signs of pancreatitis.
Contact your provider if you have a personal or family history of high triglyceride levels.
Prevention
There is no way to prevent someone from inheriting this syndrome.
Related Information
MetabolismReferences
Genest J, Mora S, Libby P. Lipoprotein disorders and cardiovascular disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 27.
Robinson JG. Disorders of lipid metabolism. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 190.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 5/8/2024
Reviewed By: Thomas S. Metkus, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
