Pancreas divisum
Pancreatic divisum
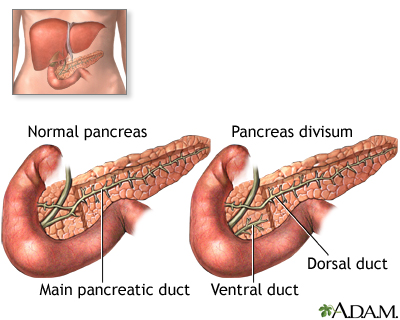
Pancreas divisum is a birth defect in which parts of the pancreas do not join together. The pancreas is a long, flat organ located between the stomach and spine. It helps in food digestion.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Pancreas divisum is the most common birth defect of the pancreas. In many cases, this defect goes undetected and causes no problems. The cause of the defect is unknown.
As a baby develops in the womb, two separate pieces of tissue join together to form the pancreas. Each part has a tube, called a duct. When the parts join together, a final duct, called the pancreatic duct, is formed. Fluid and digestive juices (enzymes) produced by the pancreas normally flow through this duct.
Pancreas divisum occurs if the ducts do not join while the baby develops. Fluid from the two parts of the pancreas drains into separate areas of the upper portion of the small intestine (duodenum). This occurs in 5% to 15% of people.
If a pancreatic duct becomes blocked, swelling and tissue damage (pancreatitis) may develop.
Symptoms
Many people do not have any symptoms. If you have pancreatitis, symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain, most often in the upper abdomen that may be felt in the back
- Abdominal swelling (distention)
- Nausea or vomiting
Exams and Tests
You may have the following tests:
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Abdominal CT scan
- Amylase and lipase blood test
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
Treatment
The following treatments may be needed if you have symptoms of the condition, or if pancreatitis keeps returning:
- ERCP with a cut to enlarge the opening where the pancreatic duct drains
- Placement of a stent to prevent the duct from getting blocked
You may need surgery if these treatments do not work.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, the outcome is good.
Possible Complications
The main complication of pancreas divisum is pancreatitis.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you develop symptoms of this disorder.
Prevention
Because this condition is present at birth, there is no known way to prevent it.
References
Adams DB, Cote GA. Pancreas divisum and other variants of dominant dorsal duct anatomy. In: Cameron AM, Cameron JL, eds. Current Surgical Therapy. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:515-521.
Kumar V, Abbas AK, Astre JC. Pancreas. In: Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC, eds. Robbins Basic Pathology. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 17.
Mehta MS, Barth BA, Husain SZ. Anatomy, histology, embryology and developmental anomalies of the pancreas. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 55.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 10/25/2021
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
