Dislocation
Joint dislocation
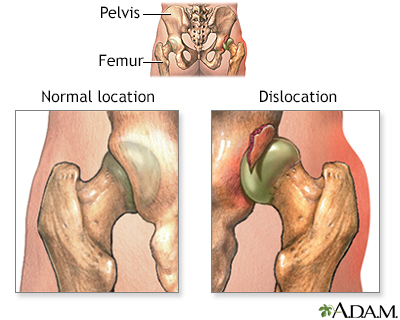
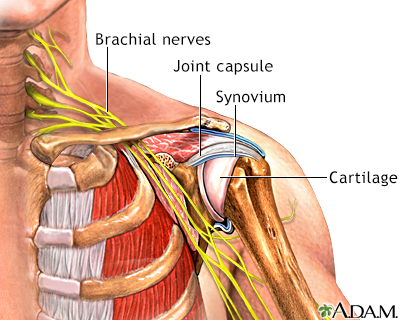
A dislocation is a disruption of the normal position of the ends of two or more bones where they meet at a joint. A joint is the place where two bones connect, which allows movement.
A dislocated joint is a joint where the bones are no longer in their normal positions.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Considerations
It may be hard to tell a dislocated joint from a broken bone. Both are emergencies that need first aid treatment.
Most dislocations can be treated in your health care provider's office or an emergency room. You may be given medicine to make you sleepy and to numb the area. Sometimes, general anesthesia that puts you into a deep sleep is needed.
When treated early, most dislocations do not cause permanent injury.
You should expect that:
- Injuries to the surrounding tissues generally take 6 to 12 weeks to heal. Sometimes, surgery to repair a ligament that tears when the joint is dislocated is needed.
- Injuries to nerves and blood vessels may result in more long-term or permanent problems.
Once a joint has been dislocated, it is more likely to happen again. After being treated in the emergency room, you should follow-up with an orthopedic surgeon (a bone and joint specialist).
Causes
Dislocations are usually caused by a sudden impact to the joint. This usually occurs following a blow, fall, or other trauma.
Symptoms
A dislocated joint may be:
- Accompanied by numbness or tingling at the joint or beyond it
- Very painful, especially if you try to use the joint or put weight on it
- Limited in movement
- Swollen or bruised
- Visibly out of place, discolored, or misshapen
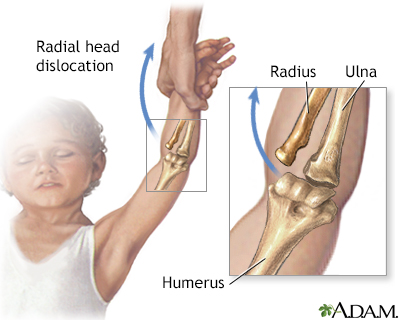
Nursemaid's elbow, or pulled elbow, is a partial dislocation that is common in toddlers. The main symptom is pain so that the child doesn't want to use the arm. This dislocation can be easily treated in your provider's office.
First Aid
First aid steps to take:
- Call 911 or the local emergency number before you begin treating someone who may have a dislocation, especially if the accident that caused the injury may be life threatening.
- If the person has a serious injury, check their airway, breathing, and circulation. If necessary, begin CPR, or bleeding control.
- Do not move the person if you think that their head, back, or leg has been injured. Keep the person calm and still.
- If the skin is broken, take steps to prevent infection. Do not blow on the wound. Rinse the area gently with clean water to remove any dirt you can see, but do not scrub or probe. Cover the area with sterile dressings before immobilizing the injured joint. Do not attempt to put the bone back in place unless you are a bone specialist.
- Apply a splint or sling to the injured joint in the position in which you found it. Do not move the joint. Also immobilize the area above and below the injured area.
- Check blood circulation around the injury by pressing firmly on the skin in the affected area. It should turn white, then regain color within a couple of seconds after you stop pressing on it. To reduce the risk for developing infection, do not do this step if the skin is broken.
- Apply ice packs to ease pain and swelling, but do not put ice directly on the skin. Wrap the ice in a clean cloth.
- Take steps to prevent shock. Unless there is a head, leg, or back injury, lay the victim flat, elevate their feet about 12 inches (in) or 30 centimeters (cm), and cover the person with a coat or blanket.
Do Not
- Do not move the person unless the injury has been completely immobilized.
- Do not move a person with an injured hip, pelvis, or upper leg unless it is absolutely necessary. If you are the only rescuer and the person must be moved, drag them by their clothing.
- Do not attempt to straighten a misshapen bone or joint or try to change its position.
- Do not test a misshapen bone or joint for loss of function.
- Do not give the person anything by mouth.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number right away if the person has any of the following:
- A bone projecting through the skin
- A known or suspected dislocation or broken bone
- An area below the injured joint that is pale, cold, clammy, or blue
- Severe bleeding
- Signs of infection, such as warmth or redness at the injured site, pus, or a fever
Prevention
To help prevent injuries in children:
- Create a safe environment around your home.
- Help prevent falls by placing gates at stairways and keeping windows closed and locked.
- Keep a watchful eye on children at all times. There is no substitute for close supervision, no matter how safe the environment or situation appears to be.
- Teach children how to be safe and look out for themselves.
To help prevent dislocations in adults:
- To avoid falls, do not stand on chairs, countertops, or other unstable objects.
- Eliminate throw rugs, especially around older adults.
- Wear protective gear when participating in contact sports.
For all age groups:
- Keep a first aid kit handy.
- Remove electrical cords from floors.
- Use handrails on staircases.
- Use nonskid mats on the bottom of bathtubs and do not use bath oils.
Related Information
Broken boneOsteonecrosis
References
Klimke A, Furin M, Overberger R. Prehospital immobilization. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
Mascioli AA. Acute dislocations. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 60.
Naples RM, Ufberg JW. Management of common dislocations. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 49.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2025 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
