SmartEngageTM
Sickle cell disease - InDepth
An in-depth report on the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of sickle cell disease.
I Would Like to Learn About:
- Anemia
- Infections
- Pulmonary hypertension (increased pressure in the arteries of the lungs)
- Stroke
- Kidney problems
- Priapism (prolonged and painful erections)
- Liver problems
- Gallbladder disease
- Spleen damage
- Bone and joint problems
- Leg sores and ulcers
- Retina (eye) damage
- Hemoglobin A (HbA). HbA is the hemoglobin molecule found in normal red blood cells during childhood and adulthood. People who do not have sickle cell disease generally have this type of hemoglobin in their blood cells.
- Hemoglobin S (HbS). HbS (S is for sickle) is the abnormal variant of hemoglobin A, which occurs in sickle-red blood cells and is the primary problem in the disease. The difference between hemoglobin A (HbA) and hemoglobin S (HbS) is only 1 amino acid out of about 300 that are common to both. This difference in the amino acid sequence makes the hemoglobin protein fold abnormally.
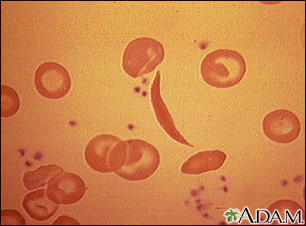
- When the sickle hemoglobin molecule loses its oxygen, red blood cells deform into a sickle or crescent shape.
- These sickle-shaped cells stick to the walls and cannot squeeze through the capillaries. Blood flow through tiny blood vessels slows or stops in many parts of the body. This deprives tissues and organs of oxygen.
- When this blood flow slows or stops suddenly in a certain part of the body, the decrease in oxygen (hypoxia) can cause severe pain (the sickle cell crisis). Over time, it leads to gradual destruction in organs and tissues throughout the body.
- The higher the concentration of sickle hemoglobin, and the more acidic the environment, the faster the sickle cell process. When blood cells dry out (dehydrate), the density of hemoglobin S within the cell increases, which speeds the sickling process.
- Sickle cells have a shorter life span (10 to 20 days) than normal red blood cells (90 to 120 days). Every day the body produces new red blood cells to replace old ones, but sickle cells become destroyed so fast that the body cannot keep up. The red blood cell count drops, which results in anemia. This gives sickle cell disease its more common name, sickle cell anemia.
- If one normal hemoglobin gene and one sickle cell gene are inherited, a person will have sickle cell trait. People who have sickle cell trait are protected from malaria and do not develop sickle cell disease, but they are "carriers" who can pass the abnormal gene on to their children. In general, most people with sickle cell trait are healthy, although some individuals may face kidney complications and other health problems.
- If two sickle genes are inherited, a person will have sickle cell disease.
- If both parents have sickle cell trait (each has one normal and one sickle cell gene), the child has a 50% chance of inheriting sickle cell trait, 25% chance of inheriting sickle cell disease (two sickle cell genes), and 25% chance of inheriting two normal genes (having neither the trait nor the disease).
- If one parent has sickle cell trait (one normal gene and one sickle cell gene) and the other parent has two normal hemoglobin genes, the child has a 50% chance of inheriting sickle cell trait (one normal gene and one sickle cell gene) and a 50% of inheriting neither the trait nor the disease (two normal genes). The child is not at risk of inheriting sickle cell disease.
- If one parent has sickle cell disease (two sickle cell genes) and the other parent has sickle cell trait (one normal gene, one sickle cell gene), the child has a 50% chance of inheriting sickle cell trait and a 50% chance of inheriting sickle cell disease.
- If one parent has sickle cell disease and the other parent has two normal hemoglobin genes, the child has a 100% chance of inheriting sickle cell trait, but not the disease.
- If both parents have sickle cell disease, the child has a 100% chance of inheriting the disease.
- Fever
- Swelling of the hands and feet
- Pain in the chest, abdomen, limbs, and joints
- Nosebleeds and frequent upper respiratory infections
- Fatigue and shortness of breath (signs of anemia)
- Irritability
- Jaundice (yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes)
- Delayed puberty (in young teenagers)
- Severe joint pain
- Progressive anemia
- Leg sores
- Gum disease
- Vision problems
- In general, any activity that boosts the body's requirement for oxygen, such as illness, physical stress, or being at high altitudes, increases the risk for a sickle pain crisis. Very often, however, the trigger is unknown.
- People typically describe the pain as sharp, intense, and throbbing. Severe sickle cell pain is described as comparable to cancer pain, and more severe than postsurgical pain. Shortness of breath is common.
- Pain most commonly occurs in the chest, arms, legs, lower back, or stomach, and can migrate from one location to another. Episodes usually recur in the same areas. Attacks can last anywhere from several hours to several days. In some cases, the person may need to stay in the hospital.
- When a large number of sickled red blood cells collect and pool in the person's spleen, a condition called splenic sequestration can occur. The spleen becomes enlarged and swollen, causing pain and leading to anemia. Repeated episodes of splenic sequestration can cause scarring and permanent damage to the spleen. Sickle cell crises can also occur in, and damage the liver.
- Males of any age may have prolonged, often painful erections, a condition called priapism.
- Sickle blood cells block blood vessels in the lungs during a sickle cell crisis.
- Fat embolisms (clots), which are particles formed from fatty tissue in the bone marrow, block small blood vessels and arteries of the lungs.
- Infections such as pneumonia cause problems with lung function.
- Fever of 101.3°F (38.5°C) or above
- Rapid or labored breathing
- Wheezing or cough
- Chest pain
- Back or stomach pain
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (can cause pneumonia, blood infections, or meningitis)
- Haemophilus influenzae (also a cause of pneumonia, blood infections, and meningitis)
- Chlamydia pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. These are the important infections in acute chest syndrome (see above).
- Gram-negative bacteria. This group of bacteria mostly infects hospitalized people and can cause serious pneumonias and other infections.
- Transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasonography measures the speed of blood flow in the brain. It can be used for identifying children at risk for stroke. However, high-risk children are still vulnerable to stroke even if the TCD screening diagnoses normal blood flow velocities.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect small blockages in blood vessels and may help confirm high risk in people identified by TCD ultrasound.
- Angiography is an invasive diagnostic technique useful for detecting aneurysms. (An aneurysm is a bulging in the blood vessel wall, which can result in stroke if it bursts in the brain.)
- Genetic markers may eventually be used to help identify people with sickle cell disease at higher risk for stroke.
- Antibiotics, usually penicillin, are commonly given to infants and young children, as well as adults, to help prevent infections.
- Pain relief medications ranging from nonprescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to opioids are given to control pain.
- Hydroxyurea (Hydrea/Droxia) is prescribed for people with moderate-to-severe sickle cell disease to help reduce the frequency of pain episodes and acute chest syndrome. It may also be an option for select children found to be at high risk for stroke.
- L-glutamine (Endari) is prescribed to reduce the acute complications of sickle cell disease in adults and children over 5 years of age.
- Oxbryta (Voxelotor) may be prescribed to reduce the sickling of cells in patients over the age of 12.
- Crizanlizumab (Adakveo) may be prescribed to reduce the frequency of pain crises in patients over the age of 16.
- To manage sudden severe events, including acute chest syndrome, stroke, widespread infection (septicemia), and multi-organ failure.
- To manage severe anemia, usually caused by splenic sequestration (dangerously enlarged spleen) or aplasia (halting of red blood cell production, most often caused by parvovirus). Transfusions are generally not necessary for mild or moderate anemia.
- Before surgery. Preoperative transfusions may be given to help prevent complications.
- Stroke prevention for first or recurrent strokes. Evidence shows that regular (every 3 to 4 weeks) blood transfusions can reduce the risk for a first stroke by 90% in high-risk children. In addition, studies indicate that as many as 90% of people who have experienced a stroke do not experience another stroke after 5 years of transfusions.
- Pulmonary hypertension and chronic lung disease.
- Heart failure.
- Chronic kidney failure and severe anemia.
- To reduce episodes of pain and acute chest syndrome.
- Simple Transfusion. Simple transfusions involve the infusion of one or two units of donor blood to restore blood volume levels and oxygen flow. It is used for moderately severe anemia, severe fatigue, and non-emergency situations when there is a need for increased oxygen. It is also used for acute chest syndrome.
- Exchange Transfusion. Exchange transfusion involves drawing out the person's blood while exchanging it for donor red blood cells. Exchange transfusions may be used when there is any evidence that the person's condition is deteriorating. It prevents stroke and may also be used in people with severe acute chest syndrome. It reduces the risk for iron overload in people who require chronic transfusion therapy.
- Immune reactions. An immune reaction may occur in response to donor blood. In such cases, the person develops antibodies that target and destroy the transfused cells. This reaction, which can occur 5 to 20 days after transfusion, can result in severe anemia and may be life-threatening in some cases. It can usually be prevented with careful screening and matching of donor blood groups before the transfusion.
- Hyperviscosity. With this condition, a mixture of hemoglobin S and normal hemoglobin causes the blood to become too "thick". The person is at risk for high blood pressure, altered mental status, and seizures. Careful monitoring can prevent this condition.
- Transmission of viral illness. Before widespread blood screening, transfusions were highly associated with a risk for hepatitis and HIV. This complication has decreased considerably.
- Intravenous administration of fluids
- Supplementary oxygen and monitoring of oxygen levels
- Breathing treatments
- Antibiotics
- Pain relievers
- Blood transfusions may be necessary
- Have regular physical examinations every 3 to 6 months.
- Have periodic and careful eye examinations.
- Have sufficient rest, warmth, and increased fluid intake. (These are critical precautions for reducing oxygen loss and the risk for dehydration.)
- Avoid situations, such as crowds, that increase risk for infections.
- Avoid excessive demands on the body that increase oxygen needs (such as physical overexertion and stress). Low impact exercise (such as leg lifts and light weights) may be useful and safe for maintaining strength, particularly in the legs and hips, but people should consult their doctor before starting any exercise program.
- Avoid high altitudes if possible. If flying is necessary, be sure that the airline can provide oxygen.
- Do not smoke, and avoid exposure to second-hand smoke. Both active and passive smoking may promote acute chest syndrome in people with sickle cell disease.
- Pneumococcal vaccines. All sickle cell people should be vaccinated with the pneumococcal vaccine. There are two types of pneumococcal vaccines; the choice between them depends on the age of the person.
- Meningitis vaccination. The CDC recommends that children with sickle cell disease receive either the MenHibrix or Menveo vaccines starting at age 2 months. The MenHibrix vaccine protects against both the Neisseria meningitidis and Haemophilus influenzae strains that cause bacterial meningitis. Menveo protects against four strains of N. meningitidis.
- Influenza vaccines ("flu shots") should be given every winter, starting at age 6 months.
- Hepatitis B vaccine. All children should receive this vaccine.
- Fluids are extremely important. The person should drink as much water as possible each day to prevent dehydration.
- Diet should provide adequate calories, protein, fats, and vitamins and minerals. People and families should discuss vitamin and mineral supplements with their doctors and nurses.
- Some studies suggest that omega-three fatty acids, found in fish and soybean oil as well as dietary supplements, might make red blood cell membranes less fragile and possibly less likely to sickle, although no studies have proven this definitively.
- Stress Reduction. Stress reduction techniques and relaxation methods appear to be helpful. Breathing and mediation techniques may be very helpful.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy. Studies suggest that cognitive-behavioral therapies that teach coping skills can result in less negative thinking and possibly less pain. Coping skills can help the person's ability to manage symptoms such as pain.
- Support Associations. Support groups and online support communities can offer valuable advice and advocacy for people and their families.
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) -- www.nhlbi.nih.gov
- U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention -- www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/index.html
- American Society of Hematology -- www.hematology.org
- Sickle Cell Information Center -- scinfo.org
- Find clinical trials -- www.clinicaltrials.gov
Highlights
What is Sickle Cell Disease?
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder in which the body produces abnormally shaped red blood cells. In sickle cell disease, the hemoglobin in red blood cells clumps together. This causes red blood cells to become stiff and C-shaped. These sickle cells block blood flow in blood vessels. Sickle cells break down more rapidly than normal red blood cells, which results in anemia.
What Causes Sickle Cell Disease?
Sickle cell disease is a genetic disorder. People who have sickle cell disease are born with two sickle cell genes, one from each parent. If one normal hemoglobin gene and one sickle cell gene are inherited, a person will have sickle cell trait. People who have sickle cell trait do not develop sickle cell disease, but they are "carriers" who can pass the abnormal gene on to their children.
Complications of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease can block the flow of blood in small arteries in many parts of the body, causing many complications. The hallmark of sickle cell disease is the sickle cell crisis, which causes sudden attacks of severe pain. An infection or blockage of blood vessels in the lungs can trigger acute chest syndrome, another common and serious occurrence. Additional medical complications include:
Recent Findings about Sickle Cell Disease
On November 15, 2019, the FDA approved crizanlizumab-tmca (Adakveo) to reduce the frequency of pain crises in patients over the age of 16.
On November 25, 2019, the FDA approved voxelotor (Oxbryta) for patients over the age of 12. This drug improves the red blood cell count.
Introduction
Sickle cell disease (also called sickle cell anemia) is an inherited blood disorder that affects red blood cells. The sickle cell gene causes the body to produce abnormal hemoglobin. In sickle cell disease, the hemoglobin clumps together, causing red blood cells to become stiff and develop a C-shaped ("sickle") form. These sickled red blood cells can block blood vessels, reducing blood flow in many parts of the body. This process results in tissue and organ damage.
Hemoglobin and Iron
Each red blood cell contains about 280 million hemoglobin molecules. Hemoglobin is the most important component of red blood cells. It is composed of protein (globulin) and a molecule (heme), which binds to iron. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
In the lungs, the heme component takes up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide. The red blood cells carry the oxygen to the body's tissues, where the hemoglobin releases the oxygen in exchange for carbon dioxide, and the cycle repeats. The oxygen is essential for all cells in the body to function.
Sickle cell disease reduces or denies adequate oxygen to many parts of the body. This contributes to the severe pain experienced as a sickle cell crisis and both short- and long-term organ damage.
Causes
Sickle Cell Disease and Hemoglobin
Sickle cell disease occurs from genetic changes that cause abnormalities in hemoglobin molecules:
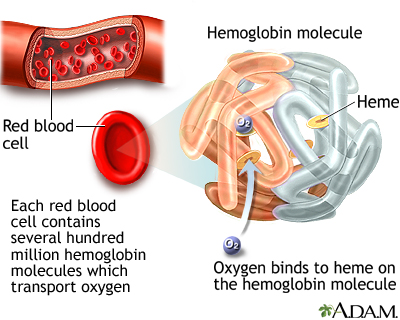
Hemoglobin is the most important component of red blood cells. It is composed of a protein called heme, which binds oxygen. In the lungs, oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Abnormalities of an individual's hemoglobin value can indicate defects in red blood cell balance. Both low and high values can indicate disease states.
The Sickle Cell Disease Process
The symptoms and problems of sickle cell disease are a result of the hemoglobin S (HbS) molecule:
Risk Factors
The sickle cell gene for hemoglobin S (HbS) is the most common inherited blood condition in the United States. About 70,000 to 100,000 Americans -- mostly African Americans -- have sickle cell disease. About 2.5 million Americans have the sickle cell trait.
Sickle cell disease is inherited. People at risk for inheriting the gene for sickle cell descend from people who are or were originally from Africa or parts of India and the Mediterranean. The sickle cell gene also occurs in people from South and Central America, the Caribbean, and the Middle East. The high prevalence of the sickle cell gene in these regions of the world is due to the sickle cell's ability to make red blood cells resistant to the malaria parasite.
People inherit a pair of genes that regulate hemoglobin, with one gene coming from each parent:
Risk of Inheritance
The risk for a child inheriting sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait is as follows:
Symptoms
General Symptoms in Infants
In infants, symptoms do not usually appear until late in the baby's first year. Most commonly, they include:
General Symptoms in Children
Pain, which can be very severe, is the most common complaint. It can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term). The pain usually arises from orthopedic problems in the legs and low back. Other symptoms can include:
Additional Symptoms in Adolescence or Adulthood
Symptoms from childhood continue in adolescence and adulthood. In addition, people may have:
Sickle Cell Crisis
Sickle cell crises are sudden and unpredictable episodes of pain that occur with varying frequency and severity in different people, and are usually followed by periods of remission. Severe sickle cell pain has been described as being equivalent to cancer pain and more severe than postsurgical pain. It most commonly occurs in the lower back, leg, abdomen, and chest, usually in two or more locations. Episodes usually recur in the same areas. (See "Sickle Cell (Vaso-Occlusive) Crisis" in Complications section of this report.)
Complications
Sickle Cell (Vaso-Occlusive) Crisis
The hallmark complication of sickle cell disease is the sickle cell crisis (also called vaso-occlusive crisis), which is a sudden and severe episode of pain. These crises occur when sickled cells block the flow of blood through the body.
The pattern of a sickle cell crisis may occur as follows:
Episodes cannot be predicted, and they vary widely among different individuals. Episodes sometimes become less frequent with increasing age. Generally, people can resume a relatively normal life between crises.
Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS)
Acute chest syndrome (ACS) is a sudden condition that occurs when the lung tissues are deprived of oxygen. ACS can occur when:
ACS can be very painful, dangerous, and even life-threatening. Once ACS occurs, it is likely to happen again. ACS is a leading cause of illness among people with sickle cell disease. Children with asthma are at particular risk for having ACS.
Symptoms of ACS include:
Infections
Infections are common and an important cause of severe complications. Before early screening for sickle cell disease and the use of preventive antibiotics in children, many infants with sickle cell died from infections. Fortunately, the use of required sickle cell screening tests for newborns, and the use of preventive antibiotics and immunizations in babies who are born with the disease, have significantly reduced mortality rates.
Infections in Infants and Toddlers with Sickle Cell Disease
The most common organisms causing infection in children with sickle cell disease include:
Such infections pose a serious threat to infants and very young children with sickle cell disease. They can rapidly progress to fatal pneumonia in infants, and death can occur within a few hours after onset of fever. The risk for pneumococcal meningitis, a dangerous infection of the central nervous system, is also significant.
Infections in Children and Adults
Infections are also common in older children and adults with sickle cell disease, particularly respiratory infections such as pneumonia, kidney infections, and osteomyelitis, a serious infection in the bone. (The organisms causing them, however, tend to differ from those in young children.) Infection-causing organisms include:
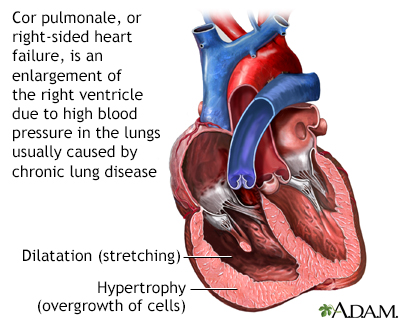
Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is a serious and potentially deadly condition that develops when pressure in the arteries of the lungs increases. It is an often-unrecognized complication and a significant cause of death in sickle cell disease. Many doctors recommend that all adults with sickle cell disease have echocardiographic testing to identify if they are at risk for pulmonary hypertension and need treatment.
The primary symptom of pulmonary hypertension is shortness of breath, which is often severe. Pulmonary hypertension can be very serious and life-threatening in the short- and long-term. If pulmonary hypertension develops suddenly it can cause respiratory failure, which is life-threatening. Over time, pulmonary hypertension may cause a condition called cor pulmonale, in which the right side of the heart increases in size. In some cases, this enlargement can lead to heart failure.
Stroke
After acute chest syndrome, stroke is the most common killer of people with sickle cell disease who are above 3 years of age. Between 8% and 10% of people suffer strokes, typically at about age 7. People may also suffer small strokes that may not be immediately noticeable. However, people who have many of these small strokes may over time start behaving differently or have worsening mental functioning.
Strokes are usually caused by blockages of vessels carrying oxygen to the brain. People with sickle cell disease are also at high risk for strokes caused by aneurysm, a weakened blood vessel wall that can rupture and hemorrhage. Multiple aneurysms are common in people with sickle cell disease, but they are often located where they cannot be treated surgically.
Anemia
Anemia is a significant characteristic in sickle cell disease (which is why the disease is commonly referred to as sickle cell anemia). People with sickle cell disease have a chronic shortage of healthy red blood cells, which leads to persistent anemia.
Hemolytic Anemia
Because of the short lifespan of the sickle red blood cells, the body is often unable to replace red blood cells as quickly as they are destroyed. This causes a particular form of anemia called hemolytic anemia. Most people with sickle cell disease have hemoglobin levels of about 8 g/dL, much lower than hemoglobin levels in healthy people. Chronic anemia reduces oxygen levels and increases the demand on the heart to pump more oxygen-bearing blood through the body. Eventually, this can cause the heart to enlarge dangerously with an increased risk for heart attack and heart failure.
Aplastic Crisis
Sometimes, people may experience an aplastic crisis. This happens when the cells in the bone marrow that are normally trying to make new red blood cells suddenly stop working and are unable to form new red cells. This leads to a sudden drop in the red blood cell count (hemoglobin level). This sudden stopping is often triggered by a virus called human parvovirus B19.
Splenic Sequestration
Children, adolescents, and possibly young adults may experience splenic sequestration, which can be a life-threatening condition. This happens when a large number of sickled red blood cells collect in the person's spleen. In addition to pain and abdominal swelling, splenic sequestration can cause a sudden drop in hemoglobin levels.
Priapism
Many males with sickle cell disease, including children, suffer from priapism. Priapism causes prolonged and painful erections that can last from several hours to days. If priapism is not treated, permanent partial or complete erectile dysfunction can occur.
Kidney Problems
The kidneys are particularly susceptible to damage from the sickling process. Persistent injury can cause a number of kidney disorders, including infection. Problems with urination are very common, particularly uncontrolled urination during sleep. People may have blood in the urine, although this is usually mild and painless and resolves without damaging consequences. Kidney failure is a major danger in older people and accounts for 10% to 15% of deaths in people with sickle cell disease. Renal medullary carcinoma is an aggressive, rapidly destructive tumor in the kidney that is rare but can occur in association with sickle cell disease.
Liver Problems
Enlargement of the liver (hepatomegaly) occurs in many people with sickle cell disease, which can lead to permanent liver damage and failure. In addition, because sickle cell people often need blood transfusions, they are at higher risk for acquiring hepatitis C. This risk, however, has decreased since screening procedures for donated blood have been implemented.
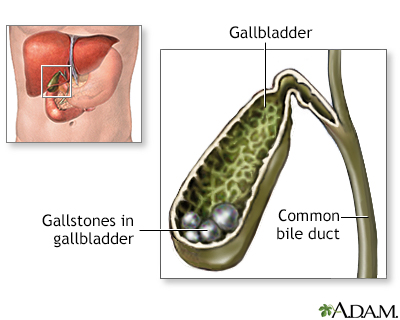
Gallbladder Disease
Gallstones are a common complication of sickle cell disease. In most cases, gallstones do not cause symptoms for years. When symptoms develop, people may feel overly full after meals, have pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen, or have nausea and vomiting. Acute attacks can be confused with a sickle cell crisis in the liver. Ultrasound is usually used to confirm a diagnosis of gallstones. If the person does not have symptoms, usually no treatment is necessary. If there is recurrent or severe pain from gallstones, the gallbladder may need to be removed.
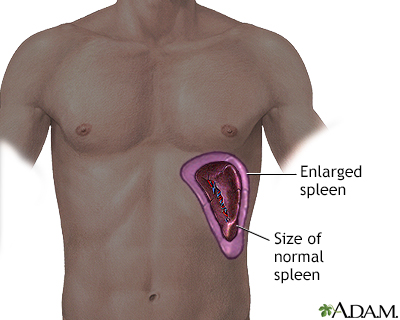
Spleen Damage
The spleen of most adults with sickle cell anemia is nonfunctional due to recurrent episodes of oxygen deprivation that eventually destroy it. Injury to spleen increases the risk for serious infection. Acute splenic sequestration crisis (sudden spleen enlargement) can occur when the spleen suddenly enlarges as a result of trapped blood.
Bone and Joint Problems
In some children with sickle cell disease, excessive production of blood cells in the bone marrow causes bones to grow abnormally, resulting in long legs and arms or misshapen skulls. Sickling that blocks oxygen to the bone can also cause bone loss and pain. Sickling that affects the hands and feet of children causes a painful condition called hand-foot syndrome. A condition called avascular necrosis of the hip occurs in adult sickle cell people when oxygen deprivation causes tissue death in the bone. Eventually, adult people may need surgery to remove diseased and dead bone tissue. People with severe cases may need joint replacement.
Leg Sores and Ulcers
Leg sores and ulcers may occur. They usually affect people older than age 10 years.
Eye Problems
Sickle cell disease can damage blood vessels in the eye and cause scarring and detachment of the retina, which can lead to blindness.
Pregnancy and Sickle Cell Disease
Women with sickle cell disease who become pregnant are at higher risk for complications such as miscarriage and premature birth, and their babies may have low birth weight. Sickle cell disease symptoms often worsen during pregnancy and pain crises become more frequent. However, with careful prenatal care and monitoring, serious problems can be avoided.
Other Medical Complications
Older children and adults with sickle cell are subject to other medical problems, including delayed growth and physical development. In severe cases, sickle cell disease can cause multiple organ failure.
Prognosis
New and better treatments for sickle cell disease are prolonging life and improving its quality. As recently as 1973, the average lifespan for people with sickle cell disease was only 14 years. Today, life expectancy for these people can reach 50 years and beyond. Women with sickle cell usually live longer than their male counterparts.
The damage of sickle cell disease occurs because of the logjam that sickle cells cause in the capillaries. Sickle cell disease slows the flow of blood and reduces the supply of oxygen to various tissues. Not only does pain occur when body tissues are damaged by lack of oxygen, but serious and even life-threatening complications can result from severe or prolonged oxygen deprivation.
Sickle cell disease is referred to in some African languages as "a state of suffering," but the disease has a wide spectrum of effects, which vary from person to person. In some people, the disease may trigger frequent and very painful sickle cell crises that require hospitalization. In others, it may cause less frequent and milder attacks.
Children with sickle cell disease are very susceptible to infections, mostly because their damaged spleens are unable to protect the body from bacteria. Signs of impaired lung function may occur even in very early years. Because children with sickle cell disease are living longer, older people are now facing medical problems related to the long-term adverse effects of the disease process. The most serious dangers are acute chest syndrome, long-term damage to major organs, stroke, and complications during pregnancy.
Diagnosis
Blood tests can determine whether an individual has sickle cell trait or sickle cell disease.
Screening Tests for Newborns
In the United States, hospitals routinely screen newborn babies for sickle cell disease. To perform the test, a blood sample is taken from the baby's heel using a simple needle prick. Early detection of sickle cell disease can help reduce the risk of life-threatening infections and increase the odds for survival. Babies who are diagnosed with sickle cell disease are given daily antibiotics to help prevent infections.
Prenatal diagnosis is also possible through amniocentesis. The amniotic fluid is tested for the presence of the sickle cell gene.
Diagnostic Tests for Stroke
Unfortunately, no tests can definitely determine which children are at highest risk for a stroke and, therefore, would be candidates for ongoing blood transfusions. The following are diagnostic tools currently used or under investigation:
Treatment
Treatment goals for sickle cell disease aim to relieve pain, prevent infections, and manage complications. [For specific information on complications, see Treatment of Complications section in this report.] People should seek care from a doctor who specializes in blood disorders (hematologist) or a clinic that has experience in treating sickle cell disease.
Bone marrow transplantation is the only potential cure, but it is used in only a small number of cases because few people are able to find donors who are suitable genetic matches. Blood transfusions are given to prevent worsening anemia and stroke.
Drug treatments for sickle cell disease include:
Hydroxyurea
HbF, also called fetal hemoglobin, is the form of hemoglobin present in the fetus and young infants. (Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.) Most HbF disappears early in childhood, although some HbF may persist. Fetal hemoglobin is able to block the sickling action of red blood cells. Because of this, infants with sickle cell disease do not develop symptoms of the illness until HbF levels have dropped. Adults who have sickle cell disease but still retain high levels of hemoglobin F generally have mild disease.
Hydroxyurea (Hydrea/Droxia) is a drug that reduces the severity of sickle cell disease by stimulating production of HbF. It is currently the only drug in general use to prevent acute sickle cell crises.
Hydroxyurea is recommended as first-line therapy to treat adults and adolescents with moderate-to-severe recurrent pain crises (occurring three or more times a year). Hydroxyurea reduces the frequency of acute pain crises and episodes of acute chest syndrome. It is taken daily by mouth. Hydroxyurea can be taken indefinitely and the benefits appear to be long-lasting.
Hydroxyurea is not a cure-all. Not all people respond to hydroxyurea, and the best candidates for the treatment are not yet clear. Many people who could benefit from this medication are not receiving it. Hydroxyurea is still being investigated for younger people. To date, the response to the drug in children with sickle cell disease is similar to the response in adults, and few severe adverse effects are being reported. Recent research also suggests that hydroxyurea is safe for infants.
Hydroxyurea may be a treatment option for select children at high risk for stroke. After at least one year of transfusions, children with abnormal transcranial Doppler loss findings but no imaging evidence of vascular changes otherwise may be candidates for this medicine.
Side effects include constipation, nausea, drowsiness, hair loss, leg ulcers, and inflammation of the mouth. More severe side effects include reduction of white blood cells (neutropenia) and the cells responsible for normal blood clotting (thrombocytopenia). Hydroxyurea should not be taken by pregnant women because it can cause birth defects. There have been concerns that long-term use of hydroxyurea may increase the risk of developing leukemia, but the significance of this risk remains unclear. Still for many people, the risks for untreated sickle cell disease may outweigh the risks for hydroxyurea's side effects.
People should handle hydroxyurea with care and wash their hands before and after touching the bottle or capsules. Household members who are not taking hydroxyurea (such as caregivers) should wear disposable gloves when handling the medicine or its bottle.
Blood Transfusions
Blood transfusions are often critical for treating sickle cell disease. Transfusions may be used either as treatment for specific episodes or as chronic transfusion therapy to prevent life-threatening complications. Ongoing transfusions can also help improve height and weight in children with sickle cell disease. Normal hemoglobin levels for people with sickle cell disease are around 8 g/dL. Doctors will try to keep the hemoglobin level no higher than 10 g/dL after transfusion.
Episodic Transfusions
Episodic transfusions are needed in the following situations:
Chronic Transfusions
Chronic (long-term) transfusions are used for:
Chronic blood transfusions carry their own risks, including iron overload, alloimmunization (an immune response reaction), and exposure to bloodborne microbes. Still, data from large-scale trials suggest that the risks for stroke outweigh the risks associated with transfusions. Researchers are working on ways to reduce the side effects associated with transfusion treatment.
Kinds of Transfusions
Transfusions may be either simple or exchange:
Iron Overload and Chelation Therapy
Iron overload
Increases risk for damage to the liver, heart, and other organs. A liver biopsy accurately determines whether excess iron levels are present.
Chelation therapy
Removes excess iron stores in the body. The drug deferoxamine (Desferal) is commonly used during such therapy. Unfortunately, deferoxamine has some severe side effects and must be used with a pump for about 12 hours each day. Many people do not continue treatment. A newer drug deferasirox (Exjade or Jadenu) is approved for the treatment of transfusion-related iron overload in people ages 2 years and older. It is taken once a day by mouth. This newer treatment may make chelation therapy much easier and less painful for people.
Other Complications of Transfusion Therapy
Bone Marrow or Stem Cell Transplantation
At this time, the only chance for a cure for sickle cell disease is bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. The bone marrow nurtures stem cells, which are early cells that mature into red and white blood cells and platelets. By destroying the person's sickle cell diseased bone marrow and stem cells and transplanting healthy bone marrow from a genetically matched donor, normal hemoglobin may be produced.
Bone marrow transplantations have been performed successfully in select children with sickle cell disease. Best results are obtained with matched siblings or related donors. The next best option is fully matched but unrelated donors. Unfortunately, this second option is only rarely available. However, due to a lack of available donors and the risks of developing potential complications, bone marrow transplantations for sickle cell disease are not routinely performed. Complications can include the immune system's rejection of the transplant (a condition called graft-versus-host-disease) and serious infections. People can suffer serious neurological damage if the procedure triggers bleeding in the brain. In general, younger children are considered better candidates for bone marrow transplantation than older children.
Before a bone marrow transplant can be performed, the person must undergo chemotherapy to completely destroy their own bone marrow. Bone marrow transplantation is considered too risky for adults with sickle cell disease, because they cannot tolerate the chemotherapy regimen as well as children and they tend to have long-term organ damage as a result of the condition.
Researchers are investigating new types of bone marrow transplants for children and adults with sickle cell disease. Several new approaches appear promising. They include giving less intense doses of chemotherapy prior to the transplant (a regimen known as "reduced-intensity conditioning"), or using low doses of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation in place of chemotherapy.
In recent years, researchers have reported some success with "half-matched" marrow transplants (haploidentical transplant is the medical term), which uses a donor who shares only 50% of the recipient's genes. While this approach may potentially help expand donor options for people, the research is still very preliminary. Bone marrow transplant with a fully matched donor remains the best choice at this time.
Other Investigational Treatments
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide is a natural chemical in the body that relaxes smooth muscles and widens blood vessels. People with sickle cell disease are deficient in nitric oxide. This lack of nitric oxide constricts blood vessels and causes sickle cell pain. Some studies have indicated that inhaling nitric oxide may slow the disease process and improve symptoms in acute sickle cell crises. Other studies report that nitric oxide is of no benefit. In addition, nitric oxide is difficult to administer. More studies are needed to determine if nitric oxide should have a role in sickle cell therapy. (Nitric oxide is not the same substance as nitrous oxide, the so-called laughing gas used in dentistry.)
Arginine
Arginine is an amino acid involved in producing nitric oxide. Because a lack of arginine may contribute to the development of pulmonary hypertension, (a leading cause of death in people with sickle cell disease), arginine is being studied as a potential drug treatment. Some research is also being conducted on arginine nutritional supplements. People should talk to their doctors before taking these or any other supplements.
Drugs to Prevent Dehydration
Researchers are studying various drugs, as well as mineral supplements such as magnesium pidolate and zinc sulfate, that may help prevent potassium loss and red blood cell dehydration.
Treatment of Complications
Treatment of Pain
The basic objectives for managing a sickle cell crisis are control of pain and rehydration by administration of fluids. Oxygen is typically given for acute chest syndrome. Pain medications can help reduce the severe pain of sickle cell crises. These medications can range from non-prescription pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, to more powerful narcotics, such as the opioid drug morphine. Corticosteroid drugs may also be prescribed.
All people should have a treatment plan that helps guide them and their families during a pain episode. Plans should outline which medicines to take and when to seek medical help. People and families should learn to recognize symptoms early and begin managing with an appropriate amount of pain medication.
Treatment of Acute Chest Syndrome (ACS)
Acute chest syndrome can be fatal and must be treated immediately in a hospital. Basic treatments include:
Treatment of Infections
Fever in any person with sickle cell disease should be considered an indication of infection. Temperatures over 101°F (38.3°C) in children warrant a call to the doctor. Adults with sickle cell should call the doctor if they have a have fever over 100°F (37.8°C) and any signs of infection, including chest pain, productive cough, urinary problems, or any other symptoms. Pneumonia is common among people with sickle cell disease, as are meningitis, influenza, and hepatitis. Bone infections (osteomyelitis) can develop.
When people with sickle cell develop infections, they are nearly always hospitalized immediately and treated with intravenous or high-dose injections of antibiotics in order to prevent septicemia, the dangerous spread of the infection throughout the body. Antibiotics are also given on an outpatient basis.
It is important for people with sickle cell disease, especially children, to receive vaccinations to protect against infections. [For more information, see Prevention and Lifestyle Changes section in this report.]
Treatment of Anemia
Blood transfusions are given for suddenly worsening anemia. However, transfusions can increase the risk for infections and cause a build-up of iron in the blood. [For more information, see "Transfusion Therapy" in Treatment section of this report.]
Folic acid and possibly iron supplements are often given. However, people who are given multiple transfusions should avoid iron supplements. Also, folic acid can mask pernicious anemia, which is caused by deficiency of vitamin B12.
Treatment of Kidney Complications
Kidney damage in people with sickle cell disease can cause bleeding into the urine. Mild episodes can usually be treated with bed rest and fluids. Severe bleeding may require transfusions.
Treatment of Priapism
Priapism causes prolonged and painful erections that can last from several hours to days. It is best to treat this problem within 12 hours. Relief within 36 hours is important to avoid permanent erectile dysfunction. Pain relief, oxygen, and intravenous fluids are the initial steps. Exchange transfusions have also been proposed. Drugs used to prevent priapism include terbutaline and phenylephrine, which help restrict blood flow to the penis. A surgical procedure that implants a shunt to redirect blood flow is sometimes performed.
Treatment of Acute Splenic Sequestration (Damaged Spleen)
The spleen is often removed (splenectomy) in children who have one or two acute splenic sequestration crises. Transfusion therapy is an alternative for preventing acute splenic sequestration in high-risk people.
Treatment of Leg Ulcers
Leg ulcers are difficult to treat. Simple treatment with a moist dressing usually provides the best results. To treat mild ulcers, gently wash the leg with cotton gauze soaked in mild soap or a solution of one tablespoon of household bleach to one gallon of water. A dressing soaked in diluted white vinegar may be applied every 3 to 4 hours.
More severe ulcers require debridement, which is the removal of injured tissue until only healthy tissue remains. Debridement may be accomplished using chemical (enzymes), surgical, or mechanical (irrigation) means. Hydrogels are helpful in healing ulcers and are noninvasive and soothing. Topical antibiotics, saline or zinc oxide dressings, or cocoa butter or oil are also used depending on severity. The leg should be elevated. Bed rest for a week or more is sometimes required for severe ulcers. Skin grafts and transfusions may be helpful in extreme cases.
Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease During Pregnancy
Women who are pregnant should be treated at a high-risk clinic. They should take folic acid in addition to multivitamins and iron. Standard treatment is given for sickle cell crises, which may occur more frequently during pregnancy. However, certain drugs (such as hydroxyurea) should not be taken during pregnancy. The benefits of transfusions to prevent crises during pregnancy are not yet clear and doctors recommend them only for women who experience frequent complications during pregnancy. Problems that occur more often during pregnancy include preeclampsia, HELLP syndrome, blood clots, and anemia.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
General Precautions
To prevent or reduce the severity of long-term complications of sickle cell disease, several precautions may be helpful:
Preventing Infections
Vaccinations
Everyone with sickle cell disease should have complete regular immunizations against all common infections. Children should have all routine childhood vaccinations. The following are important vaccinations for everyone with sickle cell disease:
Tuberculosis skin testing should be performed every year except in people who have tested positive in the past.
Antibiotics
In addition to regular immunizations, preventive (prophylactic) antibiotics are the best approach for protection against pneumonia and other serious infections among children with sickle cell disease. Babies diagnosed with sickle cell are given daily antibiotics, starting at 2 months of age and continuing through 5 years of age. Penicillin is usually the antibiotic given, unless a child is allergic to it.
Nutrition and Dietary Supplements
Foods
Good nutrition, while essential for anyone, is critical for people with sickle cell disease. Some dietary recommendations include:
Vitamins
People should take daily folic acid and vitamin B12 and B6 supplements. Vitamin B6 may have specific anti-sickling properties. Some doctors recommend 1 mg folic acid, 6 microgram vitamin B12, and 6 mg vitamin B6. Foods containing one or all of these vitamins include meats, oily fish, poultry, whole grains, dried fortified cereals, soybeans, avocados, baked potatoes with skins, watermelon, plantains, bananas, peanuts, and brewer's yeast. Of note, folic acid can mask pernicious anemia, which is caused by deficiency of vitamin B12 and is more common in African Americans than other populations.
Minerals
Some research suggests that zinc supplements may possibly help reduce the frequency of sickle cell crises and infections. More research is needed.
Note on Iron. Although sickle cell disease is often referred to as anemia, people who receive multiple blood transfusions should avoid iron supplements or iron-rich foods, which increase the risk for iron overload.

Psychosocial Support
Sickle cell disease presents great emotional challenges for people and their families. For the family, nothing is more heartbreaking than watching their child endure extreme pain and life-threatening medical conditions. The person endures not only the pain itself but also the stress of not knowing when a sickle cell crisis will occur. They also have to struggle with lost time and social isolation at school and work, as well as fear of death.
Any chronic illness places stress on the person and family, but people with sickle cell disease and caregivers often face particular obstacles in finding psychological support for the disease. Communities in which many sickle cell people live may lack services that can meet their needs, and professionals who work in their medical facilities are often overworked. In a study comparing people with different kinds of long-term illnesses, those with sickle cell disease gave the lowest scores to their doctors and other professional caregivers for compassion and were least satisfied with their medical care.
It is very important for people and their caregivers to find emotional and psychological support. The following are some measures that may help in dealing with this disease:
Resources
Related Reports
References
Anie KA, Green J. Psychological therapies for sickle cell disease and pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(5):CD001916. PMID: 25966336 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25966336/.
Ataga KI, Kutlar A, Kanter J, et al. Crizanlizumab for the Prevention of Pain Crises in Sickle Cell Disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(5):429-439. PMID: 27959701 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27959701/.
Azar S, Wong TE. Sickle cell disease: a brief update. Med Clin North Am. 2017;101(2):375-393. PMID: 28189177 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28189177/.
Brandow AM, Carroll CP, Creary S, et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for sickle cell disease: management of acute and chronic pain. Blood Adv. 2020;4(12):2656-2701. PMID: 32559294 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32559294/.
DeBaun MR, Jordan LC, King AA, et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for sickle cell disease: prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cerebrovascular disease in children and adults. Blood Adv. 2020;4(8):1554-1588. PMID: 32298430 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32298430/.
Dixit R, Nettem S, Madan SS, et al. Folate supplementation in people with sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;3:CD011130. PMID: 29546732 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29546732/.
Estcourt LJ, Fortin PM, Hopewell S, Trivella M, Doree C, Abboud MR. Interventions for preventing silent cerebral infarcts in people with sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;5:CD012389. PMID: 28500860 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28500860/.
Hebbel RP, Vercellotti GM. Pathobiology of sickle cell disease. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 41.
Hirst C, Owusu-Ofori S. Prophylactic antibiotics for preventing pneumococcal infection in children with sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(11):CD003427. PMID: 25375222 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25375222/.
Hussein N, Weng SF, Kai J, Kleijnen J, Qureshi N. Preconception risk assessment for thalassaemia, sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis and Tay-Sachs disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(8):CD010849. PMID: 26264938 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26264938/.
Kato GJ, Piel FB, Reid CD, et al. Sickle cell disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18010. PMID: 29542687 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29542687/.
Klings ES, Machado RF, Barst RJ, et al. An official American Thoracic Society clinical practice guideline: diagnosis, risk stratification, and management of pulmonary hypertension of sickle cell disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;189(6):727-740. PMID: 24628312 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24628312/.
Liem RI, Lanzkron S, D Coates T, et al. American Society of Hematology 2019 guidelines for sickle cell disease: cardiopulmonary and kidney disease. Blood Adv. 2019;3(23):3867-3897. PMID: 31794601 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31794601/.
Machado RF, Gladwin MT. Pulmonary complications of hematologic diseases. In: Broaddus VC, Mason RJ, Ernst JD, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 94.
Martí-Carvajal AJ, Conterno LO, Knight-Madden JM. Antibiotics for treating acute chest syndrome in people with sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(3):CD006110. PMID: 25749695 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25749695/.
McGann PT, Nero AC, Ware RE. Clinical features of ß-thalassemia and sickle cell disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1013:1-26. PMID: 29127675 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29127675/.
Nevitt SJ, Jones AP, Howard J. Hydroxyurea (hydroxycarbamide) for sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;4:CD002202. PMID: 28426137 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28426137/.
Niihara Y, Smith WR, Stark CW. A Phase 3 Trial of l-Glutamine in Sickle Cell Disease. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(19):1880. PMID : 30403943 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30403943/.
Piel FB, Steinberg MH, Rees DC. Sickle Cell Disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(16):1561-1573. PMID: 28423290 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28423290/.
Qureshi A, Kaya B, Pancham S, et al. Guidelines for the use of hydroxycarbamide in children and adults with sickle cell disease: A British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br J Haematol. 2018;181(4):460-475. PMID: 29732531 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29732531/.
Rana S, Houston PE, Wang WC, et al. Hydroxyurea and growth in young children with sickle cell disease. Pediatrics. 2014;134(3):465-472. PMID: 25157002 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25157002/.
Roy NB, Fortin PM, Bull KR, et al. Interventions for chronic kidney disease in people with sickle cell disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;7:CD012380. PMID: 28672087 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28672087/.
Saunthararajah Y, Vichinsky EP. Sickle cell disease: clinical features and management. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 42.
Smith-Whitley K, Kwiatowski JL. Hemoglobinopathies. In: Kliegman RM, Lye PS, Bordini BJ, Toth H, Basel D, eds. Nelson Pediatric Symptom-Based Diagnosis. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 489.
Vichinsky E, Hoppe CC, Ataga KI, et al. A Phase 3 Randomized Trial of Voxelotor in Sickle Cell Disease. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(6):509-519. PMID: 31199090 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31199090/.
Ware RE, de Montalembert M, Tshilolo L, Abboud MR. Sickle cell disease. Lancet. 2017;390(10091):311-323. PMID: 28159390 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28159390/.
Yawn BP, Buchanan GR, Afenyi-Annan AN, et al. Management of sickle cell disease: summary of the 2014 evidence-based report by expert panel members. JAMA. 2014;312(10):1033-1048. PMID: 25203083 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25203083/.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 6/29/2020
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
