Thyroid gland removal
Total thyroidectomy; Partial thyroidectomy; Thyroidectomy; Subtotal thyroidectomy; Thyroid cancer - thyroidectomy; Papillary cancer - thyroidectomy; Goiter - thyroidectomy; Thyroid nodules - thyroidectomyThyroid gland removal is surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located inside the front of the lower neck. The thyroid gland is part of the hormone (endocrine) system. It helps your body regulate your metabolism.
The Basics
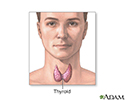
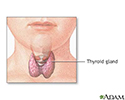
Thyroid gland
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
Thyroid gland
illustration
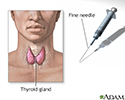
Thyroid gland biopsy
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck. It is a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, and plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism. If a sample of cells is needed from the thyroid gland a fine needle biopsy can be performed. During this procedure, a skinny needle is inserted into the thyroid gland, and a sample of thyroid cells and fluid is drawn into the needle. The needle is then withdrawn and the cells are sent for examination. This test is usually performed to determine if a thyroid nodule could be malignant (cancer).
Thyroid gland biopsy
illustration
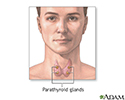
Parathyroid glands
The 4 parathyroid glands are located near or attached to the back side of the thyroid gland and produce parathyroid hormone (PTH). Parathyroid hormone regulates calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium balance within the blood and bone by maintaining a balance between the mineral levels in the blood and the bone.
Parathyroid glands
illustration
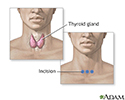
Incision for thyroid gland surgery
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck. It is a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, and plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism. If surgery or an open excisional biopsy is needed, an incision is made in front of the neck to gain access to the thyroid gland.
Incision for thyroid gland surgery
illustration
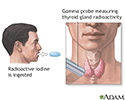
Thyroid uptake test
Radioactive iodine uptake test is a type of nuclear test performed to evaluate thyroid function. The patient ingests radioactive iodine (I-123 or I-131) capsules or liquid. After a time (usually 4 and 24-hours later), a gamma probe is placed over the thyroid gland to measure the amount of radioiodine uptake in the thyroid gland. The values are then compared.
Thyroid uptake test
illustration
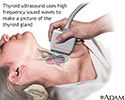
Thyroid ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound is a sound wave picture of the thyroid gland taken by a hand-held instrument and translated to a 2-dimensional picture on a monitor. It is used in diagnosis of tumors, cysts or goiters of the thyroid, and is a painless, no-risk procedure.
Thyroid ultrasound
illustration
Child thyroid anatomy
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck. It is a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, and plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism. Thyroid disorders are more common in older children and adolescents (especially in girls) than in infants. Most thyroid conditions can be treated medically, but occasionally surgery is required.
Child thyroid anatomy
illustration
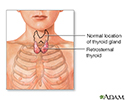
Retrosternal thyroid
The normal position of the thyroid is at the front of the neck above the sternal notch. In retrosternal thyroid, a portion of the gland extends below the sternal notch.
Retrosternal thyroid
illustration
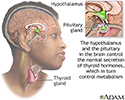
Brain-thyroid link
Although the thyroid gland releases the hormones which govern growth and metabolism, the brain (the pituitary and the hypothalamus) manages the release and the balance of the amount of hormones circulated.
Brain-thyroid link
illustration
Thyroid gland
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
Thyroid gland
illustration
Thyroid gland biopsy
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck. It is a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, and plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism. If a sample of cells is needed from the thyroid gland a fine needle biopsy can be performed. During this procedure, a skinny needle is inserted into the thyroid gland, and a sample of thyroid cells and fluid is drawn into the needle. The needle is then withdrawn and the cells are sent for examination. This test is usually performed to determine if a thyroid nodule could be malignant (cancer).
Thyroid gland biopsy
illustration
Parathyroid glands
The 4 parathyroid glands are located near or attached to the back side of the thyroid gland and produce parathyroid hormone (PTH). Parathyroid hormone regulates calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium balance within the blood and bone by maintaining a balance between the mineral levels in the blood and the bone.
Parathyroid glands
illustration
Incision for thyroid gland surgery
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck. It is a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, and plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism. If surgery or an open excisional biopsy is needed, an incision is made in front of the neck to gain access to the thyroid gland.
Incision for thyroid gland surgery
illustration
Thyroid uptake test
Radioactive iodine uptake test is a type of nuclear test performed to evaluate thyroid function. The patient ingests radioactive iodine (I-123 or I-131) capsules or liquid. After a time (usually 4 and 24-hours later), a gamma probe is placed over the thyroid gland to measure the amount of radioiodine uptake in the thyroid gland. The values are then compared.
Thyroid uptake test
illustration
Thyroid ultrasound
Thyroid ultrasound is a sound wave picture of the thyroid gland taken by a hand-held instrument and translated to a 2-dimensional picture on a monitor. It is used in diagnosis of tumors, cysts or goiters of the thyroid, and is a painless, no-risk procedure.
Thyroid ultrasound
illustration
Child thyroid anatomy
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck. It is a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, and plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism. Thyroid disorders are more common in older children and adolescents (especially in girls) than in infants. Most thyroid conditions can be treated medically, but occasionally surgery is required.
Child thyroid anatomy
illustration
Retrosternal thyroid
The normal position of the thyroid is at the front of the neck above the sternal notch. In retrosternal thyroid, a portion of the gland extends below the sternal notch.
Retrosternal thyroid
illustration
Brain-thyroid link
Although the thyroid gland releases the hormones which govern growth and metabolism, the brain (the pituitary and the hypothalamus) manages the release and the balance of the amount of hormones circulated.
Brain-thyroid link
illustration
Thyroid gland removal
Total thyroidectomy; Partial thyroidectomy; Thyroidectomy; Subtotal thyroidectomy; Thyroid cancer - thyroidectomy; Papillary cancer - thyroidectomy; Goiter - thyroidectomy; Thyroid nodules - thyroidectomyThyroid gland removal is surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located inside the front of the lower neck. The thyroid gland is part of the hormone (endocrine) system. It helps your body regulate your metabolism.
The Basics
Thyroid gland removal
Total thyroidectomy; Partial thyroidectomy; Thyroidectomy; Subtotal thyroidectomy; Thyroid cancer - thyroidectomy; Papillary cancer - thyroidectomy; Goiter - thyroidectomy; Thyroid nodules - thyroidectomyThyroid gland removal is surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located inside the front of the lower neck. The thyroid gland is part of the hormone (endocrine) system. It helps your body regulate your metabolism.
The Basics
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Debra G. Wechter, MD, FACS, General Surgery Practice Specializing in Breast Cancer, Virginia Mason Medical Center, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.