CT scan
CAT scan; Computed axial tomography scan; Computed tomography scanA computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdominal and pelvis CT scanCranial or head CT scanCervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral spine CT scanOrbit CT scanChest CT scanCT angiogram
CT scan
CT stands for computerized tomography. In this procedure, a thin X-ray beam is rotated around the area of the body to be visualized. Using very complicated mathematical processes called algorithms, the computer is able to generate a 3-D image of a section through the body. CT scans are very detailed and provide excellent information for the physician.
CT scan
illustration
CT scan of the brain
A CT or CAT scan (computed tomography) is a much more sensitive imaging technique than x-ray, allowing high definition not only of the bony structures, but of the soft tissues. Clear images of organs such as the brain, muscles, joint structures, veins and arteries, as well as anomalies like tumors and hemorrhages may be obtained with or without the injection of contrasting dye.
CT scan of the brain
illustration
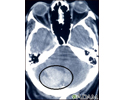
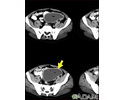
Intracerebellar hemorrhage - CT scan
Intracerebellar hemorrhage shown by CT scan. This hemorrhage followed use of t-PA.
Intracerebellar hemorrhage - CT scan
illustration
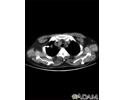
Pulmonary nodule, solitary - CT scan
This CT scan shows a single lesion (pulmonary nodule) in the right lung. This nodule is seen as the light circle in the upper portion of the dark area on the left side of the picture. A normal lung would look completely black in a CT scan.
Pulmonary nodule, solitary - CT scan
illustration
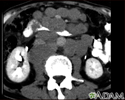
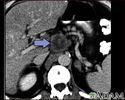
Intra-abdominal abscess - CT scan
CT scan of the pelvis showing a large intra-abdominal mass.
Intra-abdominal abscess - CT scan
illustration
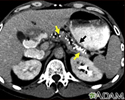
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
This abdominal CT scan shows tumor masses (malignant lymphomas) in the area behind the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal space).
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
illustration
Pancreatitis, chronic - CT scan
CT scan of the upper abdomen showing multiple white-colored calcifications. These occur in chronic pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis, chronic - CT scan
illustration
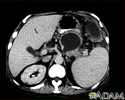
Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a pseudocyst in the corpus, or tail, of the pancreas.
Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan
illustration
Pancreatic cancer, CT scan
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a tumor (pancreas carcinoma) in the head of the pancreas, seen here in the middle of the picture.
Pancreatic cancer, CT scan
illustration
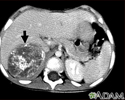
Neuroblastoma in the liver - CT scan
This CT scan of the upper abdomen shows a large tumor (neuroblastoma) on the person's right side (lower left side of picture). The tumor is behind the liver and is pushing the liver forward and may have possibly spread into the liver tissue.
Neuroblastoma in the liver - CT scan
illustration
CT scan
CT stands for computerized tomography. In this procedure, a thin X-ray beam is rotated around the area of the body to be visualized. Using very complicated mathematical processes called algorithms, the computer is able to generate a 3-D image of a section through the body. CT scans are very detailed and provide excellent information for the physician.
CT scan
illustration
CT scan of the brain
A CT or CAT scan (computed tomography) is a much more sensitive imaging technique than x-ray, allowing high definition not only of the bony structures, but of the soft tissues. Clear images of organs such as the brain, muscles, joint structures, veins and arteries, as well as anomalies like tumors and hemorrhages may be obtained with or without the injection of contrasting dye.
CT scan of the brain
illustration
Intracerebellar hemorrhage - CT scan
Intracerebellar hemorrhage shown by CT scan. This hemorrhage followed use of t-PA.
Intracerebellar hemorrhage - CT scan
illustration
Pulmonary nodule, solitary - CT scan
This CT scan shows a single lesion (pulmonary nodule) in the right lung. This nodule is seen as the light circle in the upper portion of the dark area on the left side of the picture. A normal lung would look completely black in a CT scan.
Pulmonary nodule, solitary - CT scan
illustration
Intra-abdominal abscess - CT scan
CT scan of the pelvis showing a large intra-abdominal mass.
Intra-abdominal abscess - CT scan
illustration
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
This abdominal CT scan shows tumor masses (malignant lymphomas) in the area behind the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal space).
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
illustration
Pancreatitis, chronic - CT scan
CT scan of the upper abdomen showing multiple white-colored calcifications. These occur in chronic pancreatitis.
Pancreatitis, chronic - CT scan
illustration
Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a pseudocyst in the corpus, or tail, of the pancreas.
Pancreatic pseudocyst - CT scan
illustration
Pancreatic cancer, CT scan
A CT scan of the upper abdomen showing a tumor (pancreas carcinoma) in the head of the pancreas, seen here in the middle of the picture.
Pancreatic cancer, CT scan
illustration
Neuroblastoma in the liver - CT scan
This CT scan of the upper abdomen shows a large tumor (neuroblastoma) on the person's right side (lower left side of picture). The tumor is behind the liver and is pushing the liver forward and may have possibly spread into the liver tissue.
Neuroblastoma in the liver - CT scan
illustration
CT scan
CAT scan; Computed axial tomography scan; Computed tomography scanA computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdominal and pelvis CT scanCranial or head CT scanCervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral spine CT scanOrbit CT scanChest CT scanCT angiogram
CT scan
CAT scan; Computed axial tomography scan; Computed tomography scanA computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdominal and pelvis CT scanCranial or head CT scanCervical, thoracic, and lumbosacral spine CT scanOrbit CT scanChest CT scanCT angiogram
Review Date: 7/15/2024
Reviewed By: Jason Levy, MD, FSIR, Northside Radiology Associates, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.