Wilson disease
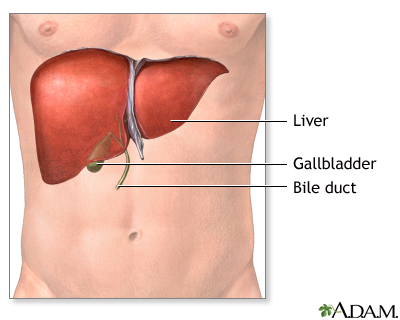
Wilson's disease; Hepatolenticular degenerationWilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous system.
Alzheimer disease - Animation
Alzheimer disease
Animation
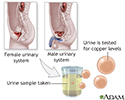
Copper urine test
The copper urine test is performed by collecting urine at specific times for a 24-hour period. The urine is tested for the amount of copper present. The copper urine test is used to determine the presence of Wilson disease, a sometimes fatal condition in which the buildup of excess copper damages the liver, and eventually the kidneys, eyes, and brain.
Copper urine test
illustration
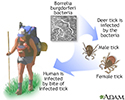
Lyme disease
Lyme disease is an acute inflammatory disease characterized by skin changes, joint inflammation and symptoms similar to the flu that is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Lyme disease is transmitted by the bite of a deer tick. Symptoms sometimes improve in 3 to 4 weeks, but secondary or tertiary disease may develop if initial infection is not treated.
Lyme disease
illustration
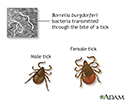
Tertiary lyme disease
Tertiary Lyme disease is a late, persistent inflammatory disease characterized by skin changes, neurological and musculoskeletal symptoms caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi transmitted by the bite of a tick. Tertiary Lyme disease is indicated by chronic arthritis.
Tertiary lyme disease
illustration
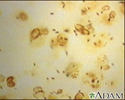
Legionnaire disease - organism legionella
Legionnaire disease was first described in 1976 after an outbreak of fatal pneumonia at a Legionnaires convention. The newly described organism which caused the disease was named Legionella pneumophila, shown in this picture. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. )
Legionnaire disease - organism legionella
illustration
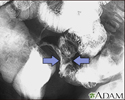
Crohn disease - X-ray
This lower abdominal x-ray shows narrowing (stenosis) of the end of the small intestine (ileum), caused by Crohn disease. Crohn disease typically affects the small intestine, whereas ulcerative colitis typically affects the large intestine. A solution containing a dye (barium), was swallowed by the patient. When it passed into the small intestines, this x-ray was taken (lower GI series).
Crohn disease - X-ray
illustration
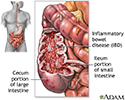
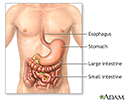
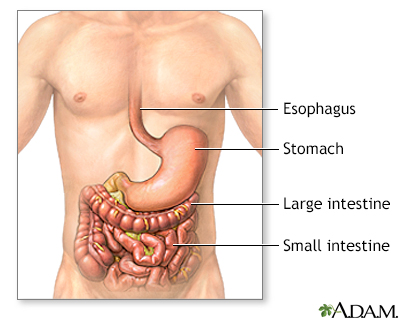
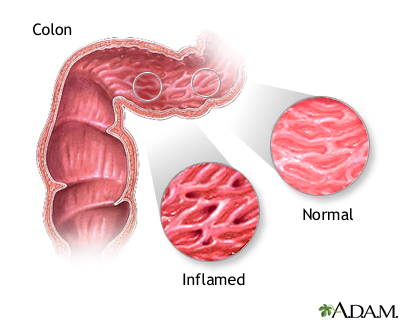
Inflammatory bowel disease
Crohn disease, also called regional enteritis, is a chronic inflammation of the intestines which is usually confined to the terminal portion of the small intestine, the ileum. Ulcerative colitis is a similar inflammation of the colon, or large intestine. These and other IBDs (inflammatory bowel disease) have been linked with an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
Inflammatory bowel disease
illustration
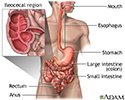
Crohn disease - affected areas
The inflammation of Crohn disease is nearly always found in the ileocecal region. The ileocecal region consists of the last few inches of the small intestine (the ileum), which moves digesting food to the beginning portion of the large intestine (the cecum). However, Crohn disease can occur anywhere along the digestive tract.
Crohn disease - affected areas
illustration
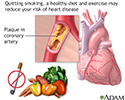
Prevention of heart disease
Heart disease may be prevented by recommended healthy diet, regular exercise and to stop smoking if you are a smoker. Follow your health care provider's recommendations for treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Prevention of heart disease
illustration
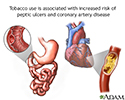
Tobacco and vascular disease
Tobacco use and exposure may cause an acceleration of coronary artery disease and peptic ulcer disease. It is also linked to cancer, stroke, COPD, fetal illness, and delayed wound healing.
Tobacco and vascular disease
illustration
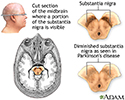
Substantia nigra and Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive disorder that affects movement, muscle control, and balance. Part of the disease process develops as cells are destroyed in certain parts of the brain stem, particularly the crescent-shaped cell mass known as the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra send out fibers to tissue located in both sides of the brain. There the cells release essential neurotransmitters that help control movement and coordination.
Substantia nigra and Parkinson disease
illustration
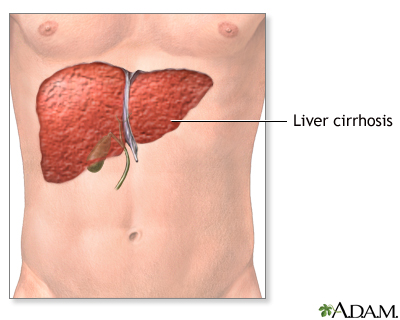
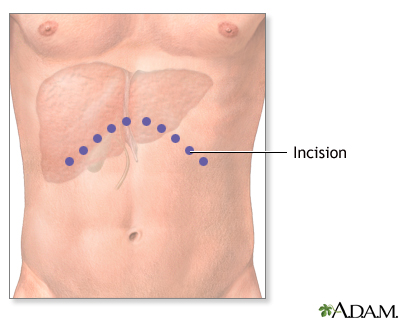
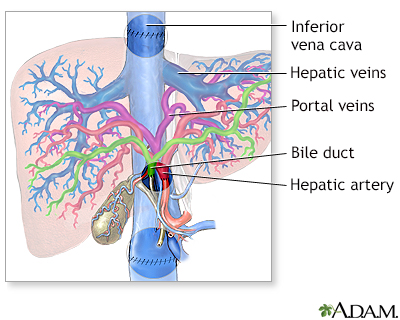
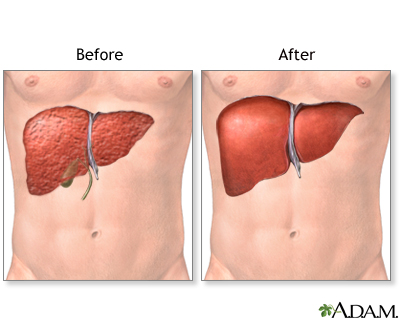
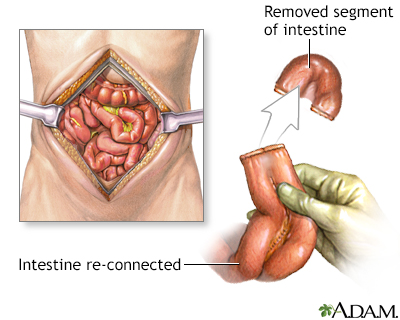
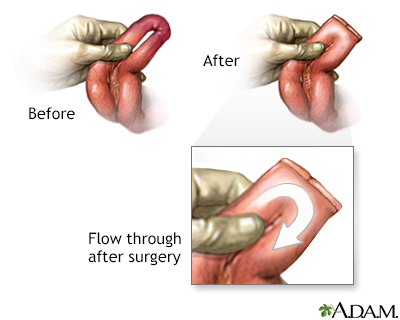
Liver transplant - series
Presentation
Liver transplant - series
Presentation
Inflammatory bowel disease - series
Presentation
Copper urine test
The copper urine test is performed by collecting urine at specific times for a 24-hour period. The urine is tested for the amount of copper present. The copper urine test is used to determine the presence of Wilson disease, a sometimes fatal condition in which the buildup of excess copper damages the liver, and eventually the kidneys, eyes, and brain.
Copper urine test
illustration
Lyme disease
Lyme disease is an acute inflammatory disease characterized by skin changes, joint inflammation and symptoms similar to the flu that is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Lyme disease is transmitted by the bite of a deer tick. Symptoms sometimes improve in 3 to 4 weeks, but secondary or tertiary disease may develop if initial infection is not treated.
Lyme disease
illustration
Tertiary lyme disease
Tertiary Lyme disease is a late, persistent inflammatory disease characterized by skin changes, neurological and musculoskeletal symptoms caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi transmitted by the bite of a tick. Tertiary Lyme disease is indicated by chronic arthritis.
Tertiary lyme disease
illustration
Legionnaire disease - organism legionella
Legionnaire disease was first described in 1976 after an outbreak of fatal pneumonia at a Legionnaires convention. The newly described organism which caused the disease was named Legionella pneumophila, shown in this picture. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. )
Legionnaire disease - organism legionella
illustration
Crohn disease - X-ray
This lower abdominal x-ray shows narrowing (stenosis) of the end of the small intestine (ileum), caused by Crohn disease. Crohn disease typically affects the small intestine, whereas ulcerative colitis typically affects the large intestine. A solution containing a dye (barium), was swallowed by the patient. When it passed into the small intestines, this x-ray was taken (lower GI series).
Crohn disease - X-ray
illustration
Inflammatory bowel disease
Crohn disease, also called regional enteritis, is a chronic inflammation of the intestines which is usually confined to the terminal portion of the small intestine, the ileum. Ulcerative colitis is a similar inflammation of the colon, or large intestine. These and other IBDs (inflammatory bowel disease) have been linked with an increased risk of colorectal cancer.
Inflammatory bowel disease
illustration
Crohn disease - affected areas
The inflammation of Crohn disease is nearly always found in the ileocecal region. The ileocecal region consists of the last few inches of the small intestine (the ileum), which moves digesting food to the beginning portion of the large intestine (the cecum). However, Crohn disease can occur anywhere along the digestive tract.
Crohn disease - affected areas
illustration
Prevention of heart disease
Heart disease may be prevented by recommended healthy diet, regular exercise and to stop smoking if you are a smoker. Follow your health care provider's recommendations for treatment and prevention of heart disease.
Prevention of heart disease
illustration
Tobacco and vascular disease
Tobacco use and exposure may cause an acceleration of coronary artery disease and peptic ulcer disease. It is also linked to cancer, stroke, COPD, fetal illness, and delayed wound healing.
Tobacco and vascular disease
illustration
Substantia nigra and Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive disorder that affects movement, muscle control, and balance. Part of the disease process develops as cells are destroyed in certain parts of the brain stem, particularly the crescent-shaped cell mass known as the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra send out fibers to tissue located in both sides of the brain. There the cells release essential neurotransmitters that help control movement and coordination.
Substantia nigra and Parkinson disease
illustration
Liver transplant - series
Presentation
Liver transplant - series
Presentation
Inflammatory bowel disease - series
Presentation
Wilson disease
Wilson's disease; Hepatolenticular degenerationWilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous system.
Wilson disease
Wilson's disease; Hepatolenticular degenerationWilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous system.
Review Date: 8/18/2024
Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.