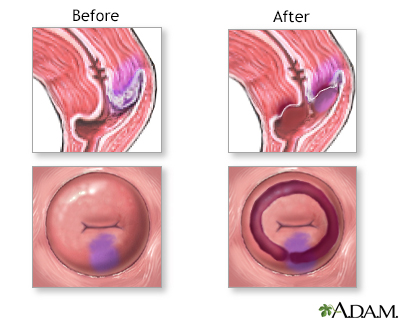
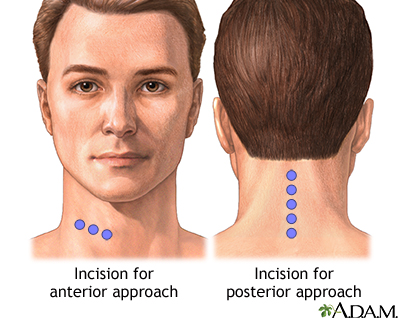
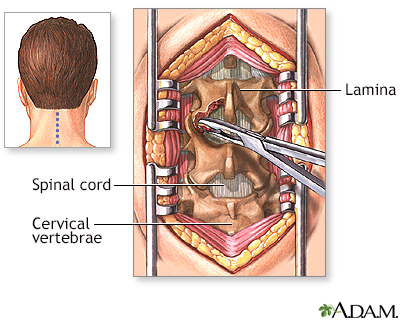
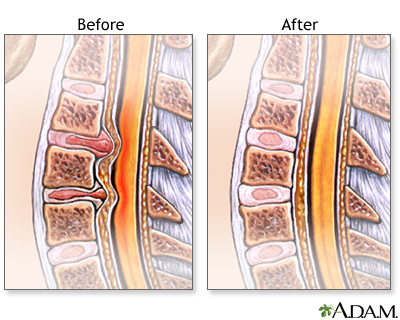
Steroid injections - tendon, bursa, joint
Corticosteroid injection; Cortisone injection; Bursitis - steroid; Tendonitis - steroidA steroid injection is a shot of medicine used to relieve a swollen or inflamed area that is often painful. It can be injected into a joint, tendon, or bursa.
A Closer Look
- Psoriasis-In-Depth (Detailed Report)
- Headaches - cluster - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Back pain and sciatica - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Multiple sclerosis - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Infertility in men - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Rheumatoid arthritis - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Hodgkin disease - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Osteoarthritis - Animation
Osteoarthritis
Animation
Herniated disk - Animation
Herniated disk
Animation
Cervical cancer - Animation
Cervical cancer
Animation
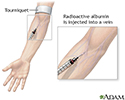
Albumin injection
Radioactive albumin injection is part of a nuclear scan test that is performed to measure the supply of blood through the lungs. After the injection, the lungs are scanned to detect the location of the radioactive particles as blood flows through the lungs.
Albumin injection
illustration
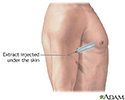
Antigen injection
Leprosy is caused by the organism Mycobacterium leprae. The leprosy test involves injection of an antigen just under the skin to determine if your body has a current or recent leprosy infection. The injection site is labeled and examined 3 days and 28 days later to see if there is a reaction.
Antigen injection
illustration
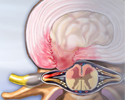
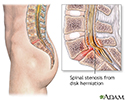
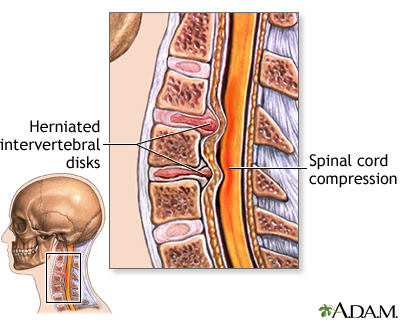
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the lumbar or cervical spinal canal. The narrowing can cause compression on nerve roots resulting in pain or weakness of the legs. Medications or steroid injections are often administered to reduce inflammation. If the pain is persistent and does not respond to these conservative measures, surgery is considered to relieve the pressure on the nerves.
Spinal stenosis
illustration
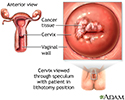
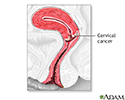
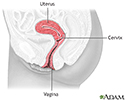
Cervical cancer
The development of cervical cancer is gradual and begins as a pre-cancerous condition called dysplasia. It is usually a slow-growing cancer and if caught early can be successfully treated. Routine Pap smears can detect early changes in the cells of the cervix allowing cervical cancer to be caught early.
Cervical cancer
illustration
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is the third most common type of cancer in women. Approximately 2% to 3% of all women over age 40 years will develop some form of cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer
illustration
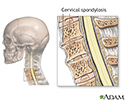
Cervical spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis is a disorder that results from abnormal growth of the bones of the neck and degeneration and mineral deposits in the cushions between the vertebrae. Progressive neck pain is a key indication of cervical spondylosis. It may be the only symptom in many cases. Examination often shows limited ability to bend the head toward the shoulders and limited ability to rotate the head. The goal of treatment is relief of pain and prevention of permanent spinal cord and nerve root injury.
Cervical spondylosis
illustration
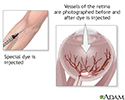
Retinal dye injection
Retinal dye injection is used to determine if there is proper circulation in the retinal vessels in the eye. When dye is injected in a vein in the arm, a rapid series of photographs are taken. Among other things this test can detect problems such as blockages or tumors.
Retinal dye injection
illustration
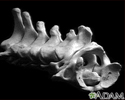
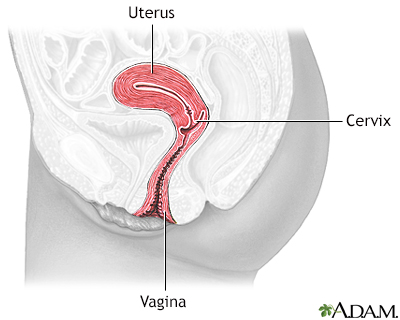
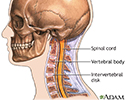
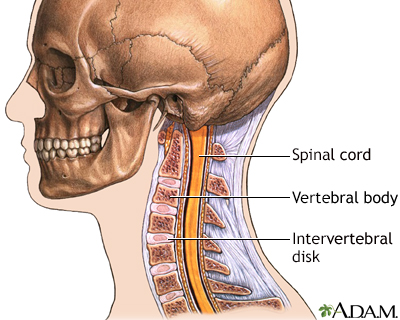
Vertebra, cervical (neck)
These are the seven bones of the neck, called the cervical vertebra. The top bone, seen on the right of this picture, is called the atlas, and is where the head attaches to the neck. The second bone is called the axis, upon which the head and atlas rotate. The vertebra are numbered from one to seven from the atlas down, and are referred to as C1, C2, C3, etc.
Vertebra, cervical (neck)
illustration
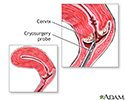
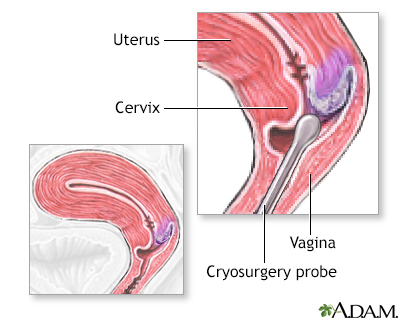
Cervical cryosurgery
Cryosurgery is super-freezing of tissue in order to destroy it. This procedure may be done to treat cervicitis or cervical dysplasia.
Cervical cryosurgery
illustration
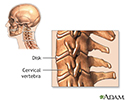
Cervical vertebrae
There are seven cervical vertebrae which are located in the neck. They are the smallest, and lightest vertebrae of the vertebral column.
Cervical vertebrae
illustration
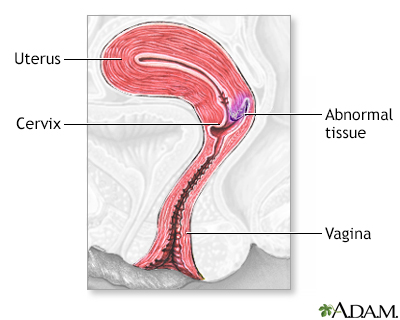
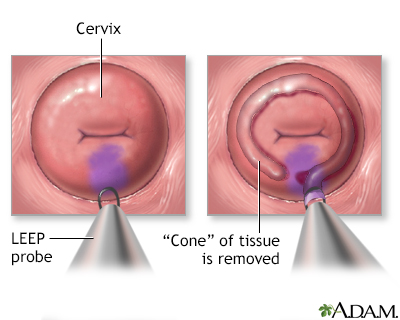
Cervical dysplasia - series
Presentation
Spinal surgery - cervical - series
Presentation
Osteoarthritis - Animation
Osteoarthritis
Animation
Herniated disk - Animation
Herniated disk
Animation
Cervical cancer - Animation
Cervical cancer
Animation
Albumin injection
Radioactive albumin injection is part of a nuclear scan test that is performed to measure the supply of blood through the lungs. After the injection, the lungs are scanned to detect the location of the radioactive particles as blood flows through the lungs.
Albumin injection
illustration
Antigen injection
Leprosy is caused by the organism Mycobacterium leprae. The leprosy test involves injection of an antigen just under the skin to determine if your body has a current or recent leprosy infection. The injection site is labeled and examined 3 days and 28 days later to see if there is a reaction.
Antigen injection
illustration
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the lumbar or cervical spinal canal. The narrowing can cause compression on nerve roots resulting in pain or weakness of the legs. Medications or steroid injections are often administered to reduce inflammation. If the pain is persistent and does not respond to these conservative measures, surgery is considered to relieve the pressure on the nerves.
Spinal stenosis
illustration
Cervical cancer
The development of cervical cancer is gradual and begins as a pre-cancerous condition called dysplasia. It is usually a slow-growing cancer and if caught early can be successfully treated. Routine Pap smears can detect early changes in the cells of the cervix allowing cervical cancer to be caught early.
Cervical cancer
illustration
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is the third most common type of cancer in women. Approximately 2% to 3% of all women over age 40 years will develop some form of cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer
illustration
Cervical spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis is a disorder that results from abnormal growth of the bones of the neck and degeneration and mineral deposits in the cushions between the vertebrae. Progressive neck pain is a key indication of cervical spondylosis. It may be the only symptom in many cases. Examination often shows limited ability to bend the head toward the shoulders and limited ability to rotate the head. The goal of treatment is relief of pain and prevention of permanent spinal cord and nerve root injury.
Cervical spondylosis
illustration
Retinal dye injection
Retinal dye injection is used to determine if there is proper circulation in the retinal vessels in the eye. When dye is injected in a vein in the arm, a rapid series of photographs are taken. Among other things this test can detect problems such as blockages or tumors.
Retinal dye injection
illustration
Vertebra, cervical (neck)
These are the seven bones of the neck, called the cervical vertebra. The top bone, seen on the right of this picture, is called the atlas, and is where the head attaches to the neck. The second bone is called the axis, upon which the head and atlas rotate. The vertebra are numbered from one to seven from the atlas down, and are referred to as C1, C2, C3, etc.
Vertebra, cervical (neck)
illustration
Cervical cryosurgery
Cryosurgery is super-freezing of tissue in order to destroy it. This procedure may be done to treat cervicitis or cervical dysplasia.
Cervical cryosurgery
illustration
Cervical vertebrae
There are seven cervical vertebrae which are located in the neck. They are the smallest, and lightest vertebrae of the vertebral column.
Cervical vertebrae
illustration
Cervical dysplasia - series
Presentation
Spinal surgery - cervical - series
Presentation
Steroid injections - tendon, bursa, joint
Corticosteroid injection; Cortisone injection; Bursitis - steroid; Tendonitis - steroidA steroid injection is a shot of medicine used to relieve a swollen or inflamed area that is often painful. It can be injected into a joint, tendon, or bursa.
A Closer Look
- Psoriasis-In-Depth (Detailed Report)
- Headaches - cluster - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Back pain and sciatica - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Multiple sclerosis - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Infertility in men - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Rheumatoid arthritis - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Hodgkin disease - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Steroid injections - tendon, bursa, joint
Corticosteroid injection; Cortisone injection; Bursitis - steroid; Tendonitis - steroidA steroid injection is a shot of medicine used to relieve a swollen or inflamed area that is often painful. It can be injected into a joint, tendon, or bursa.
A Closer Look
- Psoriasis-In-Depth (Detailed Report)
- Headaches - cluster - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Back pain and sciatica - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Multiple sclerosis - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Infertility in men - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Rheumatoid arthritis - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Carpal tunnel syndrome - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Hodgkin disease - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.