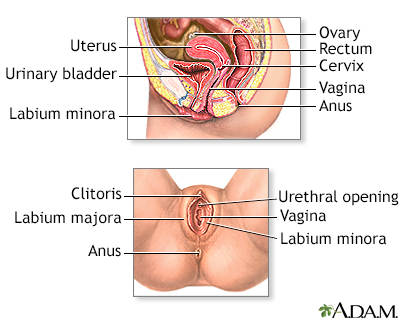
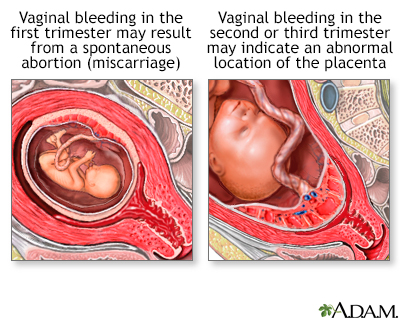
Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy
Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy is any discharge of blood from the vagina during pregnancy.
Considerations
Up to 1 in 4 women have vaginal bleeding at some time during their pregnancy. Bleeding is more common in the first 3 months (first trimester), especially with twins.
Causes
A small amount of light spotting or bleeding may be noted 10 to 14 days after conception. This spotting results from the fertilized egg attaching itself to the lining of the uterus. Assuming it is light and does not last very long, this finding is most often nothing to be concerned about.
During the first 3 months, vaginal bleeding may be a sign of a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Contact the health care provider right away.
During the first 3 months
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is any discharge of blood from the vagina. It can happen any time from conception (when the egg is fertilized) to ...
During months 4 to 9, bleeding may be a sign of:
During months 4 to 9
One out of 10 women will have vaginal bleeding during their 3rd trimester. At times, it may be a sign of a more serious problem. In the last few mo...

- The placenta separating from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born (abruptio placentae)
- Miscarriage
- The placenta covering all or part of the opening to the cervix (placenta previa)
Placenta previa
Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vasa previa (the baby's blood vessels exposed across or near the internal opening of the uterus)
Other possible causes of vaginal bleeding during pregnancy:
- Cervical polyp or growth
- Early labor (bloody show)
- Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pregnancy that occurs outside the womb (uterus).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection of the cervix
- Trauma to the cervix from intercourse (small amount of bleeding) or recent pelvic exam
Home Care
Avoid sexual intercourse until your provider tells you that it is safe to start having intercourse again.
Consume only fluids if the bleeding and cramping are severe.
You may need to cut down your activity or be put on bed rest at home. Your provider will talk to you about the specific kinds of activity changes you may need to make.
Medicine is not needed in most cases. DO NOT take any medicine without talking with your provider.
Also, talk to your provider about what to look for, such as the amount of bleeding and color of the blood.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have any vaginal bleeding during pregnancy. Treat this as a potential emergency.
- You have vaginal bleeding and have placenta previa (get to the hospital right away).
- You have cramps or labor pains.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take a medical history and perform a physical exam.
You will probably have a pelvic exam, or ultrasound as well.
Tests that may be done include:
- Blood tests
- Pregnancy ultrasound
- Ultrasound of the pelvis
You may be referred to a high risk pregnancy specialist (maternal fetal medicine specialist or perinatologist) for the duration of the pregnancy.
Reviewed By
LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Henn MC, Lall MD. Complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 173.
Turocy J, Williams Z. Early and recurrent pregnancy loss: etiology, diagnosis, treatment. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 16.