CBC blood test
Complete blood count; Anemia - CBCA complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:
- The number of white blood cells (WBC count)
- The number of red blood cells (RBC count)
- The number of platelets
- The total amount of hemoglobin in the blood
- The fraction of the blood composed of red blood cells (hematocrit)
The CBC test also provides information about the following measurements:
- Mean red blood cell volume (MCV)
- Mean hemoglobin amount per red blood cell (MCH)
- The mean amount of hemoglobin relative to the size of the cell (hemoglobin concentration) per red blood cell (MCHC)
-
How the Test is Performed
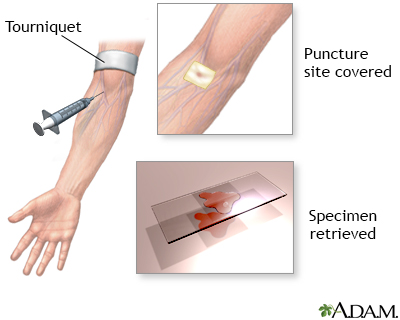
A blood sample is needed.
-
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation needed.
-
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, you may feel moderate pain. Some people feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward there may be some throbbing or slight bruising. This soon goes away.
-
Why the Test is Performed
A CBC is a commonly performed lab test. It can be used to detect or monitor many different health conditions. Your health care provider may order this test:
- If you are having symptoms, such as fatigue, weight loss, fever or other signs of an infection, weakness, bruising, bleeding, or any signs of cancer
- When you are receiving treatments (medicines or radiation) that may change your blood count results
- To monitor a long-term (chronic) health problem that may change your blood count results, such as chronic kidney disease
-
Normal Results
Blood counts may vary with altitude. In general, normal results are:
RBC count:
- Male: 4.6 to 6.2 million cells/mcL
- Female: 4.2 to 5.4 million cells/mcL
WBC count:
- 4,500 to 11,000 cells/mcL
Hematocrit:
- Male: 40% to 55%
- Female: 36% to 48%
Hemoglobin:
- Male: 13 to 18 gm/dL
- Female: 12 to 16 gm/dL
Red blood cell indices:
- MCV: 80 to 100 femtoliter
- MCH: 27 to 32 pg/cell
- MCHC: 32 to 36 gm/dL
Platelet count:
- 150,000 to 400,000/dL
The examples above are common measurements for results of these tests. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
-
What Abnormal Results Mean
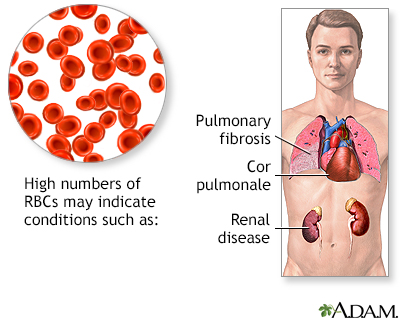
High RBC, hemoglobin, or hematocrit may be due to:
- A lack of enough water and fluids, such as from severe diarrhea, excessive sweating, or water pills used to treat high blood pressure
- Kidney disease with high erythropoietin production
- Low oxygen level in the blood for a long time, most often due to heart or lung disease, chronic carbon monoxide exposure, or living at a high altitude
- Polycythemia vera
- Smoking
- Use of testosterone
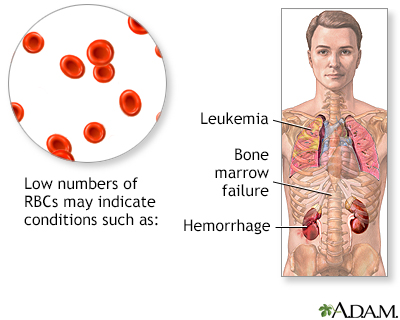
Low RBC, hemoglobin, or hematocrit is a sign of anemia, which can result from:
- Blood loss (either sudden, or from problems such as heavy menstrual periods over a long time)
- Bone marrow failure (for example, from radiation, infection, or tumor)
- Breakdown of red blood cells (hemolysis)
- Cancer and cancer treatment
- Certain long-term (chronic) medical conditions, such as chronic kidney disease, ulcerative colitis, or rheumatoid arthritis
- Iron deficiency
- Leukemia
- Long-term infections such as hepatitis
- Poor diet and nutrition, causing too little iron, folate, vitamin B12, or vitamin B6
- Multiple myeloma
A lower than normal white blood cell count is called leukopenia. A decreased WBC count may be due to:
- Alcohol overuse and liver damage
- Autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Bone marrow failure (for example, due to infection, tumor, radiation, or fibrosis)
- Chemotherapy medicines used to treat cancer
- Disease of the liver or spleen
- Enlarged spleen
- Infections caused by viruses, such as infectious mononucleosis or AIDS
- Medicines
A high WBC count is called leukocytosis. It can result from:
- Certain medicines, such as corticosteroids
- Infections
- Diseases such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or allergy
- Leukemia
- Severe emotional or physical stress
- Tissue damage (such as from burns or a heart attack)
A high platelet count may be due to:
- Bleeding
- Diseases such as cancer or blood disease
- Iron deficiency
- Problems with the bone marrow
A low platelet count may be due to:
- Disorders in which platelets are destroyed
- Pregnancy
- Enlarged spleen
- Bone marrow failure (for example, due to infection, tumor, radiation, or fibrosis)
- Chemotherapy medicines used to treat cancer
-
Risks
There is very little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another, and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
-
Considerations
RBCs transport hemoglobin which, in turn, carries oxygen. The amount of oxygen received by body tissues depends on the amount and function of RBCs and hemoglobin.
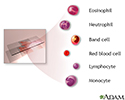
WBCs are mediators of inflammation and the immune response. There are various types of WBCs that normally appear in the blood:
- Neutrophils (polymorphonuclear leukocytes)
- Band cells (slightly immature neutrophils)
- T-type lymphocytes (T cells)
- B-type lymphocytes (B cells)
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
References
Lin JC, Benz, EJ Jr. Approach to anemia in the adult and child. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ Jr, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 35.
Means, RT Jr. Approach to the anemias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 144.
Vajpayee N, Graham SS, Bem S. Basic examination of blood and bone marrow. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 31.