Streptococcal screen
Rapid strep testA streptococcal screen is a test to detect group A streptococcus. This type of bacteria is the most common cause of strep throat.
-
How the Test is Performed
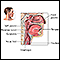
The test requires a throat swab. The swab is tested to identify group A streptococcus. It takes about 7 minutes to get the results.
-
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation. Tell your health care provider if you are taking antibiotics or have recently taken them.
-
How the Test will Feel
The back of your throat will be swabbed in the area of your tonsils. This may make you gag.
-
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may recommend this test if you have signs of strep throat, which include:
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Tender and swollen glands at the front of your neck
- White or yellow spots on your tonsils
-
Normal Results
A negative strep screen most often means group A streptococcus is not present. It is unlikely that you have strep throat.
If your provider still thinks that you may have strep throat, a throat culture will be done in children and adolescents.
-
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive strep screen most often means group A streptococcus is present and confirms that you have strep throat.
Sometimes, the test may be positive even if you do not have strep. This is called a false-positive result.
-
Risks
There are no risks.
-
Considerations
This test screens for the group A streptococcus bacteria only. It will not detect other causes of sore throat.
References
Allen CT, Nussenbaum B, Merati AL. Acute and chronic laryngopharyngitis. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 61.
Bryant AE, Stevens DL. Streptococcus pyogenes. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 197.
Stevens DL, Bryant AE, Hagman MM. Nonpneumococcal streptococcal infections and rheumatic fever. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 274.
Tanz RR. Acute pharyngitis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 409.