Femoral hernia
Groin herniaA hernia occurs when the contents of the abdomen push through a weak point or tear in the muscle wall of the belly. This layer of muscle holds the abdominal organs in place.
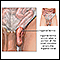
A femoral hernia is a bulge in the upper part of the thigh near the groin.
-
Causes
Most of the time, there is no clear cause of a hernia. Some hernias may be present at birth (congenital), but are not noticed until later in life.
Some factors that contribute to the development of a hernia include:
- Chronic constipation
- Chronic cough
- Heavy lifting
- Obesity
- Straining to urinate because of an enlarged prostate
Femoral hernias tend to occur more often in women than in men.
-
Symptoms
You may see a bulge in the upper thigh, just below the groin.
Most femoral hernias cause no symptoms. You may have some groin discomfort. It may be worse when you stand, lift heavy objects, or strain.
Sometimes, the first symptoms are:
- Sudden groin or thigh pain
- Abdominal pain
- Tingling feeling or numbness in the groin area
- Nausea
- Vomiting
This may mean that the intestine within the hernia is blocked. This is an emergency.
-
Exams and Tests
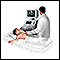
The best way to tell if there is a hernia is to have your health care provider perform a physical exam.
If there is any doubt about the exam findings, an ultrasound or CT scan may be helpful.
-
Treatment
Treatment depends on the symptoms present with the hernia.
If you feel sudden pain in your groin or thigh, a piece of intestine may be stuck in the hernia. This is called an incarcerated hernia. This problem needs treatment right away in an emergency room. You may need emergency surgery.
When you have ongoing discomfort from a femoral hernia, talk to your provider about your treatment choices.
Hernias often get larger as time passes. They do not go away on their own.
Compared to other types of hernias, femoral hernias more commonly have a piece of small intestine get stuck in the weak area.
Your surgeon may recommend femoral hernia repair surgery. The surgery is done to avoid a possible medical emergency.
If you do not have surgery right away:
- Increase your fiber intake and drink fluids to avoid constipation.
- Lose weight if you are overweight.
- See your provider if you have trouble urinating (men).
- Use proper lifting techniques.
-
Outlook (Prognosis)
The chances of a femoral hernia coming back after surgery are low.
If the intestine or other tissue becomes stuck, a portion of the intestine may need to be removed.
-
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider or go to the emergency room right away if:
- You suddenly develop pain in the hernia, and the hernia cannot be pushed back into the abdomen using gentle pressure.
- You develop nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain.
- Your hernia becomes red, purple, dark, or discolored.
Contact your provider if you have a bulge in the upper thigh next to the groin.
-
Prevention
It is difficult to prevent hernia. Making changes in your lifestyle can help, including taking precautions to avoid straining when lifting heavy things.
References
Jeyarajah DR, Dunbar KB. Abdominal hernias and gastric volvulus. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 27.
Poulose BK, Carbonell AM, Rosen MJ. Hernias. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 45.