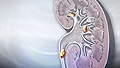
Hydronephrosis of one kidney
Hydronephrosis; Chronic hydronephrosis; Acute hydronephrosis; Urinary obstruction; Unilateral hydronephrosis; Nephrolithiasis - hydronephrosis; Kidney stone - hydronephrosis; Renal calculi - hydronephrosis; Ureteral calculi - hydronephrosis; Vesicoureteral reflux - hydronephrosis; Obstructive uropathy - hydronephrosisHydronephrosis is swelling of one kidney due to a backup of urine. This problem may occur in one kidney.
-
Causes
Hydronephrosis (kidney swelling) occurs as the result of a disease. It is not a disease itself. Conditions that may lead to hydronephrosis include:
- Blockage of a ureter due to scarring caused by prior infections, surgeries, or radiation treatments
- Blockage from an enlarged uterus during pregnancy
- Birth defects of the urinary system
- Back flow of urine from bladder to kidney, called vesicoureteral reflux (may occur as a birth defect or due to an enlarged prostate or narrowing of the urethra)
- Kidney stones
- Cancers or tumors that occur in the ureter, bladder, pelvis or abdomen
- Problems with the nerves that supply the bladder
The blockage and swelling of the kidney may occur suddenly or may develop slowly.
-
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Flank pain
- Abdominal mass, especially in children
- Nausea and vomiting
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Fever
- Painful urination (dysuria)
- Increased urinary frequency
- Increased urinary urgency
In some cases, there may be no symptoms.
-
Exams and Tests
The condition is found on an imaging test such as:
- MRI of the abdomen or pelvis
- CT scan of the kidneys, abdomen, or pelvis
- Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
- Renal nuclear scan
- Ultrasound of the kidney, abdomen, or pelvis
-
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the kidney swelling. Treatment may include:
- Placing a stent (tube) through the bladder and ureter to allow urine to flow from the kidney into the bladder
- Placing a tube into the kidney through the skin to allow the blocked urine to drain out of the body into a drainage bag
- Antibiotics for infections
- Surgery to correct the blockage or reflux
- Removal of any stone that is causing blockage
People who have only one kidney, who have a weakened immune system (such as due to diabetes or HIV), or who have had a kidney transplant will need treatment right away.
People who have long-term hydronephrosis may need antibiotics to reduce the risk of UTI.
-
Outlook (Prognosis)
Loss of kidney function, UTI, and pain may occur if the condition is left untreated.
-
Possible Complications
If hydronephrosis is not treated, the affected kidney may be permanently damaged. Kidney failure is rare if the other kidney is working normally. However, kidney failure will occur if there is only one functioning kidney. UTI and pain may also occur.
-
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have ongoing or severe flank pain, or fever, or if you think you may have hydronephrosis.
-
Prevention
Prevention of the disorders that cause this condition will prevent it from occurring.
References
Frøkiaer J. Urinary tract obstruction. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 37.
Gallagher KM, Hughes J. Urinary tract obstruction. In: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Tonelli M, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 61.