EGD discharge
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy - discharge; Upper endoscopy - discharge; Gastroscopy - dischargeEsophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine.
When You're in the Hospital
EGD is done with an endoscope. This is a flexible tube with a camera at the end.
During the procedure:
- You received medicine into a vein (IV).
Medicine into a vein (IV)
Conscious sedation uses a combination of medicines to help you relax (a sedative) and to reduce pain (an analgesic) during a medical or dental proced...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - The scope was inserted through your mouth into the esophagus (food pipe) to the stomach and first part of the small intestine (duodenum). Air was put through the endoscope to make it easier for the doctor to see.
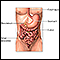
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestine, or jejunum. Aft...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - If needed, biopsies were taken through the endoscope. Biopsies are tissue samples that are looked at under the microscope.
Biopsies
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestine, or jejunum. Aft...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The test lasted about 5 to 20 minutes.
Right After the Test
You will be taken to an area to recover right after the test. You may wake up and not remember how you got there.
The nurse will check your blood pressure and pulse. Your IV will be removed.
Your doctor will come talk to you and explain the results of the test.
- Ask to have this information written down, as you may not remember what you were told later on.
- Final results for any tissue biopsies that were done may take up to 1 to 3 weeks.
Getting Home
Medicines you were given can change the way you think and make it harder to remember for the rest of the day.
As a result, it is NOT safe for you to drive a car or find your own way home.
You will not be allowed to leave alone. You will need to ask a friend or family member to take you home.
Eating and Drinking
You will be asked to wait 30 minutes or more before drinking. Try small sips of water first. When you can do this easily, you can begin with small amounts of solid foods.
You may feel a little bloated from air pumped into your stomach, and burp or pass gas more often over the day.
If your throat is sore, gargle with warm, salty water.
The Rest of the day
Do not plan to return to work for the rest of the day. It is not safe to drive or handle tools or equipment.
You should also avoid making important work or legal decisions for the rest of the day, even if you believe your thinking is clear.
Keep an eye on the site where the IV fluids and medicines were given. Watch for any redness or swelling. You can place a warm wet washcloth over the area.
Ask your doctor which medicines or blood thinners you should start taking again and when to take them.
If you had a polyp removed, your doctor may ask you to avoid lifting and other activities for up to 1 week.
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your health care provider if you have:
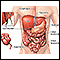
- Black, tarry stools
Black, tarry stools
Black or tarry stools with a foul smell are a sign of a problem in the upper digestive tract. It most often indicates that there is bleeding in the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Red blood in your stool
- Vomiting that will not stop or vomiting blood
- Severe pain or cramps in your belly
- Chest pain
- Blood in your stool for more than 2 bowel movements
- Chills or fever over 101°F (38.3°C)
- No bowel movement for more than 2 days
References
Koch MA, Zurad EG. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 91.
Rej A, Chew TS, Sanders DS. Gastroenterology. In: Penman ID, Ralston SH, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 23.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) - illustration
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test procedure to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine. The procedure uses an endoscope. This is a flexible tube with a light and camera at the end. A biopsy can be taken through the endoscope of any suspicious areas that are seen.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
illustration
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) - illustration
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test procedure to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine. The procedure uses an endoscope. This is a flexible tube with a light and camera at the end. A biopsy can be taken through the endoscope of any suspicious areas that are seen.
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
illustration
Review Date: 8/8/2023
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


