Laparoscopic gastric banding - discharge
Lap-Band - discharge; LAGB - discharge; Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding - discharge; Bariatric surgery - laparoscopic gastric banding - discharge; Obesity gastric banding discharge; Weight loss - gastric banding dischargeYou had laparoscopic gastric banding surgery to help with weight loss. This article tells you how to take care of yourself after the procedure.
Laparoscopic gastric banding
Laparoscopic gastric banding is surgery to help with weight loss. The surgeon places a band around the upper part of your stomach to create a small ...
When You're in the Hospital
You had laparoscopic gastric banding surgery to help with weight loss. Your surgeon placed a band around the upper part of your stomach to separate it from the lower part. The upper part of your stomach is now a small pouch with a narrow opening that goes into the larger, lower part of your stomach. You also had an access port placed under the skin on your abdomen.
Gastric banding surgery
Laparoscopic gastric banding is surgery to help with weight loss. The surgeon places a band around the upper part of your stomach to create a small ...

The surgery was done using a camera attached to a lighted tube placed in your belly. The lighted tube is called a laparoscope. This type of surgery is called laparoscopy.
What to Expect at Home
You may lose weight over the first 3 to 6 months. During this time, you may experience:
- Body aches
- Tiredness and feel cold
- Dry skin
- Mood changes
- Hair loss or hair thinning
These problems should go away as your body gets used to your weight loss and your weight becomes stable. Weight loss may be slower after this.
Activity
Being active soon after surgery will help you recover more quickly. During the first week:
- Take short walks and go up and down stairs.
- Try getting up and moving around if you are having some pain in your belly. It may help relieve the pain.
If it hurts when you do something, stop doing that activity.
If you have laparoscopic surgery, you should be able to do most of your regular activities in 2 to 4 weeks.
Diet
Laparoscopic gastric banding made your stomach smaller by closing off part of your stomach with an adjustable band. After surgery you will eat less food, and you will not be able to eat as quickly.
Your health care provider will teach you about foods you can eat and foods you should avoid. It is very important to follow these diet guidelines.
You will eat only liquid or puréed food for 2 to 3 weeks after your surgery. You will slowly add in soft foods, and then regular foods.
You will slowly add in soft foods
You had laparoscopic gastric banding. This surgery made your stomach smaller by closing off part of your stomach with an adjustable band. After sur...

Wound Care
Keep your dressings (bandage) on your wounds clean and dry. If you have sutures (stitches) or staples, they will be removed about 7 to 10 days after surgery. Some stitches can dissolve on their own. Your provider will tell if you have this kind.
Change the dressings (bandages) every day if you were told to do so. Be sure to change them more often if they get dirty or wet.
You may have bruising around your wound. This is normal. It will go away on its own. The skin around your incisions may be a little red. This is normal, too.
Do not wear tight clothing that rubs against your incisions while they heal.
Ask your provider when it is safe to shower. When you can shower, let water run over your incision, but do not scrub it or let the water beat down on it.
Do not soak in a bathtub, swimming pool, or hot tub until your surgeon tells you it is OK.
Follow-up
By the time you leave the hospital, you will likely have a follow-up appointment scheduled with your surgeon within 1 to 2 weeks. You will see your surgeon several more times in the first year after your surgery.
You may also have appointments with:
- A nutritionist or dietitian, who will teach you how to eat correctly with your smaller stomach. You will also learn about what foods and drinks you should have after surgery.
- A psychologist, who can help you follow your eating and exercise guidelines and deal with the feelings or concerns you may have after surgery.
The band around your stomach is filled with saline (saltwater). It is connected to a container (access port) that is placed under your skin in your upper belly. Your surgeon can make the band tighter or looser by increasing or decreasing the amount of saline in the band. To do this, your surgeon will insert a needle through your skin into the access port.
Your surgeon can make the band tighter or looser any time after you have this surgery. It may be tightened or loosened if you are:
- Not losing enough weight
- Having problems eating
- Vomiting after you eat
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your surgeon if:
- You have more redness, pain, warmth, swelling, or bleeding around your incision.
- You have trouble drinking the recommended amount of fluids.
- The drainage from your incision does not decrease in 3 days or increases.
- The drainage becomes thick, tan or yellow and has a bad smell (pus).
- Your temperature is above 100°F (37.7°C) for more than 4 hours.
- You have pain that your pain medicine is not helping.
- You have trouble breathing.
- You have a cough that does not go away.
- You cannot drink or eat.
- Your skin or the white part of your eyes turns yellow.
- Your stools are loose, or you have diarrhea.
- You are vomiting after eating.
- Your leg starts swelling.
References
Mechanick JI, Apovian C, Brethauer S, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the perioperative nutritional, metabolic, and nonsurgical support of the bariatric surgery patient 2019 update: cosponsored by American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology, the Obesity Society, American Society for Metabolic & Bariatric Surgery, Obesity Medicine Association, and American Society of Anesthesiologists. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2020;16(2):175-247. PMID: 31917200 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31917200/.
Powell-Wiley TM, Poirier P, Burke LE, et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021:143(21):e984-e1010. PMID: 33882682 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33882682/.
Richards WO, Khaitan L, Torquati A. Morbid obesity. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 48.
Sullivan S, Edmundowicz SA, Morton JM. Surgical and endoscopic treatment of obesity. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 8.
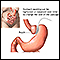
Adjustable gastric banding - illustration
Restrictive gastic operations, such as an adjustable gastric banding procedure, serve only to restrict and decrease food intake and do not interfere with the normal digestive process. In this procedure, a hollow band made of special material is placed around the stomach near its upper end, creating the small pouch and a narrow passage into the larger remaining portion of the stomach. This small passage delays the emptying of food from the pouch and causes a feeling of fullness. The band can be tightened or loosened over time to change the size of the passage. Initially, the pouch holds about 1 ounce of food and later expands to 2 to 3 ounces.
Adjustable gastric banding
illustration
Adjustable gastric banding - illustration
Restrictive gastic operations, such as an adjustable gastric banding procedure, serve only to restrict and decrease food intake and do not interfere with the normal digestive process. In this procedure, a hollow band made of special material is placed around the stomach near its upper end, creating the small pouch and a narrow passage into the larger remaining portion of the stomach. This small passage delays the emptying of food from the pouch and causes a feeling of fullness. The band can be tightened or loosened over time to change the size of the passage. Initially, the pouch holds about 1 ounce of food and later expands to 2 to 3 ounces.
Adjustable gastric banding
illustration
Review Date: 7/22/2024
Reviewed By: John E. Meilahn, MD, General and Bariatric Surgery, Wyndmoor, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


