Antiplatelet medicines - P2Y12 inhibitors
Platelets are small particles in your blood that your body uses to form clots and stop bleeding. If you have too many platelets or your platelets stick together too much, you are more likely to form clots. This clotting can take place on the inside of your arteries and lead to heart attack or stroke.
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...


Plaque buildup in arteries
A heart attack or stroke may occur when an area of plaque (atherosclerosis) ruptures and a clot forms over the location, blocking the flow of blood to the organ's tissues.
Antiplatelet medicines work to make your platelets less sticky and thereby help prevent blood clots from forming in your arteries.
- Aspirin is an antiplatelet medicine that may be used.
- P2Y12 receptor blockers are another group of antiplatelet medicines. This group of medicines includes: clopidogrel, ticlopidine, ticagrelor, prasugrel, and cangrelor.
Who Should Take Antiplatelet Drugs
Antiplatelet medicines may be used to:
- Prevent heart attack or stroke for those with peripheral arterial disease (most often blockage of an artery in the leg).
- Prevent or treat heart attacks.
- Prevent stroke or transient ischemic attacks (TIAs are early warning signs of stroke. They are also called "mini-strokes.")
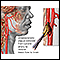
Transient ischemic attacks
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops for a brief time. A person will have stroke-like symptoms for ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Prevent clots from forming inside stents put inside your arteries to open them.
- Treat acute coronary syndrome.
- Prevent clots after bypass graft surgery that uses a man-made or prosthetic graft performed on arteries below the knee.
Clopidogrel (Plavix, generic) may be used in place of aspirin for people who have narrowing of the coronary arteries. Sometimes 2 antiplatelet medicines (one of which is almost always aspirin) are prescribed for people with acute coronary syndrome (unstable angina or heart attack).
Aspirin and a second antiplatelet medicine are usually recommended for people who are undergoing angioplasty with or without stenting.
Your health care provider will choose which one of these medicines are best for your problem.
Side Effects
Side effects of these medicines may include:
- Diarrhea
- Itching
- Nausea
- Skin rash
- Stomach pain
Before you start taking these medicines, tell your provider if:
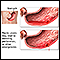
- You have bleeding problems or stomach ulcers.
Stomach ulcers
A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or intestine. There are two types of peptic ulcers:Gastric ulcer -- occurs in...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breastfeeding.
There are a number of other possible side effects, depending on which medicines you are prescribed. For example:
- Ticlopidine may lead to a very low white blood cell count or an immune disorder that destroys platelets.
- Ticagrelor may cause episodes of shortness of breath.
Taking P2Y12 Inhibitors
This medicine is taken as a pill. Your provider may change your dose from time to time.
Take this medicine with food and plenty of water to reduce side effects. You may need to stop taking clopidogrel before you have surgery or dental work. Do not just stop taking your medicine without first talking with your provider.
Talk with your provider before taking any of these medicines:
- Heparin and other blood thinners, such as warfarin (Coumadin)
- Pain or arthritis medicine that are NSAIDs (such as diclofenac, etodolac, ibuprofen, indomethacin, Advil, Aleve, Daypro, Dolobid, Feldene, Indocin, Motrin, Orudis, Relafen, or Voltaren)
- Phenytoin (Dilantin), tamoxifen (Nolvadex, Soltamox), tolbutamide (Orinase), or torsemide (Demadex)
Do not take other medicines that may have aspirin or ibuprofen in them before talking with your provider. Read the labels on cold and flu medicines. Ask what other medicines are safe for you to take for aches and pains, colds, or the flu.
If you have any type of procedure scheduled, you may need to stop these medicines 5 to 7 days before hand. However, always check with your provider first about whether it is safe to stop.
Tell your provider if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding or planning to breastfeed. Women in the later stages of pregnancy should not take clopidogrel. Clopidogrel can be passed to infants through breast milk.
Talk with your provider if you have liver or kidney disease.
If you miss a dose:
- Take it as soon as possible, unless it is time for your next dose.
- If it is time for your next dose, take your usual amount.
- Do not take extra pills to make up for a dose you have missed, unless your provider tells you to.
Store these medicines and all other medicines in a cool, dry place. Keep them where children cannot get to them.
When to Call the Doctor
Contact your provider if you have any of these side effects and they do not go away:
- Any signs of unusual bleeding, such as blood in the urine or stools, nosebleeds, any unusual bruising, heavy bleeding from cuts, black tarry stools, coughing up blood, heavier than usual menstrual bleeding or unexpected vaginal bleeding, vomit that looks like coffee grounds
- Dizziness
- Difficulty swallowing
- Tightness in your chest or chest pain
- Swelling in your face or hands
- Itching, hives, or tingling in your face or hands
- Wheezing or difficulty breathing
- Very bad stomach pain
- Skin rash
Reviewed By
Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Abraham NS, Hlatky MA, Antman EM, et al. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2010 expert consensus document on the concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and thienopyridines: a focused update of the ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents. Circulation. 2010;122(24):2619-2633. PMID: 21060077 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21060077/.
Alberts MJ. Prevention and management of ischemic stroke. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 45.
Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL, et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2024;149(1):e1-e156. PMID: 38033089 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38033089/.
Kumbhani DJ, Bhatt DL. Percutaneous coronary intervention. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 41.
Kleindorfer DO, Towfighi A, Chaturvedi S, et al. 2021 Guideline for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: A guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2021;52(7):e364-e467. PMID: 34024117 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34024117/.
Morrow DA, de Lemos JA. Stable ischemic heart disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 40.
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2019;50(12):e344-e418. PMID: 31662037 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31662037/.
Virani SS, Newby LK, Arnold SV, et al. 2023 AHA/ACC/ACCP/ASPC/NLA/PCNA guideline for the management of patients with chronic coronary disease: a report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2023;148(9):e9-e119. PMID: 37471501 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37471501/.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.