Food poisoning
Food poisoning
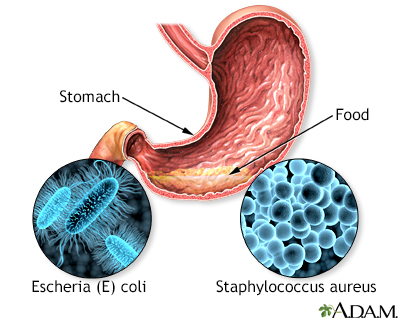
Food poisoning occurs when food contaminated with organisms is ingested. The bacteria Staphylococcus aureus can commonly be found on people, but when allowed to grow in food this bacteria can produce a toxin that causes illness such as vomiting and diarrhea. Proper hygiene and handwashing can prevent this bacteria from entering food that will be eaten. The major source of Escherichia is from the feces of infected animals. It can also be found in untreated water. Cooking at the right temperature is important in eliminating this bacteria when it has contaminated food.
Reviewed By
Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.