Atrial myxoma
Cardiac tumor - myxoma; Heart tumor - myxomaAn atrial myxoma is a noncancerous tumor in the upper left or right side of the heart. It most often grows on the wall that separates the two sides of the heart. This wall is called the atrial septum.
Causes
A myxoma is a primary heart (cardiac) tumor. This means that the tumor started within the heart. Most heart tumors start somewhere else.
Primary cardiac tumors such as myxomas are rare. About 75% of myxomas occur in the left atrium of the heart. They most often begin in the wall that divides the two upper chambers of the heart. They can occur in other intra-cardiac sites as well. Atrial myxomas are sometimes linked with valve obstruction stenosis and atrial fibrillation.
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) and atrial flutter are common types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) which affect the upper chambers (atria) of the...
Myxomas are more common in women. About 1 in 10 myxomas are passed down through families (inherited). These tumors are called familial myxomas. They tend to occur in more than one part of the heart at a time, and often cause symptoms at a younger age.
Symptoms
Many myxomas will not cause symptoms. These are often discovered when an imaging study (echocardiogram, MRI, CT) is done for another reason.
Symptoms may occur at any time, but often they go along with a change in body position.
Symptoms of a myxoma may include:
- Breathing difficulty when lying flat or on one side or the other
Breathing difficulty when lying flat
Breathing difficulty while lying down is an abnormal condition in which a person has a problem breathing normally when lying flat. The head must be ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breathing difficulty when asleep
Breathing difficulty when asleep
Breathing difficulty while lying down is an abnormal condition in which a person has a problem breathing normally when lying flat. The head must be ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest pain or tightness
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dizziness
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fainting
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Sensation of feeling your heart beat (palpitations)
Palpitations
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Shortness of breath with activity
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Symptoms due to embolism of tumor material
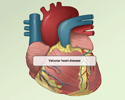
The symptoms and signs of left atrial myxomas often mimic mitral stenosis (narrowing of the valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle). Right atrial myxomas rarely produce symptoms until they have grown to be quite large (5 inches wide, or 13 cm).
Mitral stenosis
Mitral stenosis is a disorder in which the mitral valve does not fully open. This restricts the flow of blood.
Other symptoms may include:
- Bluish skin, especially on the fingers (Raynaud phenomenon)
Bluish skin
A bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. The medical term is cyanosis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cough
- Curvature of nails accompanied by soft tissue swelling (clubbing) of the fingers
Clubbing
Clubbing is changes in the areas under and around the toenails and fingernails that occur with some disorders. The nails may also show changes....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever
- Fingers that change color upon pressure or with cold or stress
Fingers that change color upon pressure
Fingers or toes may change color when they are exposed to cold temperatures or stress, or when there is a problem with their blood supply.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleStress
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - General discomfort (malaise)
Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint pain
- Swelling in any part of the body
- Weight loss without trying
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and listen to your heart through a stethoscope. Abnormal heart sounds or a murmur may be heard. These sounds may change when you change body position.
Imaging tests may include:
- Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan of chest
CT scan of chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Duplex Doppler study
Duplex Doppler study
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart MRI
Heart MRI
Heart magnetic resonance imaging is an imaging method that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the heart. It does not use ra...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Left heart angiography
Left heart angiography
Left heart ventricular angiography is a procedure to look at the left-sided heart chambers and the function of the left-sided valves. It is sometime...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Right heart angiography
Right heart angiography
Right heart ventricular angiography is a test that images the right chambers (atrium and ventricle) of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may also need blood tests including:
- Complete blood count (CBC) - may show anemia and increased white blood cells
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAnemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) - may be increased
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
ESR stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is commonly called a "sed rate. "It is a test that indirectly measures the level of certain protei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Surgery is needed to remove the tumor, especially if it is causing heart failure symptoms or an embolism.
Embolism
Arterial embolism refers to a clot (embolus) that has come from another part of the body and causes a sudden interruption of blood flow to an organ o...

Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, surgery can successfully remove the myxoma. Rarely, the tumor may come back after several years. Your provider will likely recommend regular monitoring to check for new myxomas.
Having a myxoma can also increase the risk for heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias) This can be treated with medicines or other treatments.
Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...

Untreated, a myxoma can lead to an embolism (tumor cells or a clot that breaks off and travels in the bloodstream). This can lead to a blockage of blood flow. Pieces of the tumor can move to the brain, eye, or limbs.
Embolism
Arterial embolism refers to a clot (embolus) that has come from another part of the body and causes a sudden interruption of blood flow to an organ o...

If the tumor grows inside the heart, it can block blood flow, causing symptoms of obstruction.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Arrhythmias
Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. This buildup of fluid leads to shortness of breath.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
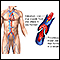
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Peripheral emboli
Emboli
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blockage of the heart valves
References
Lenihan DJ, Reardon MJ, Hundley WG. Tumors affecting the cardiovascular system. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 98.
Tazelaar HD, Maleszewski JJ. Tumors of the heart and pericardium. In: Fletcher CDM, ed. Diagnostic Histopathology of Tumors. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 2.
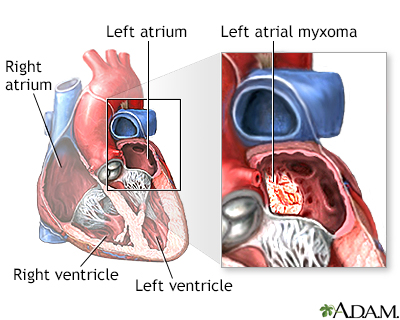
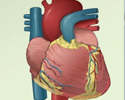
Left atrial myxoma - illustration
A myxoma is a benign tumor in the heart most commonly found in the left atrium. About 75% of myxomas are in the left atrium, usually beginning in the wall that divides the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) and growing into the atrium. Treatment is necessary to avoid metastasis and the formation of clots. In addition, untreated growth of the tumor can obstruct blood flow through the heart. Myxomas are curable with surgical removal.
Left atrial myxoma
illustration
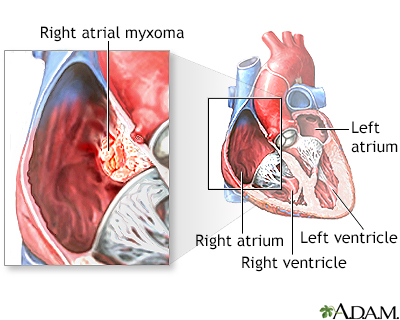
Right atrial myxoma - illustration
A myxoma is a benign tumor in the heart. Right atrial myxomas occur less frequently than left atrial myxomas. Treatment is necessary to avoid metastasis and the formation of clots. In addition, untreated growth of the tumor can obstruct blood flow through the heart. Myxomas are curable with surgical removal.
Right atrial myxoma
illustration
Left atrial myxoma - illustration
A myxoma is a benign tumor in the heart most commonly found in the left atrium. About 75% of myxomas are in the left atrium, usually beginning in the wall that divides the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) and growing into the atrium. Treatment is necessary to avoid metastasis and the formation of clots. In addition, untreated growth of the tumor can obstruct blood flow through the heart. Myxomas are curable with surgical removal.
Left atrial myxoma
illustration
Right atrial myxoma - illustration
A myxoma is a benign tumor in the heart. Right atrial myxomas occur less frequently than left atrial myxomas. Treatment is necessary to avoid metastasis and the formation of clots. In addition, untreated growth of the tumor can obstruct blood flow through the heart. Myxomas are curable with surgical removal.
Right atrial myxoma
illustration
Review Date: 5/27/2024
Reviewed By: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 11/14/2024.