Aging changes in the lungs
The lungs have two main functions. One is to get oxygen from the air into the body. The other is to remove carbon dioxide from the body. Your body needs oxygen to work properly. Carbon dioxide is a gas your body produces when it uses oxygen.
Breathing - Animation
The two lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system. Other components of the respiratory system conduct air to the lungs, such as the trachea (windpipe) which branches into smaller structures called bronchi. The process of breathing (respiration) is divided into two distinct phases, inspiration (inhalation) and expiration (exhalation). During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and pulls downward while the muscles between the ribs contract and pull upward. This increases the size of the thoracic cavity and decreases the pressure inside. As a result, air rushes in and fills the lungs. During expiration, the diaphragm relaxes, and the volume of the thoracic cavity decreases, while the pressure within it increases. As a result, the lungs contract and air is forced out.
During breathing, air enters and exits the lungs. When you breathe in (inhale), air flows through the airways into the lungs. The airways are made of stretchy tissue. Bands of muscle and other support tissue wrap around each airway to help keep them open.
Air keeps flowing into the lungs until it fills tiny air sacs called alveoli. Blood circulates around these air sacs through tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen crosses into the bloodstream at the place where the blood vessels and air sacs meet. This is also where carbon dioxide crosses from the bloodstream into the lungs to be breathed out (exhaled).
Gas exchange - Animation
Air first enters the body through the mouth or nose, quickly moves to the pharynx (throat), passes through the larynx (voice box), enters the trachea, which branches into a left and right bronchus within the lungs and further divides into smaller and smaller branches called bronchioles. The smallest bronchioles end in tiny air sacs, called alveoli, which inflate during inhalation, and deflate during exhalation. Gas exchange is the delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the bloodstream, and the elimination of carbon dioxide from the bloodstream to the lungs. It occurs in the lungs between the alveoli and a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries, which are located in the walls of the alveoli. The walls of the alveoli actually share a membrane with the capillaries in which oxygen and carbon dioxide move freely between the respiratory system and the bloodstream. Oxygen molecules attach to red blood cells, which travel back to the heart. At the same time, the carbon dioxide molecules in the alveoli are blown out of the body with the next exhalation.
AGING CHANGES IN YOUR BODY AND THEIR EFFECTS ON THE LUNGS
Changes to the bones and muscles of the chest and spine:
- Bones become thinner and change shape. This can change the shape of your ribcage. As a result, your ribcage may not expand and contract as well during breathing.
- The muscle that supports your breathing, the diaphragm, becomes weakened. This weakness may prevent you from breathing enough air in or out.
These changes in your bones and muscles may lower the oxygen level in your body. Also, less carbon dioxide may be removed from your body. Symptoms such as tiredness and shortness of breath can result.
Changes to lung tissue:
- Muscles and other tissues that are near your airways may lose their ability to keep the airways completely open. This causes the airways to close easily.
- Aging also causes the air sacs to lose their shape and become baggy.
These changes in lung tissue can allow air to get trapped in your lungs. Too little oxygen may enter your blood vessels and less carbon dioxide may be removed. This makes it hard to breathe.
Changes to the nervous system:
- The part of the brain that controls breathing may lose some of its function, weakening the automatic breathing functions. When this happens, your lungs are not able to get enough oxygen. Not enough carbon dioxide may leave the lungs. Breathing may get more difficult.
- Nerves in your airways that trigger coughing become less sensitive. Large amounts of particles like smoke or germs may collect in the lungs and may be hard to cough up.
Changes to the immune system:
- Your immune system can get weaker. This means your body is less able to fight lung infections and other diseases.
- Your lungs are also less able to recover after exposure to smoke or other harmful particles.
COMMON PROBLEMS
As a result of these changes, older people are at increased risk for:
- Lung infections, such as pneumonia and bronchitis
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBronchitis
Acute bronchitis is swelling and inflamed tissue in the bronchi, the main passages that carry air to the lungs. This swelling narrows the airways, w...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Shortness of breath
- Low oxygen level
- Abnormal breathing patterns, resulting in problems such as sleep apnea (episodes of stopped breathing during sleep)
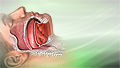
Sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a problem in which your breathing pauses during sleep. This occurs because of narrowed or blocked airways.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
PREVENTION
To decrease the effects of aging on the lungs:
- Do not smoke. Avoid exposure to cigarette smoke. Smoking and smoke exposure harm the lungs and speeds up lung aging.
- Do physical exercise to improve lung function.
- Get up and move. Lying in bed or sitting for long periods allows mucus to collect in the lungs. This puts you at risk of lung infections. This is especially true right after surgery or when you are ill.
OTHER CHANGES RELATED TO AGING
As you grow older, you will have other changes, including:
- In organs, tissues, and cells
In organs, tissues, and cells
All vital organs begin to lose some function as you age. Aging changes occur in all of the body's cells, tissues, and organs, and these changes affe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - In the bones, muscles, and joints
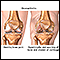
In the bones, muscles, and joints
Changes in posture and gait (walking pattern) are common with aging. The skeleton provides support and structure to the body. Joints are the areas w...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - In the heart and blood vessels
In the heart and blood vessels
Some changes in the heart and blood vessels normally occur with age. However, many other changes that are common with aging are due to or worsened b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - In vital signs
In vital signs
Vital signs include body temperature, heart rate (pulse), breathing (respiratory) rate, and blood pressure. As you age, your vital signs may change,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Davies GA, Bolton CE. Age-related changes in the respiratory system. In: Fillit HM, Rockwood K, Young J, eds. Brocklehurst's Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 17.
George G, Ramirez MI, Roman J. Lung mesenchyme. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray & Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 5.
Meuleman J, Kallas HE. Geriatrics. In: Harward MP, ed. Medical Secrets. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 18.
Walston JD. Common clinical sequelae of aging. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 24.




 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.