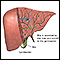
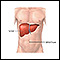
Liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
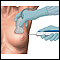
How the Test is Performed
Most of the time, the test is done in the hospital or specialized procedure unit. Before the test is done, you may be given a medicine to prevent pain or to calm you (sedative).
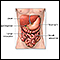
The biopsy may be done through the abdominal wall:
- You will lie on your back with your right hand under your head. You need to stay as still as you can.
- The health care provider will find the correct spot for the biopsy needle to be inserted into the liver. This is often done by using ultrasound.
- The skin is cleaned, and numbing medicine is injected into the area using a small needle.
- A small cut is made, and the biopsy needle is inserted.
- You will be told to hold your breath while the biopsy is taken. This is to reduce the chance of damage to the lung or liver.
- The needle is removed quickly.
- Pressure will be applied to stop the bleeding. A bandage is placed over the insertion site.
The procedure can also be done by inserting a needle into your liver by moving it through the jugular vein.
- If the procedure is performed this way, you will lie on your back.
- X-rays will be used to guide the provider to the vein.
- A special needle and catheter (thin tube) is used to take the biopsy sample.
If you receive sedation for this test, you will need someone to drive you home.
How to Prepare for the Test
Tell your provider about:
- Bleeding problems
- Drug allergies
- Medicines you are taking including herbs, supplements, or medicines you bought without a prescription
- Whether you are pregnant
You must sign a consent form. Blood tests are sometimes done to test your blood's ability to clot. You will be told not to eat or drink anything for the 8 hours before the test.
For infants and children:
The preparation needed for a child depends on the child's age and maturity. Your child's provider will tell you what you can do to prepare your child for this test.
How the Test will Feel
You will feel a stinging pain when the anesthetic is injected. The biopsy needle may feel like deep pressure and dull pain. Some people feel this pain in the shoulder.
Why the Test is Performed
The biopsy helps diagnose many liver diseases. The procedure also helps assess the stage (early, advanced) of liver disease. This is especially important in hepatitis B and C infection.
Liver diseases
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...

The biopsy also helps detect:
- Cancer
- Infections
- The cause of abnormal levels of liver enzymes that have been found in blood tests
- The cause of an unexplained liver enlargement
Normal Results
The liver tissue is normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
The biopsy may reveal a number of liver diseases, including cirrhosis, hepatitis, or infections such as tuberculosis. It may also indicate cancer.
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
This test also may be performed for:
- Alcoholic liver disease (fatty liver, hepatitis, or cirrhosis)
Alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease is damage to the liver and its function due to alcohol abuse.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Amebic liver abscess
Amebic liver abscess
Amebic liver abscess is a collection of pus in the liver in response to an intestinal parasite called Entamoeba histolytica.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver. It occurs when immune cells mistake the liver's normal cells for harmful invaders and attack ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Biliary atresia
Biliary atresia
Biliary atresia is a blockage in the tubes (ducts) that carry a liquid called bile from the liver to the gallbladder.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic active hepatitis
- Chronic persistent hepatitis
- Disseminated coccidioidomycosis
Disseminated coccidioidomycosis
Valley fever is an infection that occurs when the spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii enter your body through the lun...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a condition in which there is too much iron in the body. It is also called iron overload.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the liver due to infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Other types of viral hepatitis ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that leads to swelling (inflammation) of the liver. Other types of viral hepatitis include:Hepatitis AHepatitis BHepat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D
Hepatitis D is a viral infection caused by the hepatitis D virus (previously called the Delta agent). It causes symptoms only in people who also hav...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma is cancer that starts in the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, and other sites.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the buildup of fat in the liver that is not caused by drinking too much alcohol. People who have it do n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is cancer of the lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, and other organs of the immune system. W...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pyogenic liver abscess
Pyogenic liver abscess
Pyogenic liver abscess is a pus-filled pocket of fluid within the liver. Pyogenic means with pus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome is characterized by sudden (acute) brain damage and liver function problems. This condition does not have a known cause. This syndrome...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sclerosing cholangitis
Sclerosing cholangitis
Sclerosing cholangitis refers to swelling (inflammation), scarring, and destruction of the bile ducts inside and outside of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Primary biliary cholangitis
- Wilson disease
Wilson disease
Wilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous sys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
Risks may include:
- Collapsed lung
Collapsed lung
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then fills the space outside of the lung between the lung and chest wall. This buil...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complications from the sedation
- Injury to the gallbladder or kidney
- Internal bleeding
Reviewed By
Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Holmes JA, Chung RT. Hepatitis C. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 80.
Martin P. Approach to the patient with liver disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 137.
Paradis V, Zucman-Rossi J. Cellular and molecular techniques. In: Burt AD, ed. MacSween's Pathology of the Liver. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 2.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.