Echocardiogram
Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE); Echocardiogram - transthoracic; Doppler ultrasound of the heart; Surface echoAn echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a standard x-ray image. An echocardiogram does not expose you to radiation.
x-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

How the Test is Performed
TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAM (TTE)
TTE is the type of echocardiogram that most people will have.
- A specially trained technician called a sonographer performs the test. A heart doctor (cardiologist) interprets the results.
- An instrument called a transducer is placed on various locations on your chest and upper abdomen and directed toward the heart. This device releases high-frequency sound waves.
- The transducer picks up the echoes of sound waves and transmits them as electrical impulses. The echocardiography machine converts these impulses into moving pictures of the heart. Still pictures are also taken.
- Images can be two-dimensional or three-dimensional. The type of image will depend on the part of the heart being evaluated and the type of machine.
- A Doppler echocardiogram evaluates the motion of blood through the heart.
An echocardiogram shows the heart while it is beating. It also shows the heart valves and other structures.
In some cases, your lungs, ribs, air, or body tissue may prevent the sound waves and echoes from providing a clear picture of heart function. If this is a problem, the health care provider may inject a small amount of liquid (contrast) through an IV to better see the inside of the heart.
Rarely, more invasive testing using special echocardiography probes may be needed.
TRANSESOPHAGEAL ECHOCARDIOGRAM (TEE)
For a TEE, the back of your throat is numbed and a long flexible but firm tube (called a "probe") which has a small ultrasound transducer at the end is inserted down your throat.
A heart doctor with special training will guide the scope down the esophagus and into the stomach. This method is used to get clearer echocardiographic images of your heart. The doctor may use this test to look for signs of infection (endocarditis) blood clots (thrombi), or other abnormal structures or connections.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special steps are needed before a TTE test. If you are having a TEE, you will not be able to eat or drink for several hours before the test.
How the Test will Feel
During the test:
- You will need to take off your clothes from the waist up and lie on an exam table on your back.
- Electrodes will be placed on your chest to monitor your heart beat.
- A small amount of gel is spread on your chest and the transducer will be moved over your skin. You will feel a slight pressure on your chest from the transducer.
- You may be asked to breathe in a certain way or to roll over onto your left side. Sometimes, a special bed is used to help you stay in the proper position.
- If you are having a TEE, you will receive some sedating (relaxing) medicines prior to having the probe inserted and a numbing fluid may be sprayed in the back of your throat.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to evaluate the valves and chambers of your heart and the sac around your heart (pericardium) from the outside of your body. The echocardiogram can help detect:
- Abnormal heart valves
- Congenital heart disease (abnormalities present at birth)
Congenital heart disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a problem with the heart's structure and function that is present at birth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Damage to the heart muscle from a heart attack
- Heart murmurs
- Inflammation (pericarditis) or fluid in the sac around the heart (pericardial effusion)
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection on or around the heart valves (infectious endocarditis)
- Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs. It makes the right side of the heart work harder than normal....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ability of the heart to pump (for people with heart failure)
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Source of a blood clot after a stroke or TIA
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleTIA
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops for a brief time. A person will have stroke-like symptoms for ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Your provider may recommend a TEE if:
- The images from a TTE are unclear. Unclear results may be due to the shape of your chest, lung disease, or excess body fat.
- An area of the heart needs to be looked at in more detail.
Normal Results
A normal echocardiogram reveals normal heart valves and chambers and normal heart wall movement.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal echocardiogram can mean many things. Some abnormalities are very minor and do not pose major risks. Other abnormalities are signs of serious heart disease. You will need more tests by a specialist in this case. It is very important to talk about the results of your echocardiogram with your provider.
Risks
There are no known risks from an external TTE test.
TEE is an invasive procedure. There is some risk associated with the test. These may include:
- Reaction to the sedating medicines.
- Damage to the esophagus. This is more common if you already have a problem with your esophagus.
Talk with your provider about the risks associated with this test.
Considerations
Abnormal results may indicate:
- Heart valve disease
- Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is disease in which the heart muscle becomes weakened, stretched, or has another structural problem. It often contributes to the hear...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pericardial effusion
Pericardial effusion
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other heart abnormalities
This test is used to evaluate and monitor many different heart conditions.
References
Otto CM. Echocardiography. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 49.
Wu JC, Gillam L, Solomon SD, Bulwer B. Echocardiography. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 16.
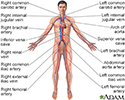
Circulatory system - illustration
Blood used by the body is brought back to the heart and lungs by the veins of the body. Once the blood has gathered more oxygen from the lungs, it is pumped back out to the body through the arteries.
Circulatory system
illustration
Review Date: 4/10/2023
Reviewed By: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.