Open lung biopsy
Biopsy - open lungAn open lung biopsy is surgery to remove a small piece of tissue from the lung. The sample is then examined for cancer, infection, or lung disease.
Cancer
Lung cancer is cancer that starts in the lungs. The lungs are located in the chest. When you breathe, air goes through your nose, down your windpipe...

Lung disease
Lung disease is any problem in the lungs that prevents the lungs from working properly. There are three main types of lung disease:Airway diseases -...
How the Test is Performed
An open lung biopsy is done in the hospital using general anesthesia. This means you will be asleep and pain free. A tube will be placed through your mouth down your throat, and into your windpipe (trachea) to help you breathe.
General anesthesia
General anesthesia is treatment with certain medicines that puts you into a deep sleep-like state so you do not feel pain during surgery. After you ...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleThe surgery is done in the following way:
- After cleaning the skin, the surgeon makes a small cut in the left or right side of your chest.
- The ribs are gently separated.
- A viewing scope may be inserted through a small hole between the ribs to see the area to be biopsied.
- Tissue is taken from the lung and sent to a lab for examination.
- After surgery, the wound is closed with stitches.
- Your surgeon may leave a small plastic tube in your chest to prevent air and fluid from building up.
The breathing tube may not be able to be removed right after surgery. So, you may need to be on a breathing machine for some time.
Breathing machine
A ventilator is a machine that breathes for you or helps you breathe. It is also called a breathing machine or respirator. The ventilator: Is attac...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleHow to Prepare for the Test
You should tell your surgeon if you are pregnant, allergic to any medicines, or if you have a bleeding problem. Be sure to tell your surgeon about all the medicines you take, including herbs, supplements, and those bought without a prescription.
Follow your surgeon's instructions for not eating or drinking before the procedure.
How the Test will Feel
When you wake up after the procedure, you will feel drowsy for several hours.
There will be some tenderness and pain where the surgical cut is located. Most surgeons inject a long-acting local anesthetic at the surgical cut site so that you will have very little pain right afterward.
You may have a sore throat from the tube. You can ease the pain by eating ice chips.
Why the Test is Performed
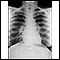
The open lung biopsy is done to evaluate lung problems seen on x-ray, CT scan, or other imaging tests of the lung.
x-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...

Normal Results
The lungs and lung tissue will be normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to:
-
Benign (not cancerous) tumors
Benign
Benign refers to a condition, tumor, or growth that is not cancerous. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body. It does not in...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cancer
- Certain infections (bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic)
- Lung diseases (fibrosis)
The procedure may help diagnose a number of different conditions, such as:
-
A group of lung problems related to rheumatoid arthritis (rheumatoid lung disease)
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It is a long-term disease. It can also aff...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article(rheumatoid lung disease
Rheumatoid lung disease is a group of lung problems related to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The condition can include:Blockage of the small airways (b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Inflammation that affects the lungs and other body tissues (sarcoidosis)
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and/or other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Inflammation of the blood vessels (granulomatosis with polyangiitis)
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) is a rare disorder in which blood vessels become inflamed. This leads to damage in major organs of the body. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
High blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs (pulmonary hypertension)
Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs. It makes the right side of the heart work harder than normal....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There is a slight chance of:
- Air leak
- Excess blood loss
- Infection
- Injury to the lung
- Collapsed lung (pneumothorax)
Pneumothorax
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then fills the space outside of the lung between the lung and chest wall. This buil...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Spahr J, Weiner DJ, Stokes DC, Kurland G. Pulmonary disease in the immunosuppressed pediatric patient. In: Bush A, Deterding R, Li AM, eds. Kendig and Wilmott's Disorders of the Respiratory Tract in Children. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 54.
Wald O, Izhar U, Sugarbaker DJ. Lung, chest wall, pleura, and mediastinum. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 58.
-
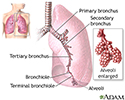
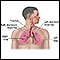
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
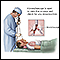
Incision for lung biopsy - illustration
In a lung biopsy, a small piece of lung tissue is removed through a surgical incision in the chest. The abnormal results may indicate cancer, benign tumors, lung diseases, and certain infections.
Incision for lung biopsy
illustration
-
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
Incision for lung biopsy - illustration
In a lung biopsy, a small piece of lung tissue is removed through a surgical incision in the chest. The abnormal results may indicate cancer, benign tumors, lung diseases, and certain infections.
Incision for lung biopsy
illustration
-
Non-small cell lung cancer - InDepth
(In-Depth)
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - InDepth
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 10/9/2024
Reviewed By: Mary C. Mancini, MD, PhD, Cardiothoracic Surgeon, Shreveport, LA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.