Myoglobin blood test
Serum myoglobin; Heart attack - myoglobin blood test; Myositis - myoglobin blood test; Rhabdomyolysis - myoglobin blood testThe myoglobin blood test measures the level of the protein myoglobin in the blood.
Myoglobin can also be measured with a urine test.
Myoglobin
The myoglobin urine test is done to detect the presence of myoglobin in urine. Myoglobin can also be measured with a blood test.
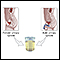
Urine test
The myoglobin urine test is done to detect the presence of myoglobin in urine. Myoglobin can also be measured with a blood test.

How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
Blood sample
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
Myoglobin is a protein in heart and skeletal muscles. When you exercise, your muscles use up available oxygen. Myoglobin has oxygen attached to it, which provides extra oxygen for the muscles to keep at a high level of activity for a longer period.
When muscle is damaged, myoglobin in muscle cells is released into the bloodstream. The kidneys help remove myoglobin from the blood into the urine. When the level of myoglobin is too high, it can damage the kidneys.
This test is ordered when your health care provider suspects you have muscle damage, most often of the skeletal muscles. It may also be ordered if you have acute kidney failure without any clear cause.
Normal Results
The normal range is 25 to 72 ng/mL (1.28 to 3.67 nmol/L).
Note: Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or may test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An increased level of myoglobin may be due to:
- Heart attack
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Malignant hyperthermia (very rare)
Malignant hyperthermia
Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a disease that causes a fast rise in body temperature and severe muscle contractions when someone receives general ane...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Disorder that causes muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue (muscular dystrophy)
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue, which get worse over time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breakdown of muscle tissue that leads to the release of muscle fiber contents into the blood (rhabdomyolysis)
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is the breakdown of muscle tissue that leads to the release of muscle fiber contents into the blood. These substances are harmful to ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Skeletal muscle myositis (inflammation)
Myositis
Myositis is an inflammation or swelling of the muscles. It is most often caused by injury, infection, medicines, or an autoimmune disorder. Dermatom...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Skeletal muscle ischemia (oxygen deficiency)
- Skeletal muscle trauma
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another, and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Nagaraju K, Aggarwal R, Lundberg IE. Inflammatory diseases of muscle and other myopathies. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, Koretzky GA, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelly's Textbook of Rheumatology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 90.
Selcen D. Muscle diseases. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 393.
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 2/28/2023
Reviewed By: Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


