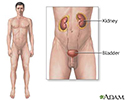
Quantitative Bence-Jones protein test
Immunoglobulin light chains - urine; Urine Bence-Jones proteinThis test measures the level of abnormal proteins called Bence-Jones proteins in the urine.
How the Test is Performed
A clean-catch urine sample is needed. The clean-catch method is used to prevent germs from the penis or vagina from getting into a urine sample. To collect your urine, your health care provider may give you a special clean-catch kit that contains a cleansing solution and sterile wipes. Follow instructions exactly so that the results are accurate.
Clean-catch urine sample
A clean catch is a method of collecting a urine sample to be tested. The clean-catch urine method is used to prevent germs from the penis or vagina ...
The sample is sent to the lab. There are many methods used to detect Bence-Jones proteins. One method, called immunoelectrophoresis, is the most accurate.
Immunoelectrophoresis
The urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP) test is used to measure how much of certain proteins are in the urine.
How the Test will Feel
The test involves only normal urination, and there is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
Bence-Jones proteins are a part of regular antibodies called light chains. These proteins are not normally in urine. Sometimes, when your body makes too many antibodies, the level of light chains also rises. Bence-Jones proteins are small enough to be filtered out by the kidneys. The proteins then spill into the urine.
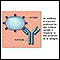
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
Your provider may order this test:
- To diagnose conditions that lead to protein in the urine
- If you have a lot of protein in your urine
- If you have signs of a blood cancer called multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts from a type of white blood cell in the bone marrow called plasma cells. Bone marrow is the soft, spon...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Normal Results
A normal result means no Bence-Jones proteins are found in your urine.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Bence-Jones proteins are rarely found in urine. If they are, it is usually associated with multiple myeloma.
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts from a type of white blood cell in the bone marrow called plasma cells. Bone marrow is the soft, spon...

An abnormal result may also be due to:
- An abnormal buildup of proteins in tissues and organs (amyloidosis)
Amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is a rare disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood cancer called chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is cancer of a type of white blood cells called lymphocytes. These cells are found in the bone marrow and other p...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lymph system cancer (lymphoma)
- Buildup in the blood of a protein called M-protein (monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance; MGUS)
-
Chronic renal failure
Chronic renal failure
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There are no risks with this test.
References
Gertz MA, Dispenzieri A. Amyloidosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 174.
Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A. Multiple myeloma and related disorders. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 101.
Riley RS, McPherson RA. Basic examination of urine. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 29.
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.