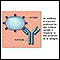
Thyroid peroxidase antibody
Thyroid peroxidase is a type of protein (called an enzyme) that cells in the thyroid gland use to make thyroid hormone. If these enzymes leak out into the bloodstream (as when thyroid cells are damaged) the immune system makes antibodies against these proteins. The thyroid peroxidase antibody test measures these antibodies in the blood.
Enzyme
Enzymes are complex proteins that cause a specific chemical change. For example, they can help break down the foods we eat so the body can use them....
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleAntibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
How the Test is Performed
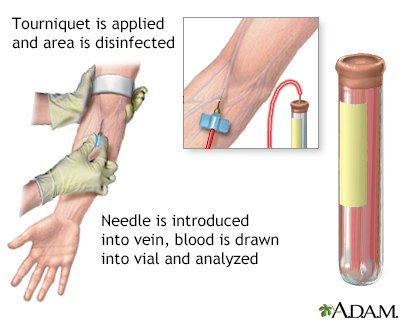
A blood sample is needed.
Blood sample
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to confirm the cause of thyroid problems, including Hashimoto thyroiditis.
Hashimoto thyroiditis
Chronic thyroiditis is caused by a reaction of the immune system against the thyroid gland. It often results in reduced thyroid function (hypothyroi...

The test is also used to find out if an immune or autoimmune disorder is damaging the thyroid.
Autoimmune disorder
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
Normal Results
A negative test means the result is normal.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or may test different specimens. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A positive test may be due to:
- Granulomatous or subacute thyroiditis (an immune reaction of the thyroid gland that often follows an upper respiratory infection)
Granulomatous or subacute thyroiditis
Subacute thyroiditis is an immune reaction of the thyroid gland that often follows an upper respiratory infection. The thyroid gland is located in th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hashimoto thyroiditis (a reaction of the immune system against the thyroid gland)
High levels of these antibodies have also been linked with an increased risk of:
- Miscarriage
- Preeclampsia (high blood pressure and protein in the urine after the 20th week of pregnancy)
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is high blood pressure and signs of liver or kidney damage that occur in women after the 20th week of pregnancy. While it is rare, pree...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Premature birth
- In vitro fertilization failure
In vitro fertilization
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is the joining of a woman's egg and a man's sperm in a laboratory dish. In vitro means outside the body. Fertilization...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Important: A positive result does not always mean that you have a thyroid condition or that you need treatment for your thyroid. A positive result may mean that you have a higher chance of developing thyroid disease in the future. This is often associated with a family history of thyroid disease.
Antithyroid microsomal antibodies may be seen in your blood if you have other autoimmune conditions, including:
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to the body's tissues. Red bloo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis causes inflammation of the liver. It occurs when immune cells mistake the liver's normal cells for harmful invaders and attack ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Autoimmune adrenal disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It is a long-term disease. It can also aff...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sjögren syndrome
Sjögren syndrome
Sjögren syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which the glands that produce tears and saliva are destroyed. This causes dry mouth and dry eyes. The...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
Hematoma
A bruise is an area of skin discoloration. A bruise occurs when small blood vessels break and leak their contents into the soft tissue beneath the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Reviewed By
Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Brent GA, Weetman AP. Hypothyroidism and thyroiditis. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 13.
Guber HA, Oprea M, Russell YX. Evaluation of endocrine function. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 25.
Pearce EN, Hollenberg AN. Thyroid. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 207.
Ramos-Levi AM, Marazuela M. Thyroiditis. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 73.
Smith JR, Wassner AJ. Thyroiditis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 604.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.