Immunofixation blood test
Serum immunofixationThe immunofixation blood test is used to identify proteins called immunoglobulins in blood. Immunoglobulins are proteins that function as antibodies, which fight infection. There are many types of immunoglobulins that fight different types of infections. Some immunoglobulins can be abnormal and may be due to some types of cancer.
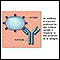
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleHow the Test is Performed
Blood sample is needed
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation for this test.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is most often used to check the levels of antibodies when certain cancers and other disorders are present or suspected.
Normal Results
A normal (negative) result means that the blood sample had normal types and levels of immunoglobulins. The level of one immunoglobulin was not higher than any other.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result may be due to:
- Amyloidosis (buildup of abnormal proteins in tissues and organs)
Amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is a rare disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Leukemia (cancer of the bone marrow)
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Waldenström macroglobulinemia (types of lymphoma)
Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is a cancer of the B lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). WM is associated with the overproduction of protei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lymphoma (cancer of the lymph tissue)
- Monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS, a type of blood disorder)
- Multiple myeloma (a type of blood cancer)
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts from a type of white blood cell in the bone marrow called plasma cells. Bone marrow is the soft, spon...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other cancers
- Infection
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
Hematoma
A bruise is an area of skin discoloration. A bruise occurs when small blood vessels break and leak their contents into the soft tissue beneath the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Gertz MA, Dispenzieri A. Amyloidosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 174.
McPherson RA. Specific proteins. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 20.
Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A. Multiple myeloma and related disorders. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 101.
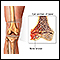
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


