Creatine phosphokinase test
CPK testCreatine phosphokinase (CPK) is an enzyme in the body. It is found mainly in the heart, brain, and skeletal muscle. This article discusses the test to measure the amount of CPK in the blood.
Enzyme
Enzymes are complex proteins that cause a specific chemical change. For example, they can help break down the foods we eat so the body can use them....
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleHow the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. This may be taken from a vein. The procedure is called a venipuncture.
Venipuncture
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

This test may be repeated over 2 or 3 days if you are a patient in the hospital.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed most of the time.
Tell your health care provider about any medicines you are taking.
Drugs that can increase CPK measurements include the following:
- Alcohol
- Amphotericin B
- Certain anesthetics
- Cocaine
- Fibrate drugs
- Statins
- Steroids, such as dexamethasone
This list is not all-inclusive.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel slight pain when the needle is inserted to draw blood. Some people feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
When the total CPK level is very high, it most often means there has been injury or stress to muscle tissue, the heart, or the brain.
Muscle tissue injury is most likely. When a muscle is damaged, CPK leaks into the bloodstream. Finding which specific form of CPK is high helps determine which tissue has been damaged.
This test may be used to:
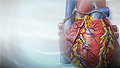
- Diagnose heart attack
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Evaluate cause of chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Determine if or how badly a muscle is damaged
- Detect dermatomyositis, polymyositis, and other muscle diseases
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a disease that involves muscle inflammation and a skin rash. Polymyositis is a similar inflammatory condition that also involves ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePolymyositis
Polymyositis and dermatomyositis are rare inflammatory diseases. (The condition is called dermatomyositis when it involves the skin. ) These disease...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tell the difference between malignant hyperthermia and postoperative infection
Malignant hyperthermia
Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a disease that causes a fast rise in body temperature and severe muscle contractions when someone receives general ane...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
The pattern and timing of a rise or fall in CPK levels can be significant in making a diagnosis. This is particularly true if a heart attack is suspected.
In most cases other tests are used instead of or with this test to diagnose a heart attack.
Normal Results
Total CPK normal values:
- 10 to 120 micrograms per liter (mcg/L)
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
High CPK levels may be seen in people who have:
- Brain injury or stroke
- Convulsions
Convulsions
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Delirium tremens
- Dermatomyositis or polymyositis
- Electric shock
Electric shock
An electrical injury is damage to the skin or internal organs when a person comes into direct contact with an electrical current.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart attack
- Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis)
- Lung tissue death (pulmonary infarction)
- Muscular dystrophies
- Myopathy
- Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis is the breakdown of muscle tissue that leads to the release of muscle fiber contents into the blood. These substances are harmful to ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Trauma
Other conditions that may give positive test results include:
- Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hyperthyroidism
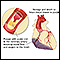
- Pericarditis following a heart attack
Pericarditis following a heart attack
Pericarditis is inflammation and swelling of the covering of the heart (pericardium). It can occur in the days or weeks following a heart attack....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
Risks associated with having blood drawn are slight but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Considerations
Other tests should be done to find the exact location of muscle damage.
Factors that may affect test results include cardiac catheterization, intramuscular injections, trauma to muscles, recent surgery, and heavy exercise.
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization involves passing a thin flexible tube (catheter) into the right or left side of the heart. The catheter is most often insert...
References
Borg K, Ensrud E. Myopathies. In: Frontera WR, Silver JK, Rizzo TD Jr, eds. Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 136.
Hamel J, Statland JM. Muscle disease. In: Wing EJ, Schiffman FJ, eds. Cecil Essentials of Medicine. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 124.
Mccullough PA. Interface between renal disease and cardiovascular illness. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 101.
Pincus MR, Carty RP. Clinical enzymology. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 21.
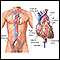
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2023
Reviewed By: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


