Coombs test
Direct antiglobulin test; Indirect antiglobulin test; Anemia - hemolyticThe Coombs test looks for antibodies that may stick to your red blood cells and cause red blood cells to die too early.
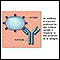
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
Blood sample
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is necessary for this test.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or slight bruising. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
There are two types of the Coombs test:
- Direct
- Indirect
The direct Coombs test is used to detect antibodies that are stuck to the surface of red blood cells. Many diseases and medicines can cause this to happen. These antibodies sometimes destroy red blood cells and cause anemia. Your health care provider may recommend this test if you have signs or symptoms of anemia or jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
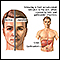
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jau...
The indirect Coombs test looks for antibodies that are in the blood. These antibodies could act against certain red blood cells. This test is most often done to determine if you may have a reaction to a blood transfusion.
Normal Results
A normal result is called a negative result. It means there was no clumping of cells and you have no antibodies to red blood cells.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal (positive) direct Coombs test means you have antibodies that act against your red blood cells. This may be due to:
-
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Hemolytic anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Normally, red ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia or similar disorder
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is cancer of a type of white blood cells called lymphocytes. These cells are found in the bone marrow and other p...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood disease in newborns called erythroblastosis fetalis (also called hemolytic disease of the newborn)
Erythroblastosis fetalis
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) is a blood disorder in a fetus or newborn infant. In some infants, it can be fatal. Normally, red blood cells...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Infectious mononucleosis
Infectious mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Mycoplasma infection
-
Syphilis
Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that is most often spread through sexual contact.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Transfusion reaction, such as one due to improperly matched units of blood
Transfusion reaction
A hemolytic transfusion reaction is a serious complication that can occur after a blood transfusion. The reaction occurs when the red blood cells th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The test result may also be abnormal without any clear cause, especially among the older people.
An abnormal (positive) indirect Coombs test means you have antibodies that will act against red blood cells that your body views as foreign. This may suggest:
- Erythroblastosis fetalis
- Incompatible blood match (when used in blood banks)
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
-
Fainting or feeling lightheaded
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Multiple punctures to locate veins
-
Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
Hematoma
A bruise is an area of skin discoloration. A bruise occurs when small blood vessels break and leak their contents into the soft tissue beneath the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Excessive bleeding
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Elghetany MT, Banki K. Erythrocytic disorders. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 33.
Michel M. Autoimmune and intravascular hemolytic anemias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 146.
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



