Splenomegaly
Spleen enlargement; Enlarged spleen; Spleen swellingSplenomegaly is a larger-than-normal spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of the belly.
Considerations
The spleen is an organ that is a part of the lymph system. The spleen filters the blood and maintains healthy red and white blood cells and platelets. It also plays a role in immune function.
Lymph system
The lymph system is a network of organs, lymph nodes, lymph ducts, and lymph vessels that make and move lymph from tissues to the bloodstream. The l...
Many health conditions can affect the spleen. These include:
- Diseases of the blood or lymph system
- Infections
- Cancer
-
Liver disease
Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms of splenomegaly include:
- Hiccups
- Inability to eat a large meal
- Pain in the upper left side of the belly
Causes
Splenomegaly can be caused by any of the following:
- Infections
- Liver diseases
- Blood diseases
- Cancer
Home Care
In rare cases, an injury can rupture the spleen. If you have splenomegaly, your health care provider may advise you to avoid contact sports. Your provider will tell you what else you need to do to take care of yourself and any medical condition.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
There are usually no symptoms from an enlarged spleen. Seek medical help right away if pain in your belly is severe or gets worse when you take a deep breath.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will ask about your symptoms and medical history.
A physical exam will be done. Your provider will feel and tap along the upper left part of your belly, especially just under the rib cage.
Tests that may be done include:
-
Abdominal x-ray, ultrasound, or CT scan
Abdominal x-ray
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. T...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUltrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) and tests of your liver function
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The treatment depends on the cause of splenomegaly.
References
Wall DJ. The spleen. In: Rumack CM, Levine D, eds. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 5.
Winter JN. Approach to the patient with lymphadenopathy or splenomegaly. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 154.
Wood VH, Cooperberg PL, Vos PM. Benign and malignant lesions of the spleen. In: Gore RM, ed. Textbook of Gastrointestinal Radiology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 62.
-
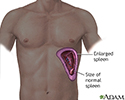
Splenomegaly - illustration
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen.
Splenomegaly
illustration
-
Enlarged spleen - illustration
Because of its wide variety of functions, the spleen may be affected by many conditions involving the blood or lymph system, and by infection, malignancies, liver disease, and parasites.
Enlarged spleen
illustration
-
Splenomegaly - illustration
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen.
Splenomegaly
illustration
-
Enlarged spleen - illustration
Because of its wide variety of functions, the spleen may be affected by many conditions involving the blood or lymph system, and by infection, malignancies, liver disease, and parasites.
Enlarged spleen
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.