Patchy skin color
Patchy skin color is areas where the skin color is irregular with lighter or darker areas. Mottling or mottled skin refers to blood vessel changes in the skin that cause a patchy appearance.
Considerations
Irregular or patchy discoloration of the skin can be caused by:
- Changes in melanin, a substance produced in the skin cells that gives skin its color
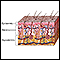
Melanin
Melanin is a natural substance that gives color (pigment) to: HairSkinThe iris of the eye It is produced by cells in the skin called melanocytes. Mel...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Growth of bacteria or other organisms on the skin
- Blood vessel (vascular) changes
- Inflammation due to certain rashes
The following can increase or decrease melanin production:
- Your genes
- Heat
- Injury
- Exposure to radiation (such as from the sun)
- Exposure to heavy metals
- Changes in hormone levels
- Certain conditions such as vitiligo
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a skin condition in which there is a loss of color (pigment) from areas of skin. This results in uneven white patches that have no pigme...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Certain fungal infections
- Certain rashes
Exposure to sun or ultraviolet (UV) light, especially after taking a medicine called psoralens, may increase skin color (pigmentation). Increased pigment production is called hyperpigmentation, and can result from certain rashes as well as sun exposure.
Hyperpigmentation
Abnormally dark or light skin is skin that has turned darker or lighter than normal.

Decreased pigment production is called hypopigmentation.
Skin color changes can be their own condition, or they may be caused by other medical conditions or disorders.
How much skin pigmentation you have can help determine which skin diseases you may be more likely to develop. For example, lighter-skinned people are more sensitive to sun exposure and damage. This raises the risk of skin cancers. But even in darker-skinned people, too much sun exposure can lead to skin cancers.
Examples of the most common skin cancers are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. Most skin cancers are basal cell cancer. Other common types of skin cancer...

Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell skin cancer is the second most common type of cancer in the United States. Other common types of skin cancer are:Basal cell cancerMelan...

Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. It is also the rarest. It is the leading cause of death from skin disease. Other common types o...
Generally, skin color changes are cosmetic and do not affect physical health. But, mental stress can occur because of pigment changes. Some pigment changes may be a sign that you are at risk for other medical problems.
Stress
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...

Causes
Causes of pigment changes may include any of the following:
- Acanthosis nigricans
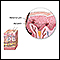
Acanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans (AN) is a skin disorder in which there is darker, thick, velvety skin in body folds and creases.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Acne
Acne
Acne is a skin condition that causes pimples or "zits. " Whiteheads, blackheads, and red, inflamed patches of skin (such as cysts) may develop....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cafe-au-lait spots
Cafe-au-lait spots
A birthmark is a skin marking that is present at birth. Birthmarks include cafe-au-lait spots, moles, and Mongolian spots. Birthmarks can be red or...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cuts, scrapes, wounds, insect bites, and minor skin infections
- Erythrasma
Erythrasma
Erythrasma is a long-term skin infection caused by a specific bacteria. It commonly occurs in skin folds.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Melasma (chloasma)
Melasma (chloasma)
Melasma is a skin condition that causes patches of dark skin on areas of the face exposed to the sun.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Melanoma
- Moles (nevi), bathing trunk nevi, or giant nevi
Nevi
A birthmark is a skin marking that is present at birth. Birthmarks include cafe-au-lait spots, moles, and Mongolian spots. Birthmarks can be red or...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dermal melanocytosis
- Pityriasis alba
Pityriasis alba
Pityriasis alba is a common skin disorder that causes patches of light-colored (hypopigmented) areas.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Radiation therapy
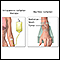
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rashes
Rashes
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sensitivity to the sun due to medicine reactions or certain medicines
- Sunburn or suntan
- Tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor is a common fungal infection of the outer layer of the skin.
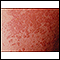 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Unevenly applying sunscreen, leading to areas of burn, tan, and no tan
- Vitiligo
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a skin condition in which there is a loss of color (pigment) from areas of skin. This results in uneven white patches that have no pigme...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Home Care
In some cases, normal skin color returns on its own.
You may use medicated creams that bleach or lighten the skin to reduce discoloration or to even the skin tone where hyperpigmented areas are large or very noticeable. Check with your health care provider first about using such products. Follow the instructions on the package about how to use such products.
Selenium sulfide (Selsun Blue), ketoconazole, or tolnaftate (Tinactin) lotion can help treat tinea versicolor, which is a fungal infection that can appear as hypopigmented patches. Apply as directed to the affected area daily until the discolored patches disappear. Tinea versicolor often returns, even with treatment.
Tinea versicolor
Tinea versicolor is a common fungal infection of the outer layer of the skin.

You may use cosmetics or skin dyes to hide skin color changes. Makeup can also help hide mottled skin, but it will not cure the problem.
Avoid too much sun exposure and use sunblock with an SPF of at least 30. Hypopigmented skin sunburns easily, and hyperpigmented skin may get even darker. In darker-skinned people, skin damage may cause permanent hyperpigmentation.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have any lasting skin color changes that do not have a known cause
- You notice a new mole or other growth
- An existing growth has changed color, size, or appearance
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will carefully examine your skin and ask about your medical history. You will also be asked about your skin symptoms, such as when you first noticed your skin color change, if it started suddenly, and if you had any skin injuries.
Tests that may be done include:
- Scrapings of skin lesions
- Skin biopsy
Skin biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined under a microscope. The skin is tested to look for skin conditi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Wood lamp (ultraviolet light) exam of the skin
Wood lamp
A Wood lamp examination is a test that uses ultraviolet (UV) light to look at the skin closely.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood tests
Treatment will depend on the diagnosis of your skin problem.
Reviewed By
Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, Billings SD. Disorders of pigmentation. In: Calonje E, Brenn T, Lazar AJ, Billings SD, eds. McKee's Pathology of the Skin. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 20.
Patterson JW. Disorders of pigmentation. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 11.
Ubriani RR, Clarke LE, Ming ME. Non-neoplastic disorders of pigmentation. In: Busam KJ, Goldblum JR, eds. Dermatopathology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 7.





 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.