Vaginal itching and discharge - child
Pruritus vulvae; Itching - vaginal area; Vulvar itching; Yeast infection - childItching, redness, and swelling of the skin of the vagina and the surrounding area (vulva) is a common problem in girls before the age of puberty. Vaginal discharge may also be present. The color, smell, and consistency of the discharge can vary, depending on the cause of the problem.
Vagina
The vagina is the female body part that connects the womb (uterus) and cervix to the outside of the body.
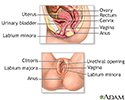
Vulva
The vulva is made up of the female genital parts that are outside the body. It includes the "lips" or folds of skin (labia), clitoris, and the openi...

Causes
Common causes of vaginal itching and discharge in young girls include:
- Chemicals such as perfumes and dyes in detergents, fabric softeners, creams, ointments, and sprays may irritate the vagina or the skin around the vagina.
- Vaginal yeast infection.
Vaginal yeast infection
Vaginal yeast infection is an infection of the vagina. It is most often due to the fungus Candida albicans.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vaginitis. Vaginitis in girls before puberty is common. If a young girl has a sexually transmitted vaginal infection, however, sexual abuse must be considered and addressed.
Vaginitis
Vulvovaginitis or vaginitis is swelling or infection of the vulva and vagina. Vaginitis is a common problem that can affect women and girls of all ag...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - A foreign body, such as toilet paper or a crayon that a young girl may place in the vagina. An infection with a discharge may occur if the foreign object remains in the vagina.
- Pinworms (a parasite infection mainly affecting children).
- Improper cleaning and hygiene
Home Care
To prevent and treat vaginal irritation, your child should:
- Avoid colored or perfumed toilet tissue and bubble bath.
- Use plain, unscented soap.
- Limit bath time to 15 minutes or less. Ask your child to urinate right after the bath.
- Use only plain warm water. DO NOT add baking soda, colloidal oats or oat extracts, or anything else to the bathwater.
- DO NOT let soap float in the bathwater. If you need to shampoo their hair, do so at the end of the bath.
Teach your child to keep the genital area clean and dry. She should:
- Pat the outer vagina and vulva dry rather than rubbing it with tissue. Doing so will help prevent small balls of tissue from breaking off.
- Move toilet tissue from front to back (vagina to anus) after urinating or having a bowel movement.
Your child should:
- Wear cotton panties. Avoid underwear made from synthetic or manmade materials.
- Change their underwear every day.
- Avoid tight pants or shorts.
- Change out of wet clothing, especially wet bathing suits or exercise clothing, as soon as possible.
DO NOT try to remove any foreign object from a child's vagina. You may push the object back farther or injure your child by mistake. Take the child to a health care provider right away for removal.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your child's provider right away if:
- Your child complains of pelvic or lower abdominal pain or has a fever.
- You suspect sexual abuse.
Also contact the provider if:
- There are blisters or ulcers on the vagina or vulva.
- Your child has a burning feeling with urination or other problems urinating.
- Your child has vaginal bleeding, swelling, or discharge.
Vaginal bleeding
This article discusses vaginal bleeding that occurs between a woman's monthly menstrual periods. Such bleeding may be called "intermenstrual bleedin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDischarge
Vaginal discharge refers to secretions from the vagina. The discharge may be:Thick, pasty, or thinClear, cloudy, bloody, white, yellow, or greenOdor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Your child's symptoms get worse, last longer than 1 week, or keep coming back.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will examine your child and may do a pelvic exam. Your child may require a pelvic exam done under anesthesia.You will be asked questions to help diagnose the cause of your child's vaginal itching. Tests may be done to find the cause.
Your provider may recommend medicines, such as:
- Cream or lotion for yeast infections
- Certain allergy medicines (antihistamines) for relief of itching
- Hydrocortisone creams or lotions that you can buy at the store (always talk to your provider first)
- Oral antibiotics
References
Lara-Torre E, Valea FA. Pediatric and adolescent gynecology: gynecologic examination, infections, trauma, pelvic mass, precocious puberty. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 12.
Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM. Vulvovaginitis. In: Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM, eds. Nelson's Essentials of Pediatrics. 8th ed. Elsevier; 2019:chap 115.
Montano GT, Torres OA. Pediatric and adolescent gynecology. In: Zitelli, BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 19.
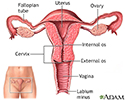
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
- Birth control options for women - InDepth(In-Depth)
- Urinary tract infection - InDepth(In-Depth)
- Cervical cancer - InDepth(In-Depth)
- Iodine(Alt. Medicine)
Review Date: 1/10/2022
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.