Urinating more at night
NocturiaNormally, the amount of urine your body produces decreases at night. This allows most people to sleep 6 to 8 hours without having to urinate.
Some people wake up from sleep more often to urinate during the night. This can disrupt sleep cycles.
Causes
Drinking too much fluid during the evening can cause you to urinate more often during the night. Caffeine and alcohol with or after dinner can also lead to this problem.
Other common causes of urination at night include:
- Infection of the bladder or urinary tract
- Drinking a lot of alcohol, caffeine, or other fluids before bedtime
- Enlarged prostate gland (benign prostatic hyperplasia, BPH)
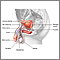
Benign prostatic hyperplasia, BPH
The prostate is a gland that produces some of the fluid that carries sperm during ejaculation. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the tube th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy
Other conditions that can lead to the problem include:
- Chronic kidney failure
- Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Drinking excessive amount of water
Drinking excessive amount of water
Excessive thirst is an abnormal feeling of always needing to drink fluids.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart failure
- High blood calcium level
- Certain medicines, including water pills (diuretics)
- Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI) is an uncommon condition in which the kidneys are unable to prevent the excretion of water. DI is not the same as diabetes me...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling of the legs
Waking often during the night to urinate can also be linked to obstructive sleep apnea and other sleeping disorders. Nocturia may go away when the sleeping problem is under control. Stress and restlessness can also cause you to wake up at night.
Home Care
To monitor the problem:
- Keep a diary of how much fluid you drink, how often you urinate, and how much you urinate.
- Record your body weight at the same times and on the same scale daily.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- Waking to urinate more often continues over several days.
- You are bothered by the number of times you must urinate during the night.
- You have a burning sensation when urinating.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions such as:
- When did the problem start and has it changed over time?
- How often do you urinate each night and how much urine do you release each time?
- Do you ever have "accidents" or bedwetting?
Bedwetting
Bedwetting or nocturnal enuresis is when a child wets the bed at night more than twice a month after age 5 or 6.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - What makes the problem worse or better?
- How much fluid do you drink before bedtime? Have you tried limiting fluids before bedtime?
- What other symptoms do you have? Do you have increased thirst, pain or burning on urination, fever, abdominal pain, or back pain?
Increased thirst
Excessive thirst is an abnormal feeling of always needing to drink fluids.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePain or burning on urination
Painful urination is any pain, discomfort, or burning sensation when passing urine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAbdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - What medicines are you taking? Have you changed your diet?
- Do you drink caffeine or alcohol? If so, how much do you consume each day and when during the day?
- Have you had any bladder infections in the past?
- Do you have a family history of diabetes?
- Does nighttime urination interfere with your sleep?
Tests that may be performed include:
- Blood sugar (glucose)
- Blood urea nitrogen
Blood urea nitrogen
BUN stands for blood urea nitrogen. Urea nitrogen is what forms when protein breaks down. A test can be done to measure the amount of urea nitrogen ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid deprivation
- Osmolality, blood
Osmolality
Osmolality blood test is a test that measures the concentration of all chemical particles found in the fluid part of blood. Osmolality in the urine c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum creatinine or creatinine clearance
Serum creatinine
The creatinine blood test measures the level of creatinine in the blood. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine in t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCreatinine clearance
The creatinine clearance test helps provide information about how well the kidneys are working. The test compares the creatinine level in urine with...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum electrolytes
Serum electrolytes
A comprehensive metabolic panel is a group of blood tests. They provide an overall picture of your body's chemical balance and metabolism. Metaboli...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine concentration
Urine concentration
A urine concentration test measures the ability of the kidneys to conserve or excrete water.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine culture
- You may be asked to keep track of how much liquid you take in and how much you void at a time (voiding diary)
Treatment depends on the cause. If excessive nighttime urination is due to diuretic medicines, you may be told to take your medicine earlier in the day.
References
Carter C. Urinary tract disorders. In: Rakel RE, Rakel DP, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2016:chap 40.
Elsamra SE. Evaluation of the urologic patient: history and physical examination. In: Partin AW, Domochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 1.
Gharavi AG, Landry DW. Approach to the patient with renal disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 100.
Lightner DJ, Gomelsky A, Souter L, Vasavada SP. Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU Guideline Amendment 2019. J Urol. 2019;202(3):558-563. PMID: 31039103 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31039103/.
Samarinas M, Gravas S. The relationship between inflammation and LUTS/BPH. In: Morgia G, ed. Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Cambridge, MA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2018:chap 3.
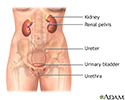
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
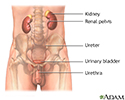
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
Review Date: 7/1/2023
Reviewed By: Kelly L. Stratton, MD, FACS, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.