Abdominal rigidity
Abdominal rigidity is stiffness of the muscles in the belly area, which can be felt when touched or pressed.
Considerations
When there is a sore area inside the belly or abdomen, the pain will often get worse when a hand presses against your belly area.
Your fear or nervousness about being touched (palpated) may cause your abdominal muscles to stiffen, but there should be no pain.
If you have pain when you are touched and you tighten the muscles to guard against more pain, it is more likely caused by a physical condition inside your abdomen. The condition may affect one or both sides of your body.
Abdominal rigidity may occur with:
- Abdominal tenderness
Abdominal tenderness
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
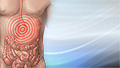 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea
Nausea
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pain
- Swelling
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vomiting
Vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Causes
Causes can include:
- Abscess inside the abdomen
Abscess inside the abdomen
An abdominal abscess is a pocket of infected fluid and pus located inside the belly (abdominal cavity). This type of abscess can be located near or ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Appendicitis
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a condition in which your appendix gets inflamed. The appendix is a small pouch attached to the end of the large intestine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cholecystitis caused by gallstones
Cholecystitis
Acute cholecystitis is sudden swelling and irritation of the gallbladder. It causes severe belly pain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hole that develops through the entire wall of the stomach, small intestine, large bowel, or gallbladder (gastrointestinal perforation)
Gastrointestinal perforation
A perforation is a hole that develops through the wall of a body organ. This problem may occur in the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Injury to the abdomen
- Peritonitis
Peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation (irritation) of the peritoneum. This is the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of t...
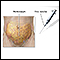 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Get medical care right away if you have pain when the belly is gently pressed and then released.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
You will probably be seen in an emergency room.
The health care provider will examine you. This may include a pelvic exam, and possibly a rectal exam.
The provider will ask questions about your symptoms, such as:
- When did they first start?
- What other symptoms do you have at the same time? For example, do you have abdominal pain?
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may have the following tests:
- Abdominal and pelvic CT scan
- Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound
- Blood tests
- Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is an exam that views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum, using a tool called a colonoscope. The colonoscope has a sm...
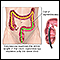 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
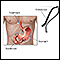
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine (the duodenum)....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Paracentesis
- Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy using a flexible scope is a procedure used to see inside the sigmoid colon and rectum. The sigmoid colon is the area of the large inte...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stool analysis
- Urine tests
- X-rays of the chest or abdomen
Chest
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAbdomen
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. T...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You will probably not be given any pain relievers until a diagnosis is made. Pain relievers can hide your symptoms.
Pain relievers
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers can help relieve pain or lower a fever. Over-the-counter means you can buy these medicines without a prescript...

Reviewed By
Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Abdomen. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2023:chap 18.
Landmann A, Bonds M, Postier R. Acute abdomen. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46.
McQuaid KR. Approach to the patient with gastrointestinal disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 118.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.