Abdomen - swollen
A swollen abdomen is when your belly area is bigger than usual.
Causes
Abdominal swelling, or distention, is more often caused by overeating than by a serious illness. This problem also can be caused by:
- Air swallowing (a nervous habit)
- Buildup of fluid in the abdomen (this can be a sign of a serious medical problem)
- Gas in the intestines from eating foods that are high in fiber (such as fruits and vegetables)
- Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a disorder that leads to pain in abdomen and changes in bowel movements. IBS is not the same as inflammatory bowel...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lactose intolerance
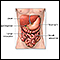
Lactose intolerance
Lactose is a type of sugar found in milk and other dairy products. An enzyme called lactase is needed by the body to digest lactose. Lactose intoler...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ovarian cyst or cancer
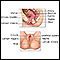
Ovarian cyst or cancer
An ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid that forms on or inside an ovary. This article is about cysts that form during your monthly menstrual cycl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Partial bowel blockage
Bowel blockage
Intestinal obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the bowel. The contents of the intestine cannot pass through it.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy
- Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) refers to a wide range of symptoms. The symptoms start during the second half of the menstrual cycle (14 or more days af...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Uterine fibroids
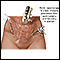
Uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are tumors that grow in a woman's womb (uterus). These growths are typically not cancerous (benign), and do not become cancerous....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weight gain
Weight gain
Unintentional weight gain is when you gain weight without trying to do so and you are not eating or drinking more.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Home Care
A swollen abdomen that is caused by eating a heavy meal will go away when you digest the food. Eating smaller amounts will help prevent swelling.
For a swollen abdomen caused by swallowing air:
- Avoid carbonated beverages.
- Avoid chewing gum or sucking on candies.
- Avoid drinking through a straw or sipping the surface of a hot beverage.
- Eat slowly.
For a swollen abdomen caused by malabsorption, try changing your diet and limiting milk. Talk to your health care provider.
Malabsorption
Malabsorption involves problems with the body's ability to take in (absorb) nutrients from food.

For irritable bowel syndrome:
- Decrease emotional stress.
Stress
Stress is a feeling of emotional or physical tension. It can come from any event or thought that makes you feel frustrated, angry, or nervous. Stres...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increase dietary fiber.
Fiber
Fiber is a substance found in plants. Dietary fiber, which is the type of fiber you can eat, is found in fruits, vegetables, and grains. It is an i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Talk to your provider.
For a swollen abdomen due to other causes, follow the treatment prescribed by your provider.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- The abdominal swelling is getting worse and does not go away.
- The swelling occurs with other unexplained symptoms.
- Your abdomen is tender to the touch.
- You have a high fever.
- You have severe diarrhea or bloody stools.
- You are unable to eat or drink for more than 6 to 8 hours.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask questions about your medical history, such as when the problem began and when it occurs.
The provider will also ask about other symptoms you may be having, such as:
- Absent menstrual period
- Diarrhea
- Excessive fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Excessive gas or belching
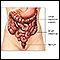
Excessive gas
Gas is air in the intestine that is passed through the rectum. Air that moves from the digestive tract through the mouth is called belching. Gas is ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBelching
Belching is the act of bringing up air from the stomach.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Irritability
- Vomiting
- Weight gain or loss
Tests that may be done include:
- Abdominal and pelvic CT scan
Abdominal and pelvic CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound
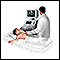
Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood tests
- Colonoscopy
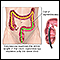
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is an exam that views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum, using a tool called a colonoscope. The colonoscope has a sm...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) is a test to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine (the duodenum)....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Paracentesis
Paracentesis
An abdominal tap is used to remove fluid (ascites) from the area between the belly wall and the spine. This space is called the abdominal cavity or ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy using a flexible scope is a procedure used to see inside the sigmoid colon and rectum. The sigmoid colon is the area of the large inte...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stool analysis
- Urine tests
- X-rays of the chest or abdomen
X-rays of the chest or abdomen
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. T...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW. Abdomen. In: Ball JW, Dains JE, Flynn JA, Solomon BS, Stewart RW, eds. Seidel's Guide to Physical Examination. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 18.
Landmann A, Bonds M, Postier R. Acute abdomen. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46.
McQuaid KR. Approach to the patient with gastrointestinal disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 118.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.