Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty may involve:
- Difficult breathing
- Uncomfortable breathing
- Feeling like you are not getting enough air
Considerations
There is no standard definition for difficulty breathing. Some people feel breathless with only mild exercise (for example, climbing stairs), even though they don't have a medical condition. Others may have advanced lung disease, but may never feel short of breath. Breathing difficulty is a subjective feeling; only the person feeling it can decide if it is present.
Wheezing is one form of breathing difficulty in which you make a high-pitched sound when you breathe out.
Wheezing
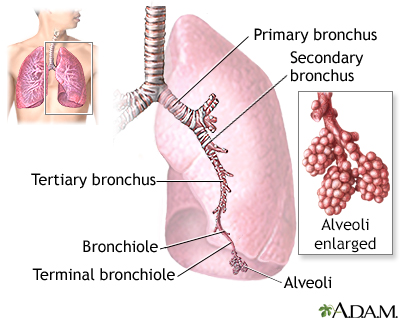
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing. It occurs when air moves through narrowed breathing tubes in the lungs.

What causes wheezing? - Animation
Wheezing can be a normal healthy response to an unhealthy environment. Or, wheezing can be a sign of asthma. I'm Dr. Alan Greene and I want to talk with you for a moment about how to tell the difference, what causes wheezing anyway, and when is it healthy and when is it not. Well to understand that, first let's all take a deep breath together (inhales). When you breathe in, the air comes through your nose or mouth, through the big windpipe and breaks into 2 big bronchi, one into each lung. And from there they break into a whole bunch of little, smaller bronchioles. It's almost like a tree's branches branching out. And those bronchioles are where the wheezing happens. Let's look at a bronchiole. Here's one of those small airways. Now if you happen to walk into a cloud of something that's toxic, your body is going to respond instantly to try to protect you. The first thing that will happen is the muscles around the bronchioles will tighten, will constrict down almost like a boa constrictor, and you get the tight airways. If that toxic cloud is still there, to protect your delicate tissues deep in your lungs, swelling of the lining will happen. Inflammatory stuff to help protect you from those toxins. And if it's still there, still irritating, mucus will begin to be secreted to be able again to capture and protect you from those toxins. That's wheezing. Asthma happens when your airways are hyper-responsive. When they're twitchy. When they're hyper-alert and they respond to something that's not truly dangerous. The problem with that is when your bronchioles are constricted and swollen and has mucus in them, that narrow little opening is hard to breathe through. You have to work to breathe, especially to breath out. And that hard breathing through a narrow passageway is what creates the sound we know as wheezing.
Causes
Shortness of breath has many different causes. For example, heart disease can cause breathlessness if your heart is unable to pump enough blood to supply oxygen to your body. If your brain, muscles, or other body organs do not get enough oxygen, a sense of breathlessness may occur.
Breathing difficulty may also be due to problems with the lungs, airways, or other health problems.
Problems with the lungs:
- Blood clot in the arteries of the lungs (pulmonary embolism)
Pulmonary embolism
A pulmonary embolus is a blockage of an artery in the lungs. The most common cause of the blockage is a blood clot.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling and mucus buildup in the smallest air passages in the lungs (bronchiolitis)
Bronchiolitis
Bronchiolitis is swelling and mucus buildup in the smallest air passages in the lungs (bronchioles). It is usually due to a viral infection....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), such as chronic bronchitis or emphysema
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs (pulmonary hypertension)
Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs. It makes the right side of the heart work harder than normal....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other lung disease
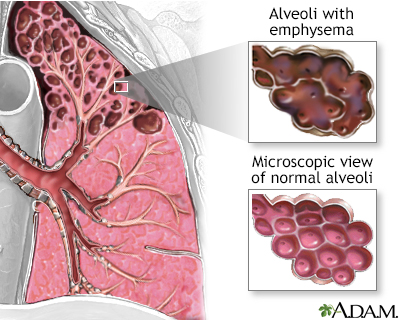
Emphysema
Emphysema is a lung disease involving damage to the air sacs (alveoli). There is progressive destruction of alveoli and the surrounding tissue that supports the alveoli. With more advanced disease, large air cysts develop where normal lung tissue used to be. Air is trapped in the lungs due to lack of supportive tissue which decreases oxygenation.
Problems with the airways leading to the lungs:
- Blockage of the air passages in your nose, mouth, or throat
- Choking on something stuck in the airways
- Swelling around the vocal cords (croup)
Croup
Croup is an infection of the upper airways that causes breathing difficulty and a barking cough. Croup is due to swelling around the vocal cords. I...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Inflammation of the tissue (epiglottis) that covers the windpipe (epiglottitis)
Epiglottitis
Epiglottitis is inflammation of the epiglottis. This is the tissue-lined cartilage that covers the trachea (windpipe) while swallowing. Epiglottiti...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Problems with the heart:
- Chest pain due to poor blood flow through the blood vessels of the heart (angina)
Angina
Angina is a type of chest discomfort or pain due to poor blood flow through the blood vessels (coronary arteries) of the heart muscle (myocardium). ...
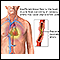 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart attack
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart defects from birth (congenital heart disease)
Congenital heart disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a problem with the heart's structure and function that is present at birth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias)
Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other causes:
- Allergies (such as to mold, dander, or pollen)
Allergies
An allergy is an immune response or reaction to substances that are usually not harmful.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High altitudes where there is less oxygen in the air
- Compression of the chest wall
- Dust in the environment
- Emotional distress, such as anxiety
- Hiatal hernia (condition in which part of the stomach extends through an opening of the diaphragm into the chest)
Hiatal hernia
Hiatal hernia is a condition in which part of the stomach extends through an opening of the diaphragm into the chest. The diaphragm is the sheet of ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Obesity
Obesity
Overweight and obesity mean having a weight than is higher than what is healthy for a given height. A person may be overweight from extra muscle, bo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Panic attacks
Panic attacks
Panic disorder is a type of anxiety disorder in which you have repeated attacks of intense fear that something bad will happen.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Anemia (low hemoglobin)
- Blood problems (when your blood cells cannot pick up oxygen normally; the disease methemoglobinemia is an example)
- Neuromuscular problems leading to weakness of the breathing muscles
Home Care
Sometimes, mild breathing difficulty may be normal and is not a cause for concern. A very stuffy nose is one example. Strenuous exercise, especially when you do not exercise often, is another example.
If breathing difficulty is new or is getting worse, it may be due to a serious problem. Though many causes are not dangerous and are easily treated, contact your health care provider for any breathing difficulty.
If you are being treated for a long-term problem with your lungs or heart, follow your provider's directions to help with that problem.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if:
- Breathing difficulty comes on suddenly or seriously interferes with your breathing and even talking
- Someone completely stops breathing
See your provider if any of the following occur with breathing difficulties:
- Chest discomfort, pain, or pressure. These are symptoms of angina.
- Fever.
- Shortness of breath after only slight activity or while at rest.
- Shortness of breath that wakes you up at night or requires you to sleep propped up to breathe.
- Shortness of breath with simple talking.
- Tightness in the throat or a barking, croupy cough.
- You have breathed in or choked on an object (foreign object aspiration or ingestion).
- Wheezing.
- Significant worsening of baseline shortness of breath.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will examine you. You'll be asked about your medical history and symptoms. Questions may include how long you've had difficulty breathing and when it started. You may also be asked if anything worsens it and if you make grunting or wheezing sounds when breathing.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Blood oxygen saturation (pulse oximetry)
- Blood tests (may include arterial blood gases)
Arterial blood gases
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan of the chest
CT scan of the chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Exercise testing
- Lung function tests
Lung function tests
Pulmonary function tests are a group of tests that measure breathing and how well the lungs are functioning.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If the breathing difficulty is severe, you may need to go to a hospital. You may receive medicines to treat the cause of breathing difficulty.
If your blood oxygen level is very low, you may need oxygen.
Reviewed By
Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Braithwaite SA, Wessel AL. Dyspnea. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 21.
Kraft M. Approach to the patient with respiratory disease. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 77.
Schwartzstein RM, Adams L. Dyspnea. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 36.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.