Coughing up blood
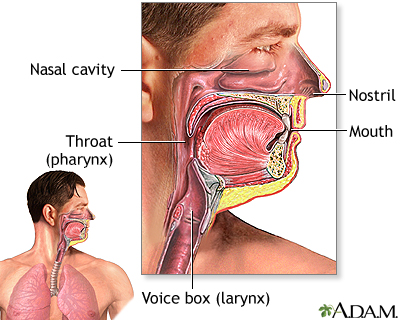
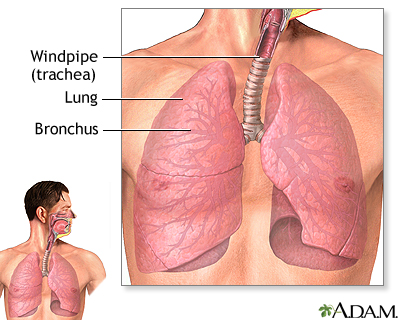
Coughing up blood is the spitting up of blood or bloody mucus from the lungs and throat (respiratory tract).
Hemoptysis is the medical term for coughing up blood from the respiratory tract.
Considerations
Coughing up blood is not the same as bleeding from the mouth, throat, or gastrointestinal tract.
Blood that comes up with a cough often looks bubbly because it is mixed with air and mucus. It is most often bright red, although it may be rust-colored. Sometimes the mucus contains only streaks of blood.
The outlook depends on what is causing the problem. Most people do well with treatment to treat the symptoms and the underlying disease. People with severe hemoptysis may die.
Causes
A number of conditions, diseases, and medical tests may make you cough up blood. These include:
- Blood clot in the lung
- Breathing food or other material into the lungs (pulmonary aspiration)
- Bronchoscopy with biopsy
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which the large airways in the lungs are damaged. This causes the airways to become permanently wider. Bronchiectasis...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bronchitis
Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is swelling and inflamed tissue in the bronchi, the main passages that carry air to the lungs. This swelling narrows the airways, w...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung cancer
- Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a disease that causes thick, sticky mucus to build up in the lungs, digestive tract, and other areas of the body. It is one of th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Inflammation of the blood vessels in the lung (vasculitis)
- Injury to the arteries of the lungs
- Irritation of the throat from violent coughing (small amounts of blood)
- Pneumonia or other lung infections
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. This buildup of fluid leads to shortness of breath.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Very thin blood (from blood thinning medicines, most often at higher than recommended levels)
Home Care
Medicines that stop coughing (cough suppressants) may help if the problem comes from heavy coughing. These medicines may lead to airway blockages, so check with your health care provider before using them.
Keep track of how long you cough up blood, and how much blood is mixed with the mucus. Call your provider any time you cough up blood, even if you do not have any other symptoms.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Get medical help right away if you cough up blood and have:
- A cough that produces more than a few teaspoons of blood
- Blood in your urine or stools
- Chest pain
- Dizziness
- Fever
- Lightheadedness
- Severe shortness of breath
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
In an emergency, your provider will give you treatments to control your condition. The provider will then ask you questions about your cough, such as:
- How much blood are you coughing up? Are you coughing up large amounts of blood at a time?
- Do you have blood-streaked mucus (phlegm)?
- How many times have you coughed up blood and how often does it happen?
- How long has the problem been going on? Is it worse at some time such as at night?
- What other symptoms do you have?
The provider will do a complete physical exam and check your chest and lungs. Tests that may be done include:
- Bronchoscopy, a test to view the airways
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest CT scan
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung biopsy
Lung biopsy
A lung needle biopsy is a method to remove a piece of lung tissue for examination. If it is done through the wall of your chest, it is called a tran...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung scan
Lung scan
Lung gallium scan is a type of nuclear scan that uses radioactive gallium to identify inflammation in the lungs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pulmonary arteriography
Pulmonary arteriography
Pulmonary angiography is a test to see how blood flows through the lung. Angiography is an imaging test that uses x-rays and a special dye to see th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sputum culture and smear
Sputum culture
Routine sputum culture is a laboratory test that looks for germs that cause infection. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when y...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Test to see if the blood clots normally, such as PT or PTT
PT
Prothrombin time (PT) is a blood test that measures the time it takes for the liquid portion (plasma) of your blood to clot. It measures the functio...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePTT
Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is a blood test that looks at how long it takes for blood to clot. It can help tell if you have a bleeding problem...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Brown CA. Hemoptysis. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 20.
Swartz MH. The chest. In: Swartz MH, ed. Textbook of Physical Diagnosis: History and Examination. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 13.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.