Vagina
The vagina is the female body part that connects the womb (uterus) and cervix to the outside of the body.
Cervix
The cervix is the lower end of the womb (uterus). It is at the top of the vagina. It is about 2. 5 to 3. 5 centimeters (1 to 1. 3 inches) long. Th...
Information
The vagina is a muscular tube lined with mucous membranes. Its opening is between the urethra (where urine leaves the body) and the anus (where stool leaves the body).
Menstrual blood leaves the body through the vagina. The vagina also allows for sexual intercourse, and it is the passageway a baby goes through when it is born.
Inflammation of the vagina is called vaginitis.
Vaginitis
Vaginal dryness is present when the tissues of the vagina are not well-lubricated and healthy.

References
Dolan MS, Hill C, Valea FA. Benign gynecologic lesions: vulva, vagina, cervix, uterus, oviduct, ovary, ultrasound imaging of pelvic structures. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 18.
Nunziato JD, Valea FA. Reproductive anatomy: gross and microscopic, clinical correlations. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 3.
-
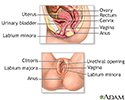
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
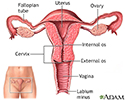
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
-
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
-
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Review Date: 11/1/2023
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.