Peristalsis
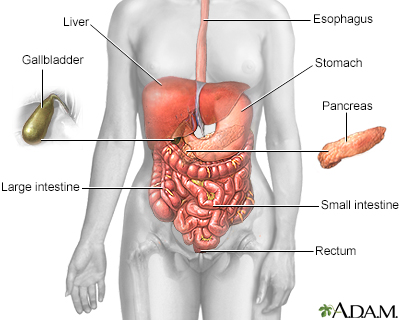
Peristalsis is a series of muscle contractions. These contractions occur in your digestive tract. Peristalsis is also seen in the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder.
Peristalsis is an automatic and important process. It moves:
- Food through the digestive system
- Urine from the kidneys into the bladder
- Bile from the gallbladder into the duodenum
Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acid...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDuodenum
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestine, or jejunum. Aft...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Peristalsis is a normal function of the body. It can sometimes be felt in your belly (abdomen) as gas moves along.
Peristalsis - Animation
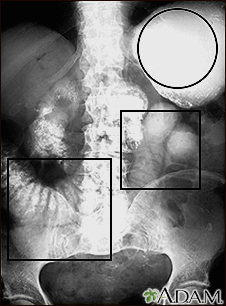
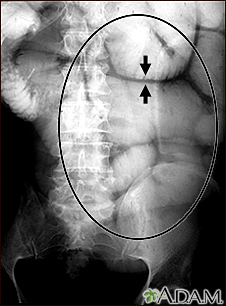
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract. It starts in the esophagus where strong wave-like motions of the smooth muscle move balls of swallowed food to the stomach. There, the food is churned into a liquid mixture called chyme that moves into the small intestine where peristalsis continues. Stretching out a piece of intestine will make it easier to see the wave-like motion. The motion mixes and shifts the chyme back and forth. This lets the bloodstream absorb nutrients through the walls of the small intestine. In the large intestine peristalsis helps water from undigested food be absorbed into the blood stream. Then, the remaining waste products are excreted through the rectum and anus.
Reviewed By
Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Hall JE, Hall ME. General principles of gastrointestinal function - motility, nervous control, and blood circulation. In: Hall JE, Hall ME, eds. Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 63.
Merriam-Webster's Medical Dictionary. Peristalsis. www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/peristalsis. Accessed August 2, 2024.


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.