Penis
The penis is the male organ used for urination and sexual intercourse. The penis is located above the scrotum. It is made of spongy tissue and blood vessels.
Scrotum
The scrotum is a part of a male's body that is located below the penis. The scrotum is the sac (pouch) that contains the testes, epididymis, and the...
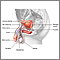
The shaft of the penis surrounds the urethra and is connected to the pubic bone.
The foreskin covers the head (glans) of the penis. The foreskin is removed if the boy is circumcised. This is often done shortly after birth, but can be done later in life for various medical and religious reasons.
Circumcised
Circumcision is the surgical removal of the foreskin of the penis.
Information
During puberty, the penis lengthens. The ability to ejaculate begins at around age 12 to 14. Ejaculation is the release of sperm-containing fluid from the penis during an orgasm.
Conditions of the penis include:
- Chordee -- downward curve of the penis
-
Epispadias -- urethra opening is on the top of the penis, rather than the tip
Epispadias
Epispadias is a rare defect that is present at birth. In this condition, the urethra does not develop into a full tube. The urethra is the tube tha...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hypospadias -- urethra opening is on the underside of the penis, rather than at the tip
Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a birth (congenital) defect in which the opening of the urethra is on the underside of the penis. The urethra is the tube that carrie...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Palmatus or webbed penis -- penis is enclosed by the scrotum
-
Peyronie disease -- a curve during an erection
Peyronie disease
Curvature of the penis is an abnormal bend in the penis that occurs during erection. In adults, it is most often due to Peyronie disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Buried penis -- penis is hidden by a pad of fat
- Micropenis -- penis does not develop and is small
- Erectile dysfunction -- inability to achieve or maintain an erection
Other related topics include:
-
Ambiguous genitalia
Ambiguous genitalia
Ambiguous genitalia is a rare condition where a child is born with outer genitals that do not clearly look either male or female. They may have feat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Penile prosthesis
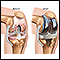
Prosthesis
A prosthesis is a device designed to replace a missing part of the body or to make a part of the body work better. Diseased or missing eyes, arms, h...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Priapism
Priapism
Penis pain is any pain or discomfort in the penis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Elder JS. Anomalies of the penis and urethra. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 559.
Netto GJ, Amin MB. The lower urinary tract and male genital system. In: Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC, eds. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 21.
Palmer LS, Palmer JS. Management of abnormalities of the external genitalia in boys. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 44.
Ro JY, Divatia MK, Kim K-R, Amin MB, Ayala AG. Penis and scrotum. In: Cheng L, MacLennan GT, Bostwick DG, eds. Urologic Surgical Pathology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 15.
-
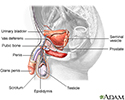
Male reproductive anatomy - illustration
The male reproductive structures include the penis, the scrotum, the testicles (testes), the epididymis, the seminal vesicles, and the prostate.
Male reproductive anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 4/1/2023
Reviewed By: Kelly L. Stratton, MD, FACS, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.