Allergen
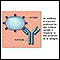
An allergen is a substance that can cause an allergic reaction. In some people, the immune system recognizes allergens as foreign or dangerous. As a result, the immune system reacts by making a type of antibody called immunoglobulin E (IgE) to defend against the allergen. This reaction leads to allergy symptoms.
Allergic reaction
Allergic reactions are sensitivities to substances called allergens that come into contact with the skin, nose, eyes, respiratory tract, and gastroin...

Antibody
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
Information
Common allergens include:
- Animal proteins and animal dander
- Dust
- Foods (such as egg, peanut, milk, nuts, soy, fish, animal meat, and wheat)
- Fungal spores
- Insect and mite feces
- Insect bites and stings (their venom)
- Medicines (such as antibiotics or medicines you put on your skin)
- Natural latex rubber
- Pollen
References
Custovic A, Tovey E. Allergen control for prevention and management of allergic diseases. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 84.
Stewart GA, Robinson C. The structure and function of allergens. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 26.
Positive reaction to allergen - illustration
Allergic reaction is a sensitivity to a specific substance, called an allergen, that is contacted through the skin, inhaled into the lungs, swallowed or injected. The body's reaction to an allergen can be mild, such as a localized rash, or life-threatening, such as anaphylactic shock.
Positive reaction to allergen
illustration
Positive reaction to allergen - illustration
Allergic reaction is a sensitivity to a specific substance, called an allergen, that is contacted through the skin, inhaled into the lungs, swallowed or injected. The body's reaction to an allergen can be mild, such as a localized rash, or life-threatening, such as anaphylactic shock.
Positive reaction to allergen
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor Emeritus, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


