Ellis-van Creveld syndrome
Chondroectodermal dysplasia; EVCEllis-van Creveld syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects bone growth.
Causes
Ellis-van Creveld is passed down through families (inherited). It is caused by defects in 1 of 2 Ellis-van Creveld syndrome genes (EVC and EVC2). These genes are positioned next to each other on the same chromosome.
The severity of the disease varies from person to person. The highest rate of the condition is seen among the Old Order Amish population of Lancaster County, Pennsylvania. It is fairly rare in the general population.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
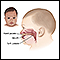
- Cleft lip or palate
Cleft lip or palate
Cleft lip and palate are birth defects that affect the upper lip and the roof of the mouth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
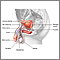
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Epispadias or undescended testicle (cryptorchidism)
Epispadias
Epispadias is a rare defect that is present at birth. In this condition, the urethra does not develop into a full tube. The urethra is the tube tha...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleUndescended testicle
Undescended testicle occurs when one or both testicles fail to move into the scrotum before birth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Extra fingers (polydactyly)
Polydactyly
Polydactyly is a condition in which a person has more than 5 fingers per hand or 5 toes per foot.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Limited range of motion
Limited range of motion
Limited range of motion is a term meaning that a joint or body part cannot move through its normal range of motion.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
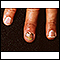
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nail problems, including missing or deformed nails
Nail problems
Nail abnormalities are problems with the color, shape, texture, or thickness of the fingernails or toenails.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Short arms and legs, especially forearm and lower leg
- Short height, between 3.5 to 5 feet (1 to 1.5 meters) tall
- Sparse, absent, or fine textured hair
- Tooth abnormalities, such as peg teeth, widely-spaced teeth
Peg teeth
An abnormally shaped tooth is any tooth that deviates from its regular shape.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleWidely-spaced teeth
Widely spaced teeth can be a temporary condition related to normal growth and development of adult teeth. Wide spacing can also occur as a result of...
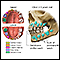
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Teeth present at birth (natal teeth)
Natal teeth
Natal teeth are teeth that are already present at birth. They are different from neonatal teeth, which grow in during the first 30 days after birth....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
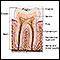
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Delayed or missing teeth
Delayed or missing teeth
When a person's teeth grow in, they may be delayed or not occur at all.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Signs of this condition include:
- Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency means the pituitary gland does not make enough growth hormone.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
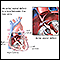
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart defects, such as a hole in the heart (atrial septal defect), occur in about half of all cases
Atrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a heart defect that is present at birth (congenital). As a baby develops in the womb, a wall (septum) forms that divide...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Tests include:
- Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Echocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Genetic testing may be performed for genetic variants in one of the two EVC genes
- Skeletal x-ray
x-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ultrasound
- Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on which body system is affected and the severity of the problem. The condition itself is not treatable, but many of the complications can be treated.
Support Groups
More information and support for people with EVC and their families can be found at:
- National Foundation for Ectodermal Dysplasias (NFED) -- rarediseases.org/organizations/national-foundation-for-ectodermal-dysplasias-nfed/
- Little People of America, Inc -- rarediseases.org/organizations/little-people-of-america-inc/
Outlook (Prognosis)
Many babies with this condition die in early infancy. Most often this is due to a small chest or heart defect. Stillbirth is common.
Stillbirth
A stillbirth is when a baby dies in the womb during the last 20 weeks of pregnancy. A miscarriage is a fetal loss in the first half of pregnancy...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleThe outcome depends on which body system is involved and to what extent that body system is involved. Like many genetic conditions involving bones or the physical structure, intelligence is normal.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Bone abnormalities
- Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Congenital heart disease (CHD) especially atrial septal defect (ASD)
Congenital heart disease
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a problem with the heart's structure and function that is present at birth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAtrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a heart defect that is present at birth (congenital). As a baby develops in the womb, a wall (septum) forms that divide...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney disease
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your child has symptoms of this syndrome. If you have a family history of EVC syndrome and your child has any symptoms, visit your provider.
Genetic counseling can help families understand the condition and how to care for the person.
Prevention
Genetic counseling is recommended for prospective parents from a high-risk group, or who have a family history of EVC syndrome.
References
Chitty LS, Wilson LC, Ushakov F. Diagnosis and management of fetal skeletal abnormalities. In: Pandya PP, Oepkes D, Sebire NJ, Wapner RJ, eds. Fetal Medicine: Basic Science and Clinical Practice. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 34.
Hecht JT, Horton WA. Other inherited disorders of skeletal development. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 720.
National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center website. Ellis-van-Creveld syndrome. rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/1301/ellis-van-creveld-syndrome. Updated February 2023. Accessed October 17, 2023.
Polydactyly - an infant's hand - illustration
Extra digits may be present as an isolated finding, or they may occur as part of a syndrome, in which case other abnormalities are usually present.
Polydactyly - an infant's hand
illustration
Chromosomes and DNA - illustration
Humans typically have 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 chromosomes in total. Chromosomes are made up of long strands of DNA, which contain all the body's genes.
Chromosomes and DNA
illustration
Polydactyly - an infant's hand - illustration
Extra digits may be present as an isolated finding, or they may occur as part of a syndrome, in which case other abnormalities are usually present.
Polydactyly - an infant's hand
illustration
Chromosomes and DNA - illustration
Humans typically have 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 chromosomes in total. Chromosomes are made up of long strands of DNA, which contain all the body's genes.
Chromosomes and DNA
illustration
Review Date: 9/18/2023
Reviewed By: Anna C. Edens Hurst, MD, MS, Associate Professor in Medical Genetics, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



