Nipple discharge
Nipple discharge is any fluid that comes out of the nipple area in your breast.
Causes
Sometimes discharge from your nipples is OK and will get better on its own. You are more likely to have nipple discharge if you have been pregnant at least once.
Nipple discharge is most often not due to cancer, but rarely, it can be a sign of breast cancer. It is important to find out what is causing it and to get treatment. Here are some reasons for nipple discharge:
- Pregnancy
- Recent breastfeeding
- Rubbing on the area from a bra or t-shirt
- Injury to the breast
- Breast infection
- Inflammation and clogging of the breast ducts
- Noncancerous pituitary tumors
- Small growth in the breast that is usually not cancer
- Severe underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism)
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
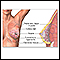
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fibrocystic breast (normal lumpiness in the breast)
Fibrocystic breast
Fibrocystic breasts are painful, lumpy breasts. Formerly called fibrocystic breast disease, this common condition is, in fact, not a disease. Many ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Use of certain medicines, such as birth control pills or antidepressants
- Use of certain herbs, such as anise, blessed thistle, and fennel
- Widening of the milk ducts
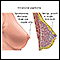
- Intraductal papilloma (benign tumor in the milk duct)
Intraductal papilloma
Intraductal papilloma is a small, noncancerous (benign) tumor that grows in a milk duct of the breast.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Illicit drug use, including cocaine, opioids and marijuana
Sometimes, babies can have nipple discharge. This is caused by hormones from the mother before birth. It should go away in 2 weeks.
Cancers such as Paget disease (a rare type of cancer involving the skin of the nipple) can also cause nipple discharge.
Symptoms
Nipple discharge that is not normal is:
- Bloody
- Comes from only one nipple
- Comes out on its own without you squeezing or touching your nipple
Nipple discharge is more likely to be normal if it:
- Comes out of both nipples
- Happens when you squeeze your nipples
The color of the discharge does not tell you whether it is normal. The discharge can look milky, clear, yellow, green, or brown.
Squeezing your nipple to check for discharge can make it worse. Leaving the nipple alone may make the discharge stop.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and ask questions about your symptoms and medical history.
Tests that may be done include:
- Prolactin blood test
Prolactin blood test
Prolactin is a hormone released by the pituitary gland. The prolactin blood test measures the amount of prolactin in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thyroid blood tests
Thyroid blood tests
Thyroid function tests are used to check whether your thyroid is working normally. The most common thyroid function tests are:Free T4 (free thyroxine...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Head CT scan or MRI to look for pituitary tumor
Head CT scan
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Mammography
Mammography
A mammogram is an x-ray picture of the breasts. It is used to evaluate some breast symptoms and to find breast cancer in women with no symptoms (cal...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ultrasound of the breast
Ultrasound of the breast
Breast ultrasound is a test that uses sound waves to examine the breasts.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breast biopsy
Breast biopsy
A breast biopsy is the removal of breast tissue to examine it for signs of breast cancer or other disorders. There are several types of breast biopsi...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Ductography or ductogram: an x-ray with contrast dye injected into the affected milk duct
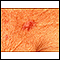
- Skin biopsy, if Paget disease is a concern
Skin biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined under a microscope. The skin is tested to look for skin conditi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Once the cause of your nipple discharge is found, your provider can recommend ways to treat it. You may:
- Need to change any medicine that caused the discharge
- Have lumps removed
- Have all or some of the breast ducts removed
- Receive creams to treat skin changes around your nipple
- Receive medicines to treat a health condition that is causing the nipple discharge
If all of your tests are normal, you may not need treatment. You should have another mammogram and physical exam within 1 year.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, nipple problems are not breast cancer. These problems will either go away with the right treatment, or they can be watched closely over time.
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer:Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (du...

Possible Complications
Nipple discharge may be a symptom of breast cancer or a pituitary tumor.
Skin changes around the nipple may be caused by Paget disease.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Have your provider evaluate any nipple discharge.
Reviewed By
Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Klimberg VS, Hunt KK. Diseases of the breast. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 35.
Leitch AM, Ashfaq R. Discharges and secretions of the nipple. In: Klimberg VS, Gradishar WJ, Bland KI, Korourian S, White J, Copeland EM, eds. Bland and Copeland's The Breast: Comprehensive Management of Benign and Malignant Diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 6.
Sandadi S, Rock DT, Orr JW, Valela FA. Breast diseases: detection, management, and surveillance of breast disease. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 15.
Swartz MH, Nentin FG. The breast. In: Swartz MH, ed. Textbook of Physical Diagnosis: History and Examination. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
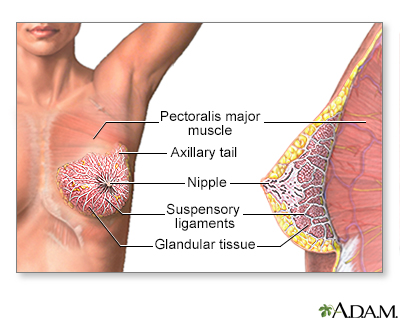

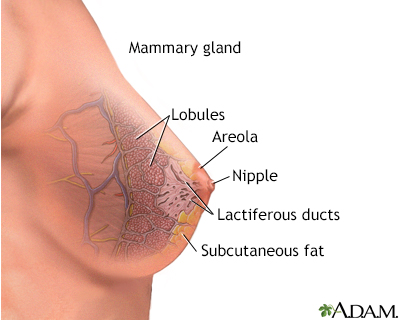


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.