Autonomic dysreflexia
Autonomic dysreflexia (AD) is an abnormal, overreaction of the involuntary (autonomic) nervous system to stimulation. This reaction may include:
- Change in heart rate
- Excessive sweating
- High blood pressure
- Muscle spasms
- Skin color changes (paleness, redness, blue-gray skin color)
Causes
The cause of AD is spinal cord injury, most often due to spine trauma. The nervous system of people with AD over-responds to the types of stimulation that do not bother healthy people.
Other conditions may cause autonomic dysfunction (not dysreflexia) which has similar symptoms, including:
- Guillain-Barré syndrome (disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks part of the nervous system)
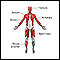
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a serious health problem that occurs when the body's defense (immune) system mistakenly attacks part of the peripher...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Side effects of some medicines
- Severe head trauma and other brain injuries
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (a form of brain bleeding)
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding in the area between the brain and the thin tissues that cover the brain. This area is called the subarachnoid sp...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Use of illegal stimulant drugs such as cocaine and amphetamines
Symptoms
Symptoms can include any of the following:
- Anxiety or worry
- Bladder or bowel problems
- Blurry vision, widened (dilated) pupils
- Lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever
- Goosebumps, flushed (red) skin above the level of the spinal cord injury
- Heavy sweating
- High blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeat, slow or fast pulse
- Muscle spasms, especially in the jaw
- Nasal congestion
- Throbbing headache
Sometimes there are no symptoms, even with a dangerous rise in blood pressure.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will do a complete nervous system and medical exam. Tell your provider about all the medicines you are taking now and that you took in the past. This helps determine which tests you need.
Tests may include:
- Blood and urine tests
- CT or MRI scan
CT
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
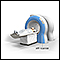
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI scan
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - ECG (measurement of the heart's electrical activity)
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lumbar puncture
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tilt-table testing (testing of blood pressure as the body position changes)
- Toxicology screening (tests for any medicines, including illegal drugs, in your bloodstream)
Toxicology screening
A toxicology screen refers to various tests that determine the type and approximate amount of legal and illegal drugs a person has taken by measuring...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - X-rays
X-rays
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other conditions share many symptoms with AD, but have a different cause. The exam and testing help your provider rule out these other conditions, including:
- Carcinoid syndrome (tumors of the small intestine, colon, appendix, and bronchial tubes in the lungs)
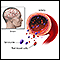
Carcinoid syndrome
Carcinoid syndrome is a group of symptoms associated with carcinoid tumors. These are tumors most often of the small intestine, colon, appendix, pan...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (a condition caused by some medicines that leads to muscle stiffness, high fever, and drowsiness)
- Pheochromocytoma (tumor of the adrenal gland)
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of adrenal gland tissue that typically arises from the adrenal gland. It results in the release of too much epineph...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serotonin syndrome (reaction to a medicine that causes the body to have too much serotonin, a chemical produced by nerve cells)
Serotonin syndrome
Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a potentially life-threatening drug reaction. It causes the body to have too much serotonin, a chemical produced by some ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Thyroid storm (life-threatening condition from an overactive thyroid)
Thyroid storm
Thyroid storm is a rare life-threatening condition of the thyroid gland. It develops in cases of untreated hyperthyroidism, or overactive thyroid (t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
AD is life threatening, so it is important to quickly find and treat the problem.
A person with symptoms of AD should:
- Sit up and raise their head
- Remove tight clothing
Proper treatment depends on the cause. If medicines or illegal drugs are worsening the symptoms, they must be stopped. Any illness needs to be treated. For example, the provider will check for a blocked urinary catheter and signs of constipation which may cause AD in someone with a spinal cord injury. The person should be checked for injuries, sores, or other irritants that may be triggering the symptoms.
If a slowing of the heart rate is causing AD, medicines called anticholinergics (such as atropine) may be used.
Very high blood pressure needs to be treated quickly but carefully, because the blood pressure can drop suddenly.
A pacemaker may be needed for an unstable heart rhythm.
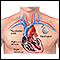
Pacemaker
A pacemaker is a small, battery-operated device. This device senses when your heart is beating too slowly. It sends a signal to your heart that mak...
Outlook (Prognosis)
Outlook depends on the cause.
People with autonomic dysfunction due to a medicine usually recover when that medicine is stopped. When AD is aggravated by other factors, recovery depends on how well the disease can be treated.
Possible Complications
Complications may occur due to side effects of medicines used to treat the condition. A sudden severe increase in blood pressure can cause a stroke or bleeding into the brain. Long-term, severe high blood pressure may cause seizures, bleeding in the eyes, stroke, or death.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if you have symptoms of AD.
Prevention
In people with spinal cord injury, the following may help lessen AD symptoms:
- Avoid medicines that make AD symptoms worse
- Do not let the bladder become too full
- Pain should be controlled
- Practice proper bowel care to avoid stool impaction
Stool impaction
A fecal impaction is a large lump of dry, hard stool that stays stuck in the rectum. It is most often seen in people who are constipated for a long ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Practice proper skin care to avoid bedsores and skin infections
- Prevent bladder infections
Reviewed By
Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Benarroch EE, Freeman R. Autonomic disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 386.
Khanna R, Fessler RD, Snyder L, Fessler RG. Spinal cord trauma. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 63.
McDonagh DL, Barden CB. Autonomic dysreflexia. In: Fleisher LA, Rosenbaum SH, eds. Complications in Anesthesia. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 131.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.