Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
Causes
Abscesses occur when an area of tissue becomes infected and the body's immune system tries to fight and contain it. White blood cells (WBCs) move through the walls of the blood vessels into the area of the infection and collect in the damaged tissue. During this process, pus forms. Pus is the buildup of fluid, living and dead white blood cells, dead tissue, and bacteria or other foreign substances.
Abscesses can form in almost any part of the body. The skin, under the skin, and around the teeth are the most common sites. Abscesses may be caused by bacteria, parasites, and foreign substances.
Abscesses in the skin are easy to see. They are red, raised, and painful. Abscesses in other areas of the body may not be seen, but they may cause organ damage.
Some types and locations of abscesses include:
- Abdominal abscess
Abdominal abscess
An abdominal abscess is a pocket of infected fluid and pus located inside the belly (abdominal cavity). This type of abscess can be located near or ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Amebic liver abscess
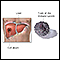
Amebic liver abscess
Amebic liver abscess is a collection of pus in the liver in response to an intestinal parasite called Entamoeba histolytica.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Anorectal abscess
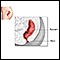
Anorectal abscess
An anorectal abscess is a collection of pus in the area of the anus and rectum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bartholin gland abscess
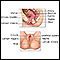
Bartholin gland abscess
Bartholin abscess is the buildup of pus that forms a lump (swelling) in one of the Bartholin glands. These glands are found on each side of the vagi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Brain abscess
Brain abscess
A brain abscess is a collection of pus, immune cells, and other material in the brain, caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Epidural abscess
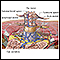
Epidural abscess
An epidural abscess is a collection of pus (infected material) and germs between the outer covering of the brain and spinal cord and the bones of the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Peritonsillar abscess
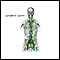
Peritonsillar abscess
Peritonsillar abscess is a collection of infected material in the area around the tonsils.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pyogenic liver abscess
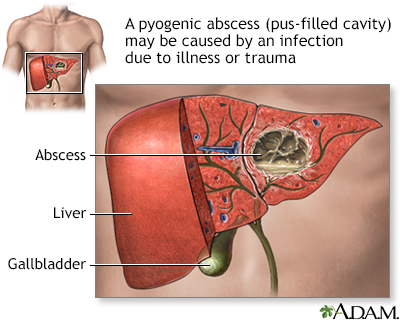
Pyogenic liver abscess
Pyogenic liver abscess is a pus-filled pocket of fluid within the liver. Pyogenic means with pus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Spinal cord abscess
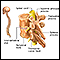
Spinal cord abscess
Spinal cord abscess is the swelling and irritation (inflammation) and the collection of infected material (pus) and germs in or around the spinal cor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Subcutaneous (skin) abscess
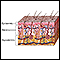
Subcutaneous (skin) abscess
A skin abscess is a buildup of pus in or on the skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tooth abscess
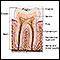
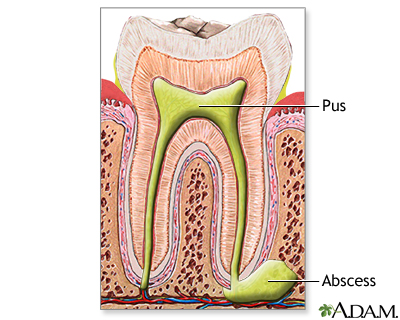
Tooth abscess
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam, focusing on the symptoms of the abscess.
Tests to locate the abscess include:
- Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRI scan
MRI scan
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - X-ray (mainly for tooth abscess)
X-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Often, a sample of fluid will be taken from the abscess and tested to see what type of germ is causing the problem.
Treatment
Treatment varies, but often surgery is needed to drain the abscess. Antibiotics can also be used.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you think that you have any type of abscess. Contact your dentist if you think that you have a tooth abscess.
Prevention
Preventing abscesses depends on where they develop. For example, good hygiene can help prevent skin abscesses. Dental hygiene and routine care will prevent tooth abscesses.
Dental hygiene
Tooth decay and gum disease are caused by plaque, a sticky combination of bacteria and food. Plaque begins to build up on teeth within a few minutes...

Reviewed By
Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Ambrose G, Berlin D. Incision and drainage. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts & Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 37.
De Prisco G, Celinski S, Spak CW. Abdominal abscesses and gastrointestinal fistulas. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 29.
Gea-Banacloche JC, Tunkel AR. Brain abscess. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 90.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.