Otitis
Ear infection; Infection - earOtitis is a term for infection or inflammation of the ear.
Causes
Otitis can affect the inner or outer parts of the ear. The condition can be:
- Acute ear infection -- Starts suddenly and lasts for a short period of time. It is often painful.
Acute ear infection
Suspected ear infections are one of the most common reasons parents take their children to their health care provider. The most common type of ear i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic ear infection -- Occurs when the ear infection does not go away or keeps coming back. It may cause long-term damage to the ear.
Chronic ear infection
Chronic ear infection is fluid, swelling, or an infection behind the eardrum that does not go away or keeps coming back. It may cause long-term or p...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Based on location otitis can be:
- Otitis externa (swimmer's ear) -- Involves the outer ear and ear canal. A more severe form can spread into the bones and cartilage around the ear.
Otitis externa
Swimmer's ear is inflammation, irritation, or infection of the outer ear and ear canal. The medical term for swimmer's ear is otitis externa. Swimme...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Otitis media (ear infection) -- Involves the middle ear, which is located just behind the eardrum.
- Otitis media with effusion -- Occurs when there is thick or sticky fluid behind the eardrum in the middle ear, but there is no ear infection. Also called serous otitis media.
Otitis media with effusion
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is thick or sticky fluid behind the eardrum in the middle ear. It occurs without an ear infection. Note: This artic...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Chole RA, Sharon JD. Chronic otitis media, mastoiditis, and petrositis. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 140.
Matlock AG, Pfaff JA. Otolaryngology. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 58.
Pelton SI. Otitis externa, otitis media, and mastoiditis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 61.
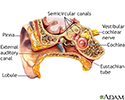
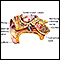
Ear anatomy - illustration
The ear consists of external, middle, and inner structures. The eardrum and the 3 tiny bones conduct sound from the eardrum to the cochlea.
Ear anatomy
illustration
Medical findings based on ear anatomy - illustration
The external structures of the ear may aid in diagnosing some conditions by the presence or absence of normal landmarks and abnormal features including earlobe creases, preauricular pits, and preauricular tags.
Medical findings based on ear anatomy
illustration
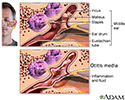
Middle ear infection (otitis media) - illustration
Otitis media is an inflammation or infection of the middle ear. Acute otitis media (acute ear infection) occurs when there is bacterial or viral infection of the fluid of the middle ear, which causes production of fluid or pus. Chronic otitis media occurs when the eustachian tube becomes blocked repeatedly due to allergies, multiple infections, ear trauma, or swelling of the adenoids.
Middle ear infection (otitis media)
illustration
Ear anatomy - illustration
The ear consists of external, middle, and inner structures. The eardrum and the 3 tiny bones conduct sound from the eardrum to the cochlea.
Ear anatomy
illustration
Medical findings based on ear anatomy - illustration
The external structures of the ear may aid in diagnosing some conditions by the presence or absence of normal landmarks and abnormal features including earlobe creases, preauricular pits, and preauricular tags.
Medical findings based on ear anatomy
illustration
Middle ear infection (otitis media) - illustration
Otitis media is an inflammation or infection of the middle ear. Acute otitis media (acute ear infection) occurs when there is bacterial or viral infection of the fluid of the middle ear, which causes production of fluid or pus. Chronic otitis media occurs when the eustachian tube becomes blocked repeatedly due to allergies, multiple infections, ear trauma, or swelling of the adenoids.
Middle ear infection (otitis media)
illustration
Review Date: 7/16/2024
Reviewed By: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.