Leukemia
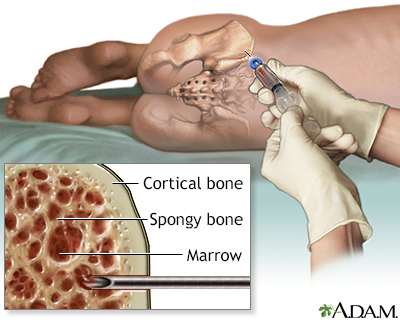
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are produced.
The term leukemia means white blood. White blood cells (leukocytes) fight infections and other foreign substances. Leukocytes are made in the bone marrow.
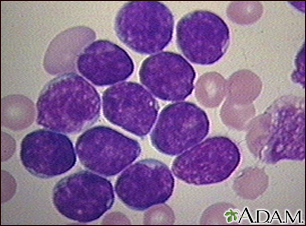
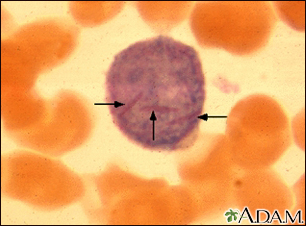
Leukemia leads to an uncontrolled increase in the number of white blood cells.
The cancerous cells prevent healthy red cells, platelets, and mature white cells (leukocytes) from being made. Life-threatening symptoms can then develop as normal blood cells decline.
The cancer cells can spread to the bloodstream and lymph nodes. They can also travel to the brain and spinal cord (the central nervous system) and other parts of the body.
Leukemia can affect children and adults.
Leukemias are divided into two major types:
- Acute (which progresses quickly)
- Chronic (which progresses more slowly)
The main types of leukemia are:
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
Acute lymphocytic leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a fast-growing cancer of a type of white blood cells called lymphocytes. ALL occurs when the bone marrow produ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is cancer that starts inside bone marrow. This is the soft tissue in the center of bones that helps form all blood cell...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is cancer of a type of white blood cells called lymphocytes. These cells are found in the bone marrow and other p...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
Chronic myeloid leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is cancer that starts inside the bone marrow. This is the soft tissue in the center of bones that helps form all ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Appelbaum FR. Acute leukemias in adults. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 95.
Brown JR. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 169.
Hunger SP, Teachey DT, Grupp S, Aplenc R. Childhood leukemia. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 93.
Radich J. Chronic myeloid leukemia. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 170.
Walter RB, Appelbaum FA. The acute leukemias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 168.




 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.